Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Manifestations
Uploaded by
Skyla FiestaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clinical Manifestations
Uploaded by
Skyla FiestaCopyright:
Available Formats
Clinical Manifestations
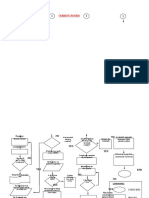
Three manifestations of autonomic neuropathy are related to the cardiac, gastrointestinal,
and renal systems.
Cardiovascular symptoms range from a fixed, slightly tachycardic heart rate and
orthostatic hypotension to silent, or painless, myocardial ischemia and infarction.
Delayed gastric emptying may occur with the typical gastrointestinal symptoms of early
satiety, bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
“Diabetic” constipation or diarrhea (especially nocturnal diarrhea) may occur as a result.
In addition, there may be unexplained wide swings in blood glucose levels related to
inconsistent absorption of the glucose from ingested foods secondary to the inconsistent
gastric emptying.
Urinary retention, a decreased sensation of bladder fullness, and other urinary symptoms
of neurogenic bladder result from autonomic neuropathy.
The patient with a neurogenic bladder is predisposed to development of urinary tract
infections because of the inability to empty the bladder completely.
This is especially true of patients with poorly controlled diabetes because hyperglycemia
impairs resistance to infection.
Hypoglycemic Unawareness
Autonomic neuropathy affecting the adrenal medulla is responsible for diminished or
absent adrenergic symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Patients may report that they no longer feel the typical shakiness, sweating, nervousness,
and palpitations associated with hypoglycemia. (pero meron padin)
Frequent blood glucose monitoring is recommended for these patients.
The inability to detect and treat these warning signs of hypoglycemia puts patients at risk
for development of dangerously low blood glucose levels.
Therefore, goals for blood glucose levels may need to be adjusted to reduce the risk for
hypoglycemia.
Patients and families need to be taught to recognize subtle and atypical symptoms of
hypoglycemia, such as numbness around the mouth and impaired ability to concentrate.
Sudomotor Neuropathy
The neuropathic condition called sudomotor neuropathy refers to a decrease or absence of
sweating (anhidrosis) of the extremities, with a compensatory increase in upper body
sweating.
Dryness of the feet increases the risk for the development of foot ulcers.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 3 2 1 Start: Current SystemDocument4 pages3 2 1 Start: Current SystemSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Code of The PhilippinesDocument55 pagesIntellectual Property Code of The PhilippinesSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Chart Data:: - She Was Given A Diamicron 60mg/tab OD - Pritor Plus 40 MG OD and Lacipil 2 MG ODDocument4 pagesChart Data:: - She Was Given A Diamicron 60mg/tab OD - Pritor Plus 40 MG OD and Lacipil 2 MG ODSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Personal and Educational Informatics Assignment (Skyla Fiesta)Document2 pagesPersonal and Educational Informatics Assignment (Skyla Fiesta)Skyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Diarrhea 2Document1 pageNursing Care Plan For Diarrhea 2Skyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesReview of Related LiteratureSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Code of The PhilippinesDocument55 pagesIntellectual Property Code of The PhilippinesSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Computer Teaching StrategiesDocument42 pagesComputer Teaching StrategiesSkyla Fiesta100% (2)
- Intro or CuesDocument2 pagesIntro or CuesSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
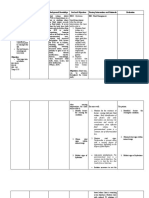
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- PBL 1Document7 pagesPBL 1Skyla Fiesta100% (1)
- Autonomic NeuropathiesDocument2 pagesAutonomic NeuropathiesSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept MapSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factor Disease Process Signs and Symptoms Medications Medical Interventions Medical DiagnosisDocument4 pagesPredisposing Factor Disease Process Signs and Symptoms Medications Medical Interventions Medical DiagnosisSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Skyla Fiesta - Carlo Acutis Reflection (BSN 3C)Document1 pageSkyla Fiesta - Carlo Acutis Reflection (BSN 3C)Skyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Preamble To The Ten CommandmentsDocument1 pagePreamble To The Ten CommandmentsSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Impaire Spontaneous VentilationDocument4 pagesImpaire Spontaneous VentilationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Application LetterDocument1 pageApplication LetterSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Research Chap 1 3Document46 pagesResearch Chap 1 3Skyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- (Keith) Sex Outside MarriageDocument1 page(Keith) Sex Outside MarriageSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)