100% found this document useful (3 votes)
3K views4 pagesAssignment - 7
This document contains 20 multiple choice and multiple select questions about digital land surveying and mapping. The questions cover topics like map projections, reconnaissance surveys, map design elements, software used for mapping survey data, specifications for topographic maps, scale and accuracy considerations, and the steps involved in automated mapping and digital map making.
Uploaded by
Chea MasangkayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (3 votes)
3K views4 pagesAssignment - 7
This document contains 20 multiple choice and multiple select questions about digital land surveying and mapping. The questions cover topics like map projections, reconnaissance surveys, map design elements, software used for mapping survey data, specifications for topographic maps, scale and accuracy considerations, and the steps involved in automated mapping and digital map making.
Uploaded by
Chea MasangkayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
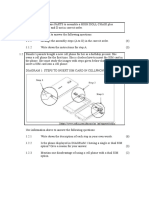
- Multiple Choice Questions on Digital Land Surveying and Mapping