Professional Documents
Culture Documents
024e500d3644c CBT 01
Uploaded by
Aman GoelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
024e500d3644c CBT 01
Uploaded by
Aman GoelCopyright:
Available Formats
CBT - 02
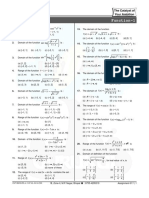
1
x, 0 x
2 7. The length of the minor axis (along y-axis) of an
1 1 4
1. given : f ( x) , x and ellipse in the standard form is . If this ellipse
2 2 3
1 x, 1 touches the line, x + 6y = 8; then its eccentricity
x 1
2 is :
2
1
g ( x) x , x R . 1 11 5
2 (a) (b)
3 3 6
Then the area (in sq.units) of the region bounded
by the curves, y = f(x) and y = g(x) between the 1 11 1 5
(c) (d)
2 3 2 3
lines, 2x = 1 and 2x = 3 , is :
1 3 1 3
(a) (b) 8. If x = 2sin– sin2 and y = 2cos– cos2[0,
2 4 3 4
d2y
1 3 3 1 2], then at is
(c) (d) 4 dx 2
2 4 4 3
3 3
2. A random variable X has the following probability (a) (b)
8 8
distribution:
3 3
X: 1 2 3 4 5 (c) (d)
4 4
2 2
P(x) : K 2k K 2K 5K 9. Let a function f : [0, 5] R be continuous,
Then P(x > 2) is equal to : f(1) = 3 and F be defined as :
x t
23 7 1 1
(a)
36
(b)
12
(c)
36
(d)
6
f ( x) t 2 g (t ) dt,where
1
g (t ) t (u ) du . Then for
1
3. If z be a complex number satisfying |Re(z)| + the function F, the point x = 1 is :
|Im(z)| = 4, then |z| cannot be:
(1) a point of local minima
17
(a) 10 (b) 8 (c) 7 (d) (2) a point of local maxima.
2
(3) not a critical point
Let a, b R, a 0 be such that the equation, ax
2
4. (4) a point of inflection.
–2bx + 5 = 0 has a repeated root , which is
2 10. Let a – 2b + c = 1,
also a root of the equation, x –2bx –10 = 0. If
is the other root of this equation, then 2 +2 is xa x2 x 1
equal to: If f ( x) x b x 3 x 2 , then :
(a) 25 (b) 26 (c) 24 (d) 28 xc x4 x3
5. If p p ~ q) is false, then the truth values of p (a) f(–50)= –1 (b) f(50) =1
and q are respectively: (c) f(50) = –501 (d) f(–50) = 501
(a) F, F (b) F, T (c) T, F (d) T, T 2
11. If one end of a focal chord AB of the parabola y
dy xy 1
6. If ;y(1)=1; then a value of x = 8x is at A , 2 , then the equation of the
dx x 2 y 2 2
satisfying y(x) = e is : tangent to it at B is :
e 1
(a) 3e (b) (c) 2e (d) 3e
2 2 (a) x –2y + 8 = 0 (b) x + 2y + 8 = 0
(c) 2x – y – 24 = 0 (d) 2x + y – 24 = 0
IJanII920 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 |1
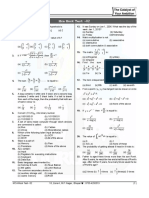
Let [t] denote the greatest integer t and A d
cos
12.
18. I tan 2 log e | f ( ) | C
lim 4 2 (tan 2 sec 2 )
2
x 0 x x A . Then the function, f(x) = [x ]
where c is a constant of integration, then the
sin(x) is discontinuous, when x is equal to : ordered pair (, f()) is equal to :
(a) A (b) A 1 (a) (1,1 + tan) (2) (–1,1 – tan)
(c) (–1,1 + tan) (4) (1,1 – tan)
(c) A5 (d) A 21
19. If A = {xR : |x| < 2} and B = {xR : |x–2| 3} ;
13. Let an be the nth term of a G.P. of positive terms. then :
100 100 200 (a) A – B = [–1, 2) (b) A B = R – (2, 5)
If
n 1
a2 n 1 200 and
n 1
a2 n 100 , then a
n 1
n is
(c) B – A = R –(–2, 5) (d) A B = (– 2, –1)
equal to : 20. The following system of linear equations
(a) 175 (b) 150 7x + 6y –2z = 0
(c) 300 (d) 225 3x + 4y +2z = 0
x – 2y – 6z = 0, has
14. If 10 different balls are to be placed in 4 distinct
boxes at random, then the probability that two of (1) infinitely many solution, (x, y, z) satisfying
these boxes contain exactly 2 and 3 balls is : y = 2z
16065 16065 (2) infinitely many solution, (x, y, z) satisfying
(a) (b) x = 2z
215 210
(3) Only the trivial solution.
945 945
(c) (d) (4) no solution.
210 211
21. The number of terms common the two A.P.'s 3, 7,
15. Let f and g be differentiable functions on R such 11, ….., 407 and 2, 9, 16, ….,709 is _________
that fog is the identity function. If for some a, (a)11 (b) 13 (c)12 (d) 14
bR, g'(a)=5 and g(a) = b, then f'(b) is equal to :
22. If the distance between the plane, 23x –10y –2z
1 2
(a) (b) +48 = 0 and the plane containing the lines
5 5 x 1 y 3 z 1
(c) 1 (d) 5 and
2 4 3
x 3 y 2 z 1 k
16. If x
n 0
(1) n tan 2 n and y cos
n 0
2n
, for 2
6
( R ) is equal to
633
,
then k is equal to ___________
0 , then (a)2 (b) 3 (c)4 (d)5
4
(a) y(1–x) = 1 (b) y(1+x) = 1 23. Let a , b and c be three vectors such that ,
(c) x(1+y) = 1 (d) x(1–y) = 1 | a | 3 , | b | 5, b c 10 and angle between b and
x 1
16
17. In the expansion of , if l1 is the c is . If a is perpendicular to the vector b c ,
cos x sin 3
least value of the term independent of x when then a b c is equal to ________
and l2 is the least value of the term (a)27 (b)28 (c)29 (d) 30
8 4
2 2 2
24. If the curves, x – 6x + y + 8 = 0 and x – 8y +
independent of x when , then the ratio 2
16 8 y + 16 – k = 0, (k > 0) touch each other at a
l2 : l1 is equal to : point, then the largest value of k is ________
(a) 1 : 8 (b) 1 : 16 (a) 36 (b)34 (c)35 (d)32
(c) 8 : 1 (d) 16 : 1 25. If Cr =
25
Cr and C0 + 5.C1 + 9.C2 +…..+
25
(101).C25 = 2 .k, then k is equal to ____
(a)50 (b) 51 (c)49 (d) 48
IJanII920 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 |2
ANSWER KEY (CBT - 02)
1. (d) 2. (a) 3. (c) 4. (a) 5. (d) 6. (a) 7. (c) 8. (b) 9. (a) 10. (b)
11. (a) 12. (b) 13. (b) 14. (a) 15. (a) 16. (a) 17. (d) 18. (c) 19. (c) 20. (b)
21. (d) 22. (b) 23. (d) 24. (a) 25. (b)
IJanII920 18, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 |2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Group Theory by Flipping The MattressDocument9 pagesGroup Theory by Flipping The Mattressvinita_95742No ratings yet
- 024cf706bacde-01.DPT LimitDocument3 pages024cf706bacde-01.DPT LimitAman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024ccc67fca33-02.DPT FunctionDocument6 pages024ccc67fca33-02.DPT FunctionAman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024cfe8a1af28-02. DPT LimitDocument2 pages024cfe8a1af28-02. DPT LimitAman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Document8 pages024eec5a83031-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 08 (07.04.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024efcb68fc74-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 09 09.04.2020Document8 pages024efcb68fc74-MOCK TEST (MATHS) - 09 09.04.2020Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024ccc5dfb3ba-01. DPT FunctionDocument3 pages024ccc5dfb3ba-01. DPT FunctionAman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024f3a63c341e-RATIO - PROPORTION - 2 (17.04.2020)Document7 pages024f3a63c341e-RATIO - PROPORTION - 2 (17.04.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024eb2783e22d-MCA MOCK TEST - 02 (31.03.2020)Document6 pages024eb2783e22d-MCA MOCK TEST - 02 (31.03.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024eeb38a0bc0-Problem On Numbers (07.04.2020)Document2 pages024eeb38a0bc0-Problem On Numbers (07.04.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024ec2a26b959-LCM - HCF - 01 (02.04.2020)Document5 pages024ec2a26b959-LCM - HCF - 01 (02.04.2020)Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e5840b21e1-Mock Test (Maths) - 04Document11 pages024e5840b21e1-Mock Test (Maths) - 04Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024ee3031d5b9-DPT AVERAGE - 2 6.4.2020Document3 pages024ee3031d5b9-DPT AVERAGE - 2 6.4.2020Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e6042fa437-CBT - 04Document3 pages024e6042fa437-CBT - 04Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Document7 pages024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e9f33fafd8-NIT MOCK TEST - 01Document8 pages024e9f33fafd8-NIT MOCK TEST - 01Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Document8 pages024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Coding Phase: Configuration - PHPDocument12 pagesCoding Phase: Configuration - PHPAman GoelNo ratings yet
- 024e500c71824-BHU MOCK - 01Document10 pages024e500c71824-BHU MOCK - 01Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Online Student Admission System Project ReportDocument58 pagesOnline Student Admission System Project ReportAman GoelNo ratings yet
- 7 Space TrussesDocument3 pages7 Space TrussesVincent Kong100% (1)
- BMAT101L Module2 Tutorial SheetDocument2 pagesBMAT101L Module2 Tutorial Sheetsneha sehgalNo ratings yet
- 9-Inverse Trigonometric Ratios PDFDocument4 pages9-Inverse Trigonometric Ratios PDFMark Abion ValladolidNo ratings yet
- A Steepest-Ascent Method For Solving Optimum Programming ProblemDocument13 pagesA Steepest-Ascent Method For Solving Optimum Programming Problemx420No ratings yet
- Differential Calculus EXAM ANSWEY KEYDocument2 pagesDifferential Calculus EXAM ANSWEY KEYlarry soiranoNo ratings yet
- 6e Liesmycomp Stu PDFDocument9 pages6e Liesmycomp Stu PDFluizmenezes2010No ratings yet
- Remainder TheoremDocument12 pagesRemainder TheoremLairepmi EmjaneNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Syllabus & Blue Print VIIIDocument3 pagesMid Term Syllabus & Blue Print VIIIVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Force VectorDocument47 pagesForce Vectoradeliene 25No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument1 pageFundamentals of Computational Fluid Dynamicsankit dimriNo ratings yet
- Maths 1 Question Paper Nov Dec 2010Document4 pagesMaths 1 Question Paper Nov Dec 2010suriteddyNo ratings yet
- Index of PonnusamyDocument3 pagesIndex of PonnusamyAnkit KambojNo ratings yet
- FFT Image ProcessingDocument116 pagesFFT Image ProcessingMarco Shrimpie CoetzerNo ratings yet
- Ex#6.1, Introductory Linear Algebra by Bernard KolmannDocument10 pagesEx#6.1, Introductory Linear Algebra by Bernard KolmannRandom Science StuffNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11ADocument12 pagesExercise 11AAdrian BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Additional Maths Note2022Document10 pagesForm 5 Additional Maths Note2022indahinsyirahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematics Module 3: Systems of Linear Equations: Prepared byDocument13 pagesAdvanced Mathematics Module 3: Systems of Linear Equations: Prepared byJohn Steven LlorcaNo ratings yet
- Courseoutline - EQT221 (STUDENTversion)Document2 pagesCourseoutline - EQT221 (STUDENTversion)一鸿No ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument9 pagesZ TransformKiran Googly JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document14 pagesChapter 18Anonymous u9HONqxnNo ratings yet
- 3 - Root Locus Design Method For DC Motor Position ControlDocument9 pages3 - Root Locus Design Method For DC Motor Position Controledgartepe4324No ratings yet
- Vibration of Continuous SystemsDocument14 pagesVibration of Continuous SystemsRidwan OlatunjiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 Lesson 2Document8 pagesMODULE 5 Lesson 2Jan JanNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercise Set 1, TMA4220: September 2, 2015Document5 pagesSolutions To Exercise Set 1, TMA4220: September 2, 2015Salomon HagenimanaNo ratings yet
- Math 1 BDocument3 pagesMath 1 BscribNo ratings yet
- SMO 2009 Junior QuestionDocument10 pagesSMO 2009 Junior QuestionwmdsgNo ratings yet
- Exercise - Types of Algebraic ExpressionsDocument4 pagesExercise - Types of Algebraic ExpressionsNarayanamurthy AmirapuNo ratings yet
- Abbott-TeachYourselfCalculus Text PDFDocument193 pagesAbbott-TeachYourselfCalculus Text PDFAce Mohan100% (1)