0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views4 pagesSyllabus Comparison: Physics Chapters 21-22 vs 24.07.21
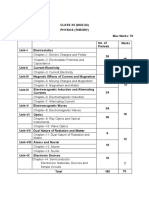
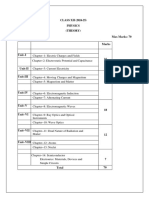
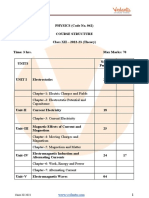
The document compares the syllabus from the academic years 2021-2022 and 2024.07.2021. It lists the chapters that have been omitted and retained between the two syllabi. The retained chapters include topics on electric charges and fields, electrostatic potential and capacitance, current electricity, magnetic effects of current and magnetism, electromagnetic induction and alternating currents, electromagnetic waves, optics, the dual nature of radiation and matter, atoms and nuclei, and semiconductor electronics.
Uploaded by
Jerr1 efxCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views4 pagesSyllabus Comparison: Physics Chapters 21-22 vs 24.07.21
The document compares the syllabus from the academic years 2021-2022 and 2024.07.2021. It lists the chapters that have been omitted and retained between the two syllabi. The retained chapters include topics on electric charges and fields, electrostatic potential and capacitance, current electricity, magnetic effects of current and magnetism, electromagnetic induction and alternating currents, electromagnetic waves, optics, the dual nature of radiation and matter, atoms and nuclei, and semiconductor electronics.
Uploaded by
Jerr1 efxCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd