Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Care of Normal Newborn in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
sidik ali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThe document outlines the care of normal newborns, including initial care at birth such as clearing the airway, temperature control, and eye care. It also discusses assessment of the newborn, classification by gestational age and birth weight, and management of low birth weight newborns. Key steps in newborn care are cleaning the airway, keeping the infant warm, encouraging breastfeeding, and monitoring for infections or other issues before discharge.
Original Description:
Original Title
Care of Normal Newborn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the care of normal newborns, including initial care at birth such as clearing the airway, temperature control, and eye care. It also discusses assessment of the newborn, classification by gestational age and birth weight, and management of low birth weight newborns. Key steps in newborn care are cleaning the airway, keeping the infant warm, encouraging breastfeeding, and monitoring for infections or other issues before discharge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesCare of Normal Newborn in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
sidik aliThe document outlines the care of normal newborns, including initial care at birth such as clearing the airway, temperature control, and eye care. It also discusses assessment of the newborn, classification by gestational age and birth weight, and management of low birth weight newborns. Key steps in newborn care are cleaning the airway, keeping the infant warm, encouraging breastfeeding, and monitoring for infections or other issues before discharge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
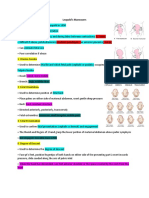
Care of Normal Newborn:
A) Care at birth:
• Clear air way ( suction mouth and pharynx)
• Temperature control ( dry and wrap with dry cloth)
• clamping the cord immediately after the birth of baby app. 2.5 cm from abdomen
• provide appropriate eye care to prevent Ophthalmia Neonatorum( TTC eye ointment)
• Identification of newborn with mothers name
• Vitamin K injection to prevent hemorrhagic disease of the newborn
• Measurement (Weight, Height, Head circumference)
• Encourage rooming-in immediately after delivery
Assessment of APGAR score:
• 7-10 well adjusted
• 5-7 mild asphyxia
• 3-4 moderate asphyxia
• < 3 severe asphyxia
B) Care in the Postnatal Ward:
• Handle the baby gentle
• Avoid infection (hand washing)
• Keep the baby warm
• Encourage and initiate exclusive breast feeding -4 months of age
• Encourage care of umbilical stump
• Give immunization ( BCG & OPV0) C)
Assessment of the newborn before discharge:
• Take vital sign
• Check for sign infections (eye , cord ,skin)
Check for birth trauma (cephalohematoma, fracture..)
• Check for anomalies ( spina-bifda, imporforate anus, club foot…)
• Carryout systematic examinations ( head to foot)
D) Classification of the newborn:
Newborns are classified based on their gestational age and birth weight.
Gestational age defined as:
Preterm defined as gestational age below 37 complete weeks
Term defined as gestational age above 37-42 weeks
post term defined as gestational age above 42 weeks
Classification of Newborn by birth weight:
Low birth weight (LBW- is defined as birth weight < 2.5 kg , they may be
Preterm or small for gestational age (SGA)
Very LBW - birth weight < 1500gm
Large for gestational age (LGA)- birth weight above 90th percentile.
Appropriate for gestational age (AGA)- birth weight between and 10th
and 90th percentile
Small for gestational age-(SGA) – birth weight below 10th percentile
4.2 Causes of Low Birth Weight (LBW):
Fetal:
1. Fetal distress
2. Multiple pregnancies
3. Erythroblastosis fetalis
Placental:
i. Premature separation
ii. Placenta previa
Uterine: Incompetent cervix
Maternal:
1. Pre-eclampsia
2. Chronic illness
3. Infection
4. PROM (prematurerapture ofmembrane)
5. Poly hydrominous >1500ml
6. Nutrition status of the mother
A) Management of low birth weight:
Clean air way
Initiate breathing
Establish circulation
Keep Warm
Administer Vit. K
Administer Silver nitrate or TTC ointment to the eyes
Apply gentian Violet to the cord
Feeding- Breast feeding
NGT feeding
Parental feeding
Treat anticipated problems (infection)
Hypothermia (cold injury). If Rectal temperature is < 350C
Hyperthermia temperature >38.50C
Normal temperature:
Rectal 36.5 - 37.20C
Axillary 36.5 - 370C
Hyperthermia caused by
Excessive environmental temperature
Infection
Dehydration (loss of ECF, Evaporation)
Immediate Newborn care:
• Drying, wrapping, close contact with mother
• Immediate breast feeding
• Prophylactic eye care, where appropriate
Routine Newborn Care:
• Exclusive breast feeding, counseling for problems
• Maintenance of body temperature
• Clean cord care
• Early postpartum visit for mother and baby (within 3 days)
• Recognition of danger signs; treatment and referral as needed
• Immunization
Special Newborn Care:
• Special care for the sick children
• Recognition and management of birth asphyxia
• Recognition and management of infection
• Special care for the LBW infant
• Skin – to- skin / kangaroo mother care
• Close surveillance for signs of infections and feeding difficulties
You might also like
- Mothers ClassDocument73 pagesMothers ClassJuliana Andres83% (6)
- Newborn Risks and Complications in the NurseryDocument131 pagesNewborn Risks and Complications in the NurseryMercy KeruboNo ratings yet
- Care of IUGR and LBW BabiesDocument30 pagesCare of IUGR and LBW BabiesjessyNo ratings yet
- PEDIAPrelims - 2. Care of The Newborn 1 (First 24 Hours To Vital Signs)Document7 pagesPEDIAPrelims - 2. Care of The Newborn 1 (First 24 Hours To Vital Signs)RenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorNo ratings yet
- Review UNIT XI High Risk NewbornDocument20 pagesReview UNIT XI High Risk NewbornShehana ShihabNo ratings yet
- High Risk NeonateDocument85 pagesHigh Risk NeonateWed Lod100% (1)
- Managing High-Risk NewbornsDocument19 pagesManaging High-Risk Newbornssantosh s u100% (1)
- Low Birth Weight GuideDocument9 pagesLow Birth Weight Guidesushma shrestha100% (1)
- Immediate Care of The NewbornDocument3 pagesImmediate Care of The NewbornAngelee OngchuaNo ratings yet
- SERVICE 2.neonatal and Infant Health Care ServicesDocument71 pagesSERVICE 2.neonatal and Infant Health Care ServicesSuvetha TamilarasanNo ratings yet
- High-Risk Newborn Identification, Classification and Nursing ManagementDocument52 pagesHigh-Risk Newborn Identification, Classification and Nursing Managementmounika ChittempallyNo ratings yet
- LBWDocument39 pagesLBWJOSLINNo ratings yet
- High-Risk Neonate & Neurodevelopmental OutcomeDocument155 pagesHigh-Risk Neonate & Neurodevelopmental OutcomeChari RivoNo ratings yet
- High Risk NewbornDocument21 pagesHigh Risk Newbornnaga maniNo ratings yet
- New Born ClassificationDocument47 pagesNew Born ClassificationEyob MizanNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of High Risk NewbornsDocument45 pagesAssessment and Management of High Risk NewbornsShiva KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Care: Dr. Bhuwan Sharma Asst. ProfessorDocument28 pagesNeonatal Care: Dr. Bhuwan Sharma Asst. Professorrevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- Care of Normal NewbornDocument41 pagesCare of Normal NewbornSamantha VeraNo ratings yet
- NICU Protocol 100Document76 pagesNICU Protocol 100Catherine Lee100% (1)
- Essential Newborn Care: Dr. Sumitra Kumara Meena Senior Resident, Pediatrics Safdarjung Hospital, New DelhiDocument75 pagesEssential Newborn Care: Dr. Sumitra Kumara Meena Senior Resident, Pediatrics Safdarjung Hospital, New DelhiDr Divyarani D CNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Class 15 Intrapartum Complications With AnswersDocument55 pagesWeek 10 Class 15 Intrapartum Complications With AnswersGlory MimiNo ratings yet
- The Low Birth Weight Infant: Julniar M Tasli Herman BermawiDocument42 pagesThe Low Birth Weight Infant: Julniar M Tasli Herman BermawiJoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Low Birth Weight BabiesDocument10 pagesNursing Care of Low Birth Weight BabiesAnnisa Yusuf80% (5)
- Birthing ReviewerDocument3 pagesBirthing ReviewerDianne T. De JesusNo ratings yet
- Classification of Newborn, - 130319150346Document45 pagesClassification of Newborn, - 130319150346Ez Ball100% (1)
- Care and Feeding of Newborns: A Guide for ParentsDocument27 pagesCare and Feeding of Newborns: A Guide for ParentsBlue WingsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Neonate Part 1Document67 pagesNursing Care of A Neonate Part 1Rani G SNo ratings yet
- NICU ProtocolDocument75 pagesNICU ProtocolCatherine Lee100% (6)
- Low Birthweight InfantDocument42 pagesLow Birthweight InfantJoNo ratings yet
- Baby at Risk - Koros E.k-1-1-1-1Document132 pagesBaby at Risk - Koros E.k-1-1-1-1victorNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn Care Saves LivesDocument14 pagesImmediate Newborn Care Saves Livesmendoza jhamNo ratings yet
- Caring for High-Risk Newborns and Their FamiliesDocument14 pagesCaring for High-Risk Newborns and Their FamiliesElaisa Mae Delos Santos100% (1)
- High Risk NeonateDocument52 pagesHigh Risk NeonateJoshua SmithNo ratings yet
- High Risk New BornDocument36 pagesHigh Risk New BornIze C VijiNo ratings yet
- Risks and Management of High-Risk NeonatesDocument102 pagesRisks and Management of High-Risk NeonatesJaya Prabha100% (2)
- Assessment of New Born.& Nursing Care of The New Born and Family.Document14 pagesAssessment of New Born.& Nursing Care of The New Born and Family.Manoj TadeNo ratings yet
- Prematurity and Hyaline Membrane Disease: Classification, Survival Rates, and ComplicationsDocument113 pagesPrematurity and Hyaline Membrane Disease: Classification, Survival Rates, and ComplicationsJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document18 pagesWeek 5Kaila AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Care NewbornDocument38 pagesCare NewbornRaja0% (1)
- Management of Low Birth Weight BabiesDocument59 pagesManagement of Low Birth Weight BabiesKiran Khasa100% (2)
- Essential New Borm Care: Presenter: DR Ifrah Osman Salad / DR SocdaalDocument35 pagesEssential New Borm Care: Presenter: DR Ifrah Osman Salad / DR SocdaalMahad Maxamed AxmedNo ratings yet
- EENC (Early Essential Newborn Care)Document74 pagesEENC (Early Essential Newborn Care)Jennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- Ante Natal Care: by Naveen Sharma J.N - Medical College Belgaum, IndiaDocument37 pagesAnte Natal Care: by Naveen Sharma J.N - Medical College Belgaum, IndiaNaveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Patient'S Profile: GROUP 1: Camposano, Cielo, Edem, Ibalin, RodriguezDocument2 pagesPatient'S Profile: GROUP 1: Camposano, Cielo, Edem, Ibalin, RodriguezDivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- Newborn CareDocument3 pagesNewborn CareLUISA CARANTESNo ratings yet
- Assessment Scientific Basis Plan of Care Intervention With Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument16 pagesAssessment Scientific Basis Plan of Care Intervention With Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentAbdullah Mascardo BarabagNo ratings yet
- Konsep NeonatusDocument26 pagesKonsep NeonatusshifaNo ratings yet
- Highrisk Newborn and PRETERMDocument15 pagesHighrisk Newborn and PRETERMchel_0520No ratings yet
- Intranatal Care Postnatal Care Neonatal Care: Reproductive Health-A Basic Right of Every WomanDocument20 pagesIntranatal Care Postnatal Care Neonatal Care: Reproductive Health-A Basic Right of Every WomanShivani ShahNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument20 pagesNeonatal SepsisJustine Nyangaresi100% (1)
- HAND OUTS - Immediate CareDocument3 pagesHAND OUTS - Immediate CareRalph Tama Mangacop BenitoNo ratings yet
- Chynna Ashley Gonzales Pendon RNDocument33 pagesChynna Ashley Gonzales Pendon RNChynna Ashley Gonzales PendonNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CareDocument29 pagesAntenatal Careعبدالكريم الاسدNo ratings yet
- 2 NEO Newborn Care 2012Document28 pages2 NEO Newborn Care 2012shambelNo ratings yet
- Management of LBW BabiesDocument67 pagesManagement of LBW BabiesEllen Angel100% (4)
- Assessing High-Risk Newborns (AHRNDocument76 pagesAssessing High-Risk Newborns (AHRNEsha KuttiNo ratings yet
- Prematurity, Sga, Lga Infant by SodalDocument39 pagesPrematurity, Sga, Lga Infant by SodalMahad Maxamed AxmedNo ratings yet
- 5 Idol Ko Si Nanay Module 5Document48 pages5 Idol Ko Si Nanay Module 5Mash JumahariNo ratings yet
- Vasa PraeviaDocument14 pagesVasa Praeviakhadzx100% (2)
- Lubchenco Curve PDF PDF Childhood Public HealthDocument1 pageLubchenco Curve PDF PDF Childhood Public HealthShaina MainitNo ratings yet
- Induction of LabourDocument20 pagesInduction of LabourNur Hanani Khan100% (1)
- Nausea and Vomiting of PregnancyDocument1 pageNausea and Vomiting of Pregnancypuskesmas ciapusNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Gynaecology ReportDocument2 pagesObstetrics Gynaecology ReportBEYOND ZFSNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Prenatal Care: Early and Continuous Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesAntenatal Prenatal Care: Early and Continuous Risk AssessmentAmalNo ratings yet
- 06 Early Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument5 pages06 Early Pregnancy ComplicationsmusNo ratings yet
- ChenescensusDocument4 pagesChenescensusHester Marie SimpiaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Abortion Care GuideDocument42 pagesComprehensive Abortion Care GuideKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Protocol PolyhydramniosDocument2 pagesProtocol PolyhydramniosFie Fie AdelaideNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CareDocument38 pagesAntenatal CareMominah MayamNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid and Its DisordersDocument9 pagesAmniotic Fluid and Its DisordersRisqi YuliNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Placenta and CordDocument47 pagesAbnormalities of Placenta and CordShrooti Shah75% (4)
- Approach To Neonate With Low Birth WeightDocument40 pagesApproach To Neonate With Low Birth Weightnirajan khanalNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument69 pagesBleeding During PregnancyMohnnad Hmood AlgaraybhNo ratings yet
- Obg Icd-10 Pregnancy, Childbirth, PuerperiumDocument11 pagesObg Icd-10 Pregnancy, Childbirth, PuerperiumarifianjuariNo ratings yet
- Lecture-13 Transeverse LieDocument15 pagesLecture-13 Transeverse LieMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Rh-Pregnancy 202240 184928Document2 pagesRh-Pregnancy 202240 184928siddharthNo ratings yet
- Knowledge of Antenatal Women Regarding Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument4 pagesKnowledge of Antenatal Women Regarding Pregnancy Induced HypertensionBADLISHAH BIN MURAD MoeNo ratings yet
- Cervical InsufficiencyDocument2 pagesCervical InsufficiencyShe that BoyNo ratings yet
- Breech-Presentation (2) - 1Document30 pagesBreech-Presentation (2) - 1ahmed shorshNo ratings yet
- EFFECTIVENESS GINGER DRINKDocument15 pagesEFFECTIVENESS GINGER DRINKakayuni mirachristinaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Presentation:: Premature Rupture of MembranesDocument31 pagesClinical Case Presentation:: Premature Rupture of Membranesjoshua remonNo ratings yet
- DR - Case Report Placenta Previa 3Document4 pagesDR - Case Report Placenta Previa 3q_t_jheng1603No ratings yet
- Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios - Background, Pathophysiology, EtiologyDocument4 pagesPolyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios - Background, Pathophysiology, EtiologyAhmad FahroziNo ratings yet
- Pico CpapDocument4 pagesPico CpapAbc DefNo ratings yet
- NadaDocument316 pagesNadaSandor CleganeNo ratings yet
- MTLB Debate PRODocument3 pagesMTLB Debate PRORHODA MAE CAPUTOLNo ratings yet
- Kode Icd-10 Maternal Dan NeonatalDocument64 pagesKode Icd-10 Maternal Dan NeonatalEndah TriNo ratings yet
- Management of Obstetric Emergencies During PregnancyDocument22 pagesManagement of Obstetric Emergencies During PregnancyGeorge NakojaNo ratings yet