Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cambridge International Examinations
Uploaded by
Aditya GhoseOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International Examinations
Uploaded by
Aditya GhoseCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International Examinations
Cambridge Ordinary Level
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/22
Paper 2 May/June 2017
MARK SCHEME
Maximum Mark: 80
Published
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements
of the examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does
not indicate the details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners’ meeting before marking
began, which would have considered the acceptability of alternative answers.
Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner
Report for Teachers.
Cambridge will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes.
Cambridge is publishing the mark schemes for the May/June 2017 series for most
Cambridge IGCSE®, Cambridge International A and AS Level and Cambridge Pre-U components,
and some Cambridge O Level components.
® IGCSE is a registered trademark.
This document consists of 14 printed pages.
© UCLES 2017 [Turn over
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
MARK SCHEME NOTES
The following notes are intended to aid interpretation of mark schemes in general, but individual mark schemes
may include marks awarded for specific reasons outside the scope of these notes.
Types of mark
M Method marks, awarded for a valid method applied to the problem.
A Accuracy mark, awarded for a correct answer or intermediate step correctly obtained. For accuracy
marks to be given, the associated Method mark must be earned or implied.
B Mark for a correct result or statement independent of Method marks.
When a part of a question has two or more ‘method’ steps, the M marks are in principle independent unless the
scheme specifically says otherwise; and similarly where there are several B marks allocated. The notation ‘dep’
is used to indicate that a particular M or B mark is dependent on an earlier mark in the scheme.
Abbreviations
awrt answers which round to
cao correct answer only
dep dependent
FT follow through after error
isw ignore subsequent working
nfww not from wrong working
oe or equivalent
rot rounded or truncated
SC Special Case
soi seen or implied
© UCLES 2017 Page 2 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
1 5x + 3 = 3x – 1 oe or 5x + 3 = 1 – 3x oe M1
x = –2 and x = –0.25 only A2 nfww
mark final answer
A1 for x = –2 ignoring extras implies M1
if no extras seen
If M0 then SC1 for any correct value with
at most one extra value
Alternative method
( 5 x + 3) = (1 − 3x ) oe soi M1
2 2
16 x 2 + 36 x + 8 = 0 oe A1
x = –0.25, x = –2 only; mark final answer A1
2 Without using a calculator…
Sufficient evidence must be seen to be convinced
that a calculator has not been used. Withhold the
mark for any step that is unsupported.
deals with the negative index soi B1 3− 5
2
e.g.
1+ 5
3 − 5 1− 5 M1 1+ 5 3 + 5
rationalises × oe allow for ×
1+ 5 1− 5 3− 5 3+ 5
3− 4 5 +5 A1 3+ 4 5 +5
multiplies out correctly oe allow for
1− 5 9−5
squares correct binomial A1
( ) = (4 + 4 )
2
allow for 2 + 5 5 +5
( ) ( )
2
−2 + 5 = 4 − 4 5 + 5 oe
9 − 4 5 cao A1 dep on all previous marks awarded
© UCLES 2017 Page 3 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
2 Alternative method 1:
dealing with the negative index soi B1
correctly squaring with at least 3 terms in the B1
numerator and denominator
3− 5 3− 5 9−6 5 +5
× = oe
1+ 5 1+ 5 1+ 2 5 + 5
14 − 6 5 6 − 2 5 M1
rationalising their × oe
6+2 5 6−2 5
multiplying out correctly; at least 3 terms in the A1
numerator but condone a single value for the
84 − 64 5 + 60
denominator oe
36 − 20
9 − 4 5 cao A1
Alternative method 2
dealing with the negative index soi B1
( )(
9 − 6 5 + 5 = a + b 5 1+ 2 5 + 5 ) M1
14 = 6a + 10b A1
oe
−6 = 2a + 6b
a = 9 cao A1
b = –4 cao A1
Alternative method 3
for dealing with the negative index soi B1
( )( )
[ 3 − 5 = c + d 5 1 + 5 leading to] M1
c + 5d = 3
c + d = −1
c = –2 and d = 1 A1
( −2 + 5 ) A1
2
=4−4 5 +5
9 − 4 5 cao A1
© UCLES 2017 Page 4 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
3 Correctly finding a correct linear factor or root B1 from a valid method, e.g. factor theorem
used or long division or synthetic
division:
( ) ( )
f ( 2 ) = 10 23 − 21 22 + 4 = 0
10 x 2 − x − 2
or x − 2 10 x 3 − 21x 2 +4
3 2
10 x − 20 x
− x2
− x2 + 2 x
− 2x + 4
−2 x + 4
0
or
2 10 −21 0 4
↓ 20 −2 −4
10 −1 −2 0
correct linear factor stated or implied by, e.g. B1 ( x − 2 ) or ( 2 x − 1) or ( 5 x + 2 )
(
( x − 2 ) 10 x 2 − x − 2 ) 1 2
do not allow x − or x +
2 5
Correct quadratic factor B2 found using any valid method;
( ) ( ) (
10 x 2 − x − 2 or 5 x 2 − 8 x − 4 or 2 x 2 − 5 x + 2 ) B1 for any 2 terms correct
( x − 2 )( 2 x − 1)( 5 x + 2 ) mark final answer B1 must be written as a correct product of all
3 linear factors; only award the final B1 if
all previous marks have been awarded
If quadratic factor is not found but correct
remaining linear factors are found using
e.g. the factor theorem or long division or
synthetic division etc. with correct,
sufficient, complete working to justify
that no calculator has been used allow:
B1 for correctly finding a correct linear
factor or root
B1 for a correct linear factor stated or
implied
SC3 for the full, complete and correct
working to find the remaining two linear
factors and arrive at the correct product of
3 linear factors
© UCLES 2017 Page 5 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
4 dy B1
= 6 x − 7 soi
dx
1 B1 finds or uses correct gradient of normal
mnormal = − soi
5
1 M1 uses m1m2 = −1 with numerical gradients
mtangent = 5 soi or ( 6 x − 7 ) − = −1 oe
5
6 x − 7 = 5 oe ⇒ x = 2 A1
y = 9 A1
k = 47 A1
Alternative method
1 B1
mnormal = −
5
mtangent = 5 M1
3 x 2 − 12 x + 11 − c = 0 oe A1
solving 3 x 2 − 12 x + 12 = 0 oe to find x = 2 A1
y = 9 A1
k = 47 A1
5(i) −5 M1 clearly applies correct form of product
( their 2 x ) (0.2 − ln 5 x) + 0.4 x
4 5
their oe or
5x rule
5
their 0.4 x 4 − ( their 2 x 4 ) ln 5 x + 0.4 x 5 their oe
5x
−2 x 4 ln 5 x isw A1 nfww
5(ii) 3ln 5x or ln 5 x + ln 5 x + ln 5 x B1
© UCLES 2017 Page 6 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
5(iii) 3 M1 FT k = 2 from (i)
∫ ( −2x ln 5 x ) dx oe
4
3
−2 allow for
2 ∫(
2 x 4 ln 5 x dx )
or, when k = −2, for
∫ ( x ln 5x ) dx = −0.2 x (0.2 − ln 5x)
4 5
2
or −
∫ (3x ln 5x ) dx = 0.4 x (0.2 − ln 5x) oe
4 5
or, when FT k = 2, for
∫ ( x ln 5x ) dx = 0.2 x (0.2 − ln 5x)
4 5
2
∫ (3x ln 5x ) dx = 0.4 x (0.2 − ln 5x) oe
4 5
or
3
3 A1 nfww; implies M1
−
2
( 0.4 x5 (0.2 − ln 5x) ) [ +c] oe isw cao An answer of 0.6 x5 (0.2 − ln 5 x) following
k = 2 from (i) implies M1 A0
6 Uses b 2 − 4ac M1
( p − q) A1 implies M1
2
− 4( p)(−q)
p 2 + 2 pq + q 2 M1 correctly simplifies
( p + q) A1
2
≥ 0 oe cao isw
Alternative method
−( p − q ) ± ( p + q ) 2 M2 or M1 for ( px + q)( x − 1) [ = 0]
( px − q)( x + 1) [ = 0] or
2p −( p − q ) ± ( p − q ) 2 − 4( p )(− q)
or
2p
q A1
x= , x = −1
p
q A1
for conclusion, e.g. p and q are real therefore is
p
real [and –1 is real]
7(a)(i) 7 B1
7(a)(ii) 1 1 B1 FT their 7 must not be 1 if following
or through
7 their 7
© UCLES 2017 Page 7 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
7(b) −
1
−
1 M1 Anti-logs
y = 81 4
or y = 3−1 or y = 9 2
oe
1 A1 nfww; implies the M1;
y = only or 0.333[3….] only y = …. must be seen at least once
3
−1 1
If M0 then SC1 for e.g. 81 4 = as final
3
answer
7(c) 2
−1)
5
( x 2 −1) 2 B1 converts the terms given left hand side to
25( x 42 32 x × 32−1 powers of 2 or 4; may have cross-
2 oe or 2
oe or 2
(22 ) x 4x 4x multiplied
2 2
or log 32 x −1 − log 4 x = log16 oe
or separates the power in the numerator
correctly
or applies a correct log law
23 x
2
−5
= 16 oe ⇒ 3x 2 − 5 = 4 oe M1 combines powers and takes logs or
3 2 5 equates powers;
x − 3 5
or 4 2 2 = 16 oe ⇒ x 2 − = 2 oe
2 2 or brings down all powers for an equation
x2 already in logs
8
or = 16 oe ⇒ x 2 log8 = log 512 oe
32
condone omission of necessary brackets
or ( x 2 − 1) log 32 − x 2 log 4 = log16 oe
for M1; condone one slip
[ x =] ± 3 isw cao A1
or ± 1.732050... rot to 3 or more figs. isw
8(i) 8 B2 8
y −8 = − ( x − ( −8)) oe isw B1 for mAB = − oe
12 12
8 8−0
or y [−0] = − ( x − 4) oe isw or M1 for oe
12 −8 − 4
or 3 y = −2 x + 8 oe isw
8(ii) ( −8 − 4 )2 + ( 8 [−0])2 oe M1 any valid method
208 isw or 4 13 isw or 14.4222051… rot to 3 or A1 implies M1 provided nfww
more sf
© UCLES 2017 Page 8 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
8(iii) [coordinates of D =] (–2, 4) soi B1 If coordinates of D not stated then a
calculation for mCD or a relevant length
with the coordinates clearly embedded
must be shown to imply B1
Gradient methods: M1 or Length of sides methods:
7 − their 4 3
mCD = 0 − their (−2) = their finds or states AC 2 = 65 or AC = 65
2
or AC 2 = ( −8 − 0 ) + ( 8 − 7 )
2 2
oe
y
A
or AC = ( −8 − 0 )2 + (8 − 7 )2 oe
65 8
C
and CD 2 = their13 or CD = their 13
6
13
or CD 2 = ( 0 − their ( −2 ) ) + ( 7 − their 4 ) oe
2 2
2 13
D 4
or CD = ( 0 − their ( −2 ) )2 + ( 7 − their 4 )2 oe
2
B and AD 2 = their 52 or AD = their 2 13
or AD 2 = ( −8 − their ( −2 ) ) + ( 8 − their 4 )
2 2
-8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 x
-2
or AD = ( −8 − their ( −2 ) )2 + ( 8 − their 4 )2
or uses a valid method with their
coordinates of D to find the exact area of
the triangle and equates to
1
( AD)(CD)sin( ADC )
2
3 8 3 A1 applies Pythagoras to confirm, using
states × − = −1 oe or is the negative integer values, that 65 = 13 + 52 or finds
2 12 2
2 e.g. AC = 65 using (2 13) 2 + ( 13)2
reciprocal of − oe
3
or finds the equation of the perpendicular bisector or
( )( 13 ) sin ADC = 13 or
3 1
of AB as y = x + 7 independently of C and solves 2 13
2 2
states that C lies on this line.
( )
2
65 = (2 13) 2 + ( 13) 2
− 2(2 13)( 13) cos ADC
to show ADC is a right angle
8(iv) −4 B1 condone coordinates
or −4i + j
1
© UCLES 2017 Page 9 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
8(v) Full valid method e.g. B2 B1 for incomplete method
JJG 4 0 4 JJG 4
for showing that e.g. CB = − = e.g. for stating that CB =
0 7 −7 −7
or showing that e.g.
JJJG 0 −8 8 JJJG 8 JJG
AC = − = oe or AC = = EB
7 8 −1 −1
JJG 4 −4 8
and EB = − = oe or just showing that one pair of opposite
0 −1 −1 sides is parallel or has the same length
or comparing gradients of both pairs of opposite or just showing that length DC = length
sides and showing they are pairwise the same DE or just showing that C, D and E are
collinear
or comparing the lengths of both pairs of
opposite sides and showing that they are
1
pairwise the same A(-8, 8) mAC = −
8 65
C(0, 7)
or showing that length AC = length AE or
that the length BC = length BE 7
65 mBC = −
D(-2, 4) 4
or comparing the gradients and lengths of a 7
mAE = − 65
pair of opposite sides 4
E(-4, 1)
or showing that D is the midpoint of CE 65 1 B (4, 0)
mEB = −
8
or showing that length DC = length DE and
that C, D and E are collinear
9(i) 2 ( x − 1.5) + 0.5 isw B3 or B3 for a = 2 and b = 1.5 and c = 0.5
2
provided not from wrong format isw
or B2 for 2 ( x − 1.5 ) + c where c ≠ 0.5
2
or a = 2 and b = 1.5
or SC2 for 2 ( x − 1.5 ) + 0.5 or
1
2 ( x − 1.5 ) + seen
2
4
or B1 for ( x − 1.5 ) seen or for b = 1.5 or
2
for c = 0.5
or SC1 for 3 correct values seen in
incorrect format e.g. 2 ( x − 1.5 x ) + 0.5 or
2 ( x 2 − 1.5 ) + 0.5
© UCLES 2017 Page 10 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
y
9(ii) B3 B1 for correct graph for f over correct
domain or correct graph for f – 1 over
5
correct domain
B1 for vertex marked for f or f – 1 and
intercept marked for f or f – 1
B1 for idea of symmetry – either
1.5
symmetrical by eye, ignoring any scale or
line y = x drawn and labelled
0.5
x
Maximum of 2 marks if not fully correct
0 0.5 1.5 5
9(iii) x – 0.5 M1 FT their a,b,c, provided their a ≠1 and
= ( y − 1.5)
2
2 a,b,c are all non-zero constants
y – 0.5
= ( x − 1.5) and reverses
2
or
2
variables at some point
x – 0.5 A1 must have selected negative square root
f −1 ( x) = 1.5 − oe only; condone y = ... etc.; must be in terms
2
of x
6 − 8x – 4
If M0 then SC2 for f −1 ( x) =
4
oe
or SC1 for
−(−6) ± 36 – 4(2)(5 − x)
f −1 ( x ) = oe
2(2)
1 B1
x≥ oe
2
10(i) 3 M1 implied by 0.848[06…]
sin −1 soi
4
0.848[06…] rot to 3 or more figs or M1 implied by a correct answer of acceptable
2.29[35…] rot to 3 or more figs accuracy
0.544 486... rot to 3 or more figs isw A1
1.03 or 1.02630... rot to 4 or more figs isw A1 Maximum 3 marks if extra angles in
range; no penalty for extra values outside
π
range 0 ≤ x ≤
2
© UCLES 2017 Page 11 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
10(ii) Correctly uses tan 2 y = sec2 y − 1 and/or M1 for using correct relationship(s) to find an
sin y equation in terms of a single trigonometric
and sin 2 y = 1 − cos 2 y ratio
cos y
3sec 2 y − 14sec y − 5 = 0 DM1 for factorising or solving their 3-term
quadratic dependent on the first M1 being
⇒ ( 3sec y + 1)( sec y − 5 ) awarded
or
5cos 2 y + 14cos y − 3 = 0
⇒ (5cos y − 1)(cos y + 3)
1 A1
[ cos y = −3 ] cos y =
5
78.5 or 78.4630... rot to 2 or more decimal places A1
isw
281.5 or 281.536.... rot to 2 or more decimal places A1 Maximum 4 marks if extra angles in
isw range; no penalty for extra values outside
range 0 ≤ x ≤ 360
11(i) x 4 4 x3 5 x 2 B2 B1 for any 3 correct terms
+ − + 5 x [+c] isw
4 3 2
11(ii) B1 y
x 3 + 4 x 2 − 5 x + 5 = 5 and rearrange to
x ( x 2 + 4 x − 5 ) = 0 oe soi
A(−5, 5) B C(1, 5)
E (−5, 0) O D(1, 0) x
Solves their x 2 + 4 x − 5 [= 0] soi M1
x = –5, x = 1 soi A1
OEAB = 25, OBCD = 5 A1
© UCLES 2017 Page 12 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
11(iii) Correct or correct FT substitution of 0, their −5 M1 dependent on at least B1 in (i)
0
x 4 4 x3 5 x 2
seen in + − + 5x
4 3 2 their −5
Correct or correct FT substitution of their 1, 0 seen M1 dependent on at least B1 in (i)
their1
x 4
4x 5x 3
2
in + − + 5x
4 3 2 0
1175 49 M1 for the strategy needed to combine the
their − theirOEAB + theirOBCD − their oe areas; may be in steps;
12 12
97.916& − 25 + 5 − 4.083&
886 5 A1 all method steps must be seen; not from
oe or 73 oe or 73.83& rot to 3 or more sig wrong working
12 6
figs
If M0 then allow SC3 for
0 1
∫−5
( x3 + 4 x 2 − 5 x) dx − ∫ ( x3 + 4 x 2 − 5 x) dx oe
0
0 1
x 4 4 x3 5 x 2 x 4 4 x3 5x 2
= + − − + −
4 3 2 −5 4 3 2 0
625 500 125 1 4 5
= 0 − − − − + − −0
4 3 2 4 3 2
443
= oe
6
or SC2 for
0 their1
∫their ( −5)
( x 3 + 4 x 2 − 5 x ) dx − ∫
0
( x 3 + 4 x 2 − 5 x) dx oe
0 their 1
x 4 4 x3 5 x 2 x 4 4 x3 5 x 2
= + − − + −
4 3 2 their ( −5) 4 3 2 0
= [ F (0) − F (their (−5)) ] − [ F (their1) − F (0) ]
12(i) B1 −3 × 2
−6 Allow −3(2 x + 1) −2 × 2 or oe
−6(2 x + 1) −2 or oe isw ( 2 x + 1)
2
( 2 x + 1)
2
Denominator or (2 x + 1) 2 is positive [and B1 −k
FT their g′( x) of the form oe
( 2 x + 1)
2
numerator negative therefore g′( x) is always
negative] oe where k > 0;
Allow (2 x + 1)−2 is always positive
12(ii) g > 0 B1
12(iii) 3k B1
+ 3 oe isw
2x + 1
© UCLES 2017 Page 13 of 14
4037/22 Cambridge O Level – Mark Scheme May/June 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Partial Marks
12(iv) 3k B1
+3=5
2(0) + 1
2 B1 implies the first B1
k= isw
3
12(v) 1 B1
x>−
2
© UCLES 2017 Page 14 of 14
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
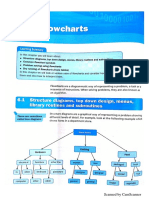
- Flowchart 1Document21 pagesFlowchart 1Aditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- 3.1 DiscusionDocument1 page3.1 DiscusionAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- The International System of Units (SI)Document97 pagesThe International System of Units (SI)varaprasadpg100% (1)
- Sylhet Airportto ResortDocument2 pagesSylhet Airportto ResortAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Pseudo CodeDocument8 pagesPseudo CodeAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- TED Talk-Elizabeth Loftus and False Memories: Attempt HistoryDocument7 pagesTED Talk-Elizabeth Loftus and False Memories: Attempt HistoryAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Physics Example Candidate ResponsesDocument114 pagesPhysics Example Candidate ResponsesAshiquzzaman AkashNo ratings yet
- Maximum Mark: 50: Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument6 pagesMaximum Mark: 50: Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- RE-IsSUECorrection Form 1st Page-1Document1 pageRE-IsSUECorrection Form 1st Page-1magnteNo ratings yet
- 9608 s19 QP 11 PDFDocument16 pages9608 s19 QP 11 PDFfaizan majidNo ratings yet
- 9608 s19 QP 41Document20 pages9608 s19 QP 41ratnaNo ratings yet
- 4037 s19 QP 12Document16 pages4037 s19 QP 12WaseemNo ratings yet
- Learner Guide For Cambridge Igcse English Second Language 0510 11 For Examination From 2019Document43 pagesLearner Guide For Cambridge Igcse English Second Language 0510 11 For Examination From 2019Doula IshamNo ratings yet
- 5054 w18 Ms 21 PDFDocument10 pages5054 w18 Ms 21 PDFWorld Cricket HighlightsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument6 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Physics Paper 1 2018Document3 pagesMark Scheme Physics Paper 1 2018humayunNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelMohammad KamrulNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument6 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- 4037 w17 Ms 23Document6 pages4037 w17 Ms 23arcanum78No ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- 4037 Additional Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument6 pages4037 Additional Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary Level: Cambridge Assessment International EducationHafizNohNo ratings yet
- 4037 Additional Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument6 pages4037 Additional Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Physics 5054/11 May/June 2018Document3 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Physics 5054/11 May/June 2018Aditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- 4037 s19 QP 11Document16 pages4037 s19 QP 11Shamvil RazaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument7 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelAditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Olevel Maths QP 4024 - w17 - QP - 21Document20 pagesOlevel Maths QP 4024 - w17 - QP - 21Muhammad ZirarNo ratings yet
- 4024 w17 QP 22Document24 pages4024 w17 QP 22Prince RohanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 1 The Polarizing Microscope: 1.1 Microscope Components and Their FunctionDocument4 pages1 The Polarizing Microscope: 1.1 Microscope Components and Their FunctionWongJowo GamingNo ratings yet
- Solar Photovoltaics: Basics: Mpepb@nus - Edu.sgDocument37 pagesSolar Photovoltaics: Basics: Mpepb@nus - Edu.sg김동욱No ratings yet
- Topics Mechatronics LabDocument2 pagesTopics Mechatronics Labsamuelsoaresvasco2020No ratings yet
- ComboNoteswSolutions11 6 04Document358 pagesComboNoteswSolutions11 6 04Jorge ChavesNo ratings yet
- Tool Model Building and Research On Cutting Simulation Experiment of Ti6Al4VDocument21 pagesTool Model Building and Research On Cutting Simulation Experiment of Ti6Al4VhaceneNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 6 Q4: Sampaloc Elementary SchoolDocument9 pagesMathematics 6 Q4: Sampaloc Elementary SchoolTinn Marion Villegas OlpindoNo ratings yet
- Perforation: Omega 2013Document73 pagesPerforation: Omega 2013Igbereyivwe TejiriNo ratings yet
- It's Electric v.2Document2 pagesIt's Electric v.2Secure Energy FutureNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Double Integral in Polar Coordinates: F (X, Y) Da, Where R Is One ofDocument8 pages2.3 Double Integral in Polar Coordinates: F (X, Y) Da, Where R Is One ofsimon georgeNo ratings yet
- Planet Report 2015Document7 pagesPlanet Report 2015api-289245128No ratings yet
- Module 4Document36 pagesModule 4MD SHAHRIARMAHMUDNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Module 1)Document22 pagesThermodynamics (Module 1)Christine SalamatNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Society NotesDocument12 pagesScience, Technology, Society NotespeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity and Charge Conservation of Charge PDFDocument9 pagesStatic Electricity and Charge Conservation of Charge PDFDavid I. Chamorro AriasNo ratings yet
- Fluid StaticsDocument53 pagesFluid StaticsUsama AlameedyNo ratings yet
- Impedance Analysis of Electrochemical Systems - VivierDocument38 pagesImpedance Analysis of Electrochemical Systems - VivierSureshBharadwajNo ratings yet
- 23AhmedAl Hassani8-18Document209 pages23AhmedAl Hassani8-18abishek TaNo ratings yet
- At Present, Adding A Filter Is A Common Method, Which Can Be Achieved by Connecting A Filter Between The Inverter and The MotorDocument21 pagesAt Present, Adding A Filter Is A Common Method, Which Can Be Achieved by Connecting A Filter Between The Inverter and The MotorAdisuNo ratings yet
- Properties of IntegersDocument6 pagesProperties of IntegerscdnaveenNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of AB MaterialsDocument48 pagesPhysical Properties of AB Materialsryeue88% (8)
- Unit I - Module 1Document9 pagesUnit I - Module 1naguitghienelNo ratings yet
- D 3014 - 04 - RDMWMTQ - PDFDocument4 pagesD 3014 - 04 - RDMWMTQ - PDFsusanaNo ratings yet
- Robust Error-State Kalman Filter For Estimating IMU OrientationDocument9 pagesRobust Error-State Kalman Filter For Estimating IMU OrientationWilliam SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Electric Potential, Energy and CapacitanceDocument10 pagesLesson 2 Electric Potential, Energy and CapacitanceanonymousNo ratings yet
- SangeethachandrikaDocument67 pagesSangeethachandrikaMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- DPP Vector Algebra Solution MathongoDocument8 pagesDPP Vector Algebra Solution MathongoSubhajit GoraiNo ratings yet
- BIO201L Lab 2 Upload DocumentDocument4 pagesBIO201L Lab 2 Upload Documentcindy tranNo ratings yet
- Design and Detailing of Retaining WallsDocument54 pagesDesign and Detailing of Retaining WallsBrahman Pathakji PradumnNo ratings yet
- Classwork or Homework Investigating Diffusion in AirDocument2 pagesClasswork or Homework Investigating Diffusion in AirPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Math - 1ST SummativeDocument2 pagesMath - 1ST SummativeericksonNo ratings yet