Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Pin Descriptions: Atmega328P (Datasheet) 4
Uploaded by
salarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1 Pin Descriptions: Atmega328P (Datasheet) 4
Uploaded by
salarCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
1 Pin Descriptions
1.1.1 VCC
Digital supply voltage.
1.1.2 GND
Ground.
1.1.3 Port B (PB7:0) XTAL1/XTAL2/TOSC1/TOSC2
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port B output buffers have
symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability. As inputs, port B pins that are externally pulled
low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes
active, even if the clock is not running.
Depending on the clock selection fuse settings, PB6 can be used as input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the
internal clock operating circuit.
Depending on the clock selection fuse settings, PB7 can be used as output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
If the internal calibrated RC oscillator is used as chip clock source, PB7..6 is used as TOSC2..1 input for the asynchronous
Timer/Counter2 if the AS2 bit in ASSR is set.
The various special features of port B are elaborated in Section 13.3.1 “Alternate Functions of Port B” on page 65 and
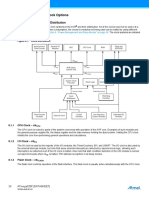
Section 8. “System Clock and Clock Options” on page 24.
1.1.4 Port C (PC5:0)
Port C is a 7-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The PC5..0 output buffers have
symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability. As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled
low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The port C pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes
active, even if the clock is not running.
1.1.5 PC6/RESET
If the RSTDISBL fuse is programmed, PC6 is used as an input pin. If the RSTDISBL fuse is unprogrammed, PC6 is used as
a reset input. A low level on this pin for longer than the minimum pulse length will generate a reset, even if the clock is not
running. The minimum pulse length is given in Table 28-4 on page 261. Shorter pulses are not guaranteed to generate a
reset.
The various special features of port C are elaborated in Section 13.3.2 “Alternate Functions of Port C” on page 68.
1.1.6 Port D (PD7:0)
Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The port D output buffers have
symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability. As inputs, port D pins that are externally pulled
low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes
active, even if the clock is not running.
The various special features of port D are elaborated in Section 13.3.3 “Alternate Functions of Port D” on page 70.
1.1.7 AVCC
AVCC is the supply voltage pin for the A/D converter, PC3:0, and ADC7:6. It should be externally connected to VCC, even if
the ADC is not used. If the ADC is used, it should be connected to VCC through a low-pass filter. Note that PC6..4 use digital
supply voltage, VCC.
1.1.8 AREF
AREF is the analog reference pin for the A/D converter.
4 ATmega328P [DATASHEET]
7810D–AVR–01/15
You might also like
- 5384 EVAir CompressorDocument88 pages5384 EVAir CompressorNanda Wicaksono100% (3)
- Analog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Ul 746B 2011 PDFDocument56 pagesUl 746B 2011 PDFShibu1992No ratings yet
- Port BDocument2 pagesPort Bgabriel sandovalNo ratings yet
- Atmega16 MicrocontrollerDocument8 pagesAtmega16 MicrocontrollerJyotirekha PatiNo ratings yet
- FINAL Documentation For EmbdedDocument11 pagesFINAL Documentation For EmbdedakashkirtyNo ratings yet
- Atmega16 Microcontroller:: 8-Bit Microcontroller With 16K Bytes In-System Programmable FlashDocument6 pagesAtmega16 Microcontroller:: 8-Bit Microcontroller With 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flashdanish sNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Arduino (Atmega 328P)Document8 pages4.1 Arduino (Atmega 328P)ALNATRON GROUPSNo ratings yet
- 8-Bit Microcontroller With 4/8K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Attiny48/88Document302 pages8-Bit Microcontroller With 4/8K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Attiny48/88sroaaNo ratings yet
- Pinout Diagram of Atmega16Document7 pagesPinout Diagram of Atmega16Harshit VermaNo ratings yet
- Atmega 328 PDocument344 pagesAtmega 328 PAlexandre100% (1)
- Data SheetDocument378 pagesData SheetErik Eustaquio MartinNo ratings yet
- M 168Document376 pagesM 168long_address_shortNo ratings yet
- FeaturesDocument4 pagesFeaturesR.abdul ShukurNo ratings yet
- ARDUINO Processor - ATMEL Microntroller DatashetDocument420 pagesARDUINO Processor - ATMEL Microntroller DatashetMauricio Rezende de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Atmel 8271 8 Bit AVR Microcontroller ATmega48A 48PA 88A 88PA 168A 168PA 328 328P - Datasheet - SummaryDocument31 pagesAtmel 8271 8 Bit AVR Microcontroller ATmega48A 48PA 88A 88PA 168A 168PA 328 328P - Datasheet - SummaryAndres PerezNo ratings yet
- Xddsafcdsvfgsadgvbzfshfscxvbxbvxzsdsafgdshgfvnbvnvnvn B: Descriptio N Alternate FunctionDocument8 pagesXddsafcdsvfgsadgvbzfshfscxvbxbvxzsdsafgdshgfvnbvnvnvn B: Descriptio N Alternate FunctionnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- Atmega328p 15azDocument26 pagesAtmega328p 15azMarco Antonio Segura LópezNo ratings yet
- Atmega 380Document420 pagesAtmega 380Prem Sharma100% (1)
- Atmel 8271 8 Bit AVR Microcontroller ATmega48A 48PA 88A 88PA 168A 168PA 328 328P - Datasheet - Complete PDFDocument650 pagesAtmel 8271 8 Bit AVR Microcontroller ATmega48A 48PA 88A 88PA 168A 168PA 328 328P - Datasheet - Complete PDFNext MillNo ratings yet
- XC VNVCN Vcnxdcvnxbcfhbxddsafcdsvfgsadgvbzfshfscxvbxbvxzsdsafgdshgf VNBVNVNVNBDocument8 pagesXC VNVCN Vcnxdcvnxbcfhbxddsafcdsvfgsadgvbzfshfscxvbxbvxzsdsafgdshgf VNBVNVNVNBnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- Sdsafgdshgfvnbvnvnvnb: Description Alternate FunctionDocument8 pagesSdsafgdshgfvnbvnvnvnb: Description Alternate FunctionnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- Description Alternate Function: SFDFDGFBGFDocument8 pagesDescription Alternate Function: SFDFDGFBGFnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- Atmega168pa Au AtmelDocument419 pagesAtmega168pa Au AtmelDeibis Francisco Paredes HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Arduino (Atmega 328P)Document37 pagesArduino (Atmega 328P)ALNATRON GROUPSNo ratings yet
- VCV CXB CCNBFVBFCGXC VNVCN Vcnxdcvnxbcfhbxddsafcdsvfgsadgvbzfshfscxvbxbvxzsdsafgdshgf VNBVNVNVNBDocument8 pagesVCV CXB CCNBFVBFCGXC VNVCN Vcnxdcvnxbcfhbxddsafcdsvfgsadgvbzfshfscxvbxbvxzsdsafgdshgf VNBVNVNVNBnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- ATmega328 DatasheetDocument567 pagesATmega328 DatasheetEthan Carlisle Couto ArchibaldNo ratings yet
- Sab80c517 N T40 - 85Document62 pagesSab80c517 N T40 - 85Carlos Eduardo Sandoval MatiasNo ratings yet
- Handling Avr Microcontroller Ports: Atmega16A Pin Out DiagramDocument5 pagesHandling Avr Microcontroller Ports: Atmega16A Pin Out DiagramM.SadatNo ratings yet
- Railway GateDocument46 pagesRailway GateRocky SinghNo ratings yet
- ATMEGA328P PU AtmelDocument448 pagesATMEGA328P PU AtmelLuckas JudockaNo ratings yet
- CSDVCXVFDXGBVFDGFDFSDFGFDGFCGGCF Gjhghfgjjmgxjgdjpin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionDocument8 pagesCSDVCXVFDXGBVFDGFDFSDFGFDGFCGGCF Gjhghfgjjmgxjgdjpin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- Enhanced 8-Bit Microcontroller With 32 KB Flash Memory: AT89C51AC2 T89C51AC2Document121 pagesEnhanced 8-Bit Microcontroller With 32 KB Flash Memory: AT89C51AC2 T89C51AC2mukhi2006No ratings yet
- At Mega 8Document305 pagesAt Mega 8Ronald KurniawanNo ratings yet
- At Mega 328Document566 pagesAt Mega 328Jeremy BartlettNo ratings yet
- Attiny 2313Document226 pagesAttiny 2313api-241773043No ratings yet
- CSDVCXVFDXGBVFDGFDFSDFGFDGFCGGCF Gjhghfgjjmgxjgdjpin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionDocument8 pagesCSDVCXVFDXGBVFDGFDFSDFGFDGFCGGCF Gjhghfgjjmgxjgdjpin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- ATmega328 DatasheetDocument35 pagesATmega328 DatasheetJoseph WhittakerNo ratings yet
- Microcomputer Components: 16-Bit CMOS Single-Chip MicrocontrollerDocument53 pagesMicrocomputer Components: 16-Bit CMOS Single-Chip MicrocontrollerpassnoNo ratings yet
- Micro Converter (Analog Device) 12-Bit Adcs and Dacs With Embedded High Speed 62-Kb Flash McuDocument20 pagesMicro Converter (Analog Device) 12-Bit Adcs and Dacs With Embedded High Speed 62-Kb Flash McushaileshNo ratings yet
- Pin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionDocument6 pagesPin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- AT89C51CC01Document167 pagesAT89C51CC01don krtekNo ratings yet
- AtMega32 Data SheetDocument313 pagesAtMega32 Data SheetSumeet TiwanaNo ratings yet
- Ppi 8255Document163 pagesPpi 8255Taufik Mage3No ratings yet
- 7 A H-Brigde For DC-Motor ApplicattionsDocument29 pages7 A H-Brigde For DC-Motor ApplicattionsJoão JoséNo ratings yet
- 8-Bit With 8kbytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega8A: FeaturesDocument20 pages8-Bit With 8kbytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega8A: FeaturesSpiky GVNo ratings yet
- Description Alternate FunctionDocument8 pagesDescription Alternate FunctionnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. OverviewDocument58 pagesChapter 1. OverviewmgitecetechNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Atmega 161 PDocument159 pagesDatasheet Atmega 161 PprincebahariNo ratings yet
- CSDVCXVFDXGBVFDGFDFSDFGFDGFCGGCF Gjhghfgjjmgxjgdjpin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionDocument8 pagesCSDVCXVFDXGBVFDGFDFSDFGFDGFCGGCF Gjhghfgjjmgxjgdjpin No. Pin Name Description Alternate FunctionnareshhhhhNo ratings yet
- Power Supply:: TransformerDocument17 pagesPower Supply:: Transformerobula863No ratings yet
- ATmega16 PDFDocument359 pagesATmega16 PDFAndre PdNo ratings yet
- At Mega 8Document302 pagesAt Mega 8RifkiHidayatNo ratings yet
- 8-Bit Microcontroller With 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega16 Atmega16LDocument349 pages8-Bit Microcontroller With 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Atmega16 Atmega16LIon CapcanariNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- 8.2 Clock Sources: 8.1.4 Asynchronous Timer Clock - CLKDocument1 page8.2 Clock Sources: 8.1.4 Asynchronous Timer Clock - CLKsalarNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Low Power Crystal Oscillator: Figure 8-2Document1 page8.3 Low Power Crystal Oscillator: Figure 8-2salarNo ratings yet
- System Clock and Clock OptionsDocument1 pageSystem Clock and Clock OptionssalarNo ratings yet
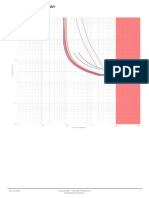
- Oscillator Source / Power Conditions Start-Up Time From Power-Down and Power-Save Additional Delay From Reset (V 5.0V) Cksel0 SUT1..0Document1 pageOscillator Source / Power Conditions Start-Up Time From Power-Down and Power-Save Additional Delay From Reset (V 5.0V) Cksel0 SUT1..0salarNo ratings yet
- 7.6 Register Description: 7.5.1 General Purpose I/O RegistersDocument1 page7.6 Register Description: 7.5.1 General Purpose I/O RegisterssalarNo ratings yet
- Sbic RJMP: Wait For Completion of Previous WriteDocument1 pageSbic RJMP: Wait For Completion of Previous WritesalarNo ratings yet
- Avr Memories: Figure 7-1. Program Memory Map Atmega328PDocument1 pageAvr Memories: Figure 7-1. Program Memory Map Atmega328PsalarNo ratings yet
- Figure 8-3. Crystal Oscillator ConnectionsDocument1 pageFigure 8-3. Crystal Oscillator ConnectionssalarNo ratings yet
- Eepm1 Eepm0 Programming Time Operation: Table 7-1. EEPROM Mode BitsDocument1 pageEepm1 Eepm0 Programming Time Operation: Table 7-1. EEPROM Mode BitssalarNo ratings yet
- 8.5 Low Frequency Crystal Oscillator: Table 8-7Document1 page8.5 Low Frequency Crystal Oscillator: Table 8-7salarNo ratings yet
- 7.4 EEPROM Data Memory: Section 27. "Memory Programming" On Page 241Document1 page7.4 EEPROM Data Memory: Section 27. "Memory Programming" On Page 241salarNo ratings yet
- Pin Configurations: Figure 1-1. PinoutDocument1 pagePin Configurations: Figure 1-1. PinoutsalarNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Instruction Execution Timing: 6.5.1 SPH and SPL - Stack Pointer High and Stack Pointer Low RegisterDocument1 page6.6 Instruction Execution Timing: 6.5.1 SPH and SPL - Stack Pointer High and Stack Pointer Low RegistersalarNo ratings yet
- In Cli Sbi Sbi Out: Store SREG ValueDocument1 pageIn Cli Sbi Sbi Out: Store SREG ValuesalarNo ratings yet
- 7.3 SRAM Data Memory: Figure 7-2Document1 page7.3 SRAM Data Memory: Figure 7-2salarNo ratings yet
- Atmel 0013Document1 pageAtmel 0013salarNo ratings yet
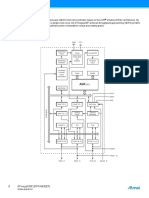
- Figure 2-1. Block DiagramDocument1 pageFigure 2-1. Block DiagramsalarNo ratings yet
- 6.4 General Purpose Register File: Figure 6-2Document1 page6.4 General Purpose Register File: Figure 6-2salarNo ratings yet
- 6.3.1 SREG - AVR Status Register: - Bit 7 - I: Global Interrupt EnableDocument1 page6.3.1 SREG - AVR Status Register: - Bit 7 - I: Global Interrupt EnablesalarNo ratings yet
- 7 Atmega328P (Datasheet) : 7810D-Avr-01/15Document1 page7 Atmega328P (Datasheet) : 7810D-Avr-01/15salarNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Flywheel DevelopmentDocument4 pagesAerospace Flywheel DevelopmentSuyambu LingamNo ratings yet
- The Common-Collector Amplifier Basic Circuit: + 2 1 1 2 BB 1 2 EE E CC + CC C BE BB EE C BB BE C EEDocument9 pagesThe Common-Collector Amplifier Basic Circuit: + 2 1 1 2 BB 1 2 EE E CC + CC C BE BB EE C BB BE C EEdominggoNo ratings yet
- Digital Swim Stopwatch Instructions PDFDocument1 pageDigital Swim Stopwatch Instructions PDFalexmilarNo ratings yet
- Module B - Short Circuit Analysis PDFDocument70 pagesModule B - Short Circuit Analysis PDFMD Shamim Hasan SajibNo ratings yet
- Lenovo G410 - G510 Compal LA-9642p UMA Rev1.0 SchematicDocument47 pagesLenovo G410 - G510 Compal LA-9642p UMA Rev1.0 SchematicMiiguel RiícoNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Date Planned: - / - / - Cbse Pattern Duration: 3 Hours Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level - 0 Maximum Marks: 70Document39 pagesDate Planned: - / - / - Cbse Pattern Duration: 3 Hours Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level - 0 Maximum Marks: 70brainx Magic100% (1)
- LightSYS - Manual de Instalacion Completo (Inglés)Document232 pagesLightSYS - Manual de Instalacion Completo (Inglés)cbongioNo ratings yet
- Manual Ti103Document2 pagesManual Ti103ajaydce05No ratings yet
- 6415 FundamentalsImprovements KZ-DC 20101025Document12 pages6415 FundamentalsImprovements KZ-DC 20101025rafeeque90No ratings yet
- User'S Manual: Portable High Current Test Set Model Number Hc1Document17 pagesUser'S Manual: Portable High Current Test Set Model Number Hc1Victor Jose Romero FernandezNo ratings yet
- CTA TehnicDocument5 pagesCTA TehnicLar Ionut AndreiNo ratings yet
- Opening Electrical Panel CoversDocument1 pageOpening Electrical Panel Coversnavneet sirohiNo ratings yet
- Connection of Embedded Generating Plant Up To 5MW: Engineering Recommendation No.3 of The Electricity Distribution CodeDocument12 pagesConnection of Embedded Generating Plant Up To 5MW: Engineering Recommendation No.3 of The Electricity Distribution CodeDrSalama Abo ZeadNo ratings yet
- GSM Paging Problem AnalysisDocument46 pagesGSM Paging Problem AnalysisedufigvirgilioNo ratings yet
- Atmel 8465 8 and 16 Bit AVR Microcontrollers XMEGA C - Manual PDFDocument358 pagesAtmel 8465 8 and 16 Bit AVR Microcontrollers XMEGA C - Manual PDFNorlan SuarezNo ratings yet
- Cpuz ReadmeDocument6 pagesCpuz Readmeforest_victorNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Syllabus Second Year - Fourth SemisterDocument9 pagesComputer Science Syllabus Second Year - Fourth SemisterTurtle17No ratings yet
- Setting VCB 200 AmpDocument5 pagesSetting VCB 200 AmpAUGUSTA WIBI ARDIKTANo ratings yet
- 08 - MGS1000BMG 7PC 0819 1Document4 pages08 - MGS1000BMG 7PC 0819 1gondrayNo ratings yet
- Lighting Lighting: Tango G3 - BVP38xDocument3 pagesLighting Lighting: Tango G3 - BVP38xRiza PyNo ratings yet
- Class 2: Servomotors - Basics & Working: Ice 3015: Control System ComponentsDocument19 pagesClass 2: Servomotors - Basics & Working: Ice 3015: Control System ComponentsArchit DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Management PresentationDocument19 pagesSpectrum Management Presentationakrs79No ratings yet
- Dissolution of Inorganic SamplesDocument11 pagesDissolution of Inorganic SamplesJames BabenNo ratings yet
- TitlesDocument24 pagesTitlesjpncorndNo ratings yet
- Anker ROAV C1 Dash CamDocument14 pagesAnker ROAV C1 Dash CamVenu RajputNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument25 pagesTransformerJerald SagusayNo ratings yet