Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bone Histology
Bone Histology
Uploaded by
For AstroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bone Histology
Bone Histology
Uploaded by
For AstroCopyright:
Available Formats
Function of Bones
1. Support
2. Protection (protect internal organs)
3. Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments and joints)
4. Mineral homeostasis (bones act as reserves of minerals important for the body like calcium or
phosphorus)
5. Hematopoiesis: blood cell formation
6. Storage of adipose tissue: yellow marrow
Shape of Bones
1. Long bones (e.g., humerus, femur)
2. Short bones (e.g., carpals, tarsals, patella)
3. Flat bones (e.g., parietal bone, scapula, sternum)
4. Irregular bones (e.g., vertebrae, hip bones)
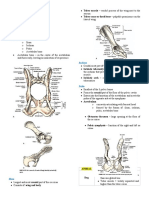
Bone Anatomy
• Diaphysis: long shaft of bone
• Epiphysis: ends of bone
• Epiphyseal plate: growth plate
• Metaphysis: b/w epiphysis and diaphysis
• Articular cartilage: covers epiphysis
• Periosteum: bone covering (pain sensitive)
• Sharpey’s fibers: periosteum attaches to underlying bone
• Medullary cavity: hollow chamber in bone
o red marrow produces blood cells
o yellow marrow is adipose
• Endosteum: thin layer lining the medullary cavity
LONG BONES
• Compact Bone – dense outer layer
• Spongy Bone – (cancellous bone) honeycomb of trabeculae (needle-like or flat pieces) filled with
bone marrow
Compact bone: Osteon, external layer
• called lamellar bone (groups of elongated tubules called lamella)
• majority of all long bones
• protection and strength (wt. bearing)
• concentric ring structure
• blood vessels and nerves penetrate
• periosteum through horizontal openings called perforating (Volkmann’s) canals.
Blood and Nerve Supply of Bone
• Bone is supplied with blood by:
o Periosteal arteries accompanied by nerves supply the periosteum and compact bone
o Epiphyseal veins carry blood away from long bones
• Nerves accompany the blood vessels that supply bones
o The periosteum is rich in sensory nerves sensitive to tearing or tension
Compact Bone
• Central (Haversian) canals run longitudinally. Blood vessels and nerves.
o around canals are concentric lamella
o osteocytes occupy lacunae which are between the lamella
o radiating from the lacunae are channels called canaliculi (finger
like processes of osteocytes)
• Lacunae are connected to one another by canaliculi
• Osteon contains:
1. central canal
2. surrounding lamellae
3. osteocytes
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Veterinary Microscopic Anatomy (Histology) Lab: Lecture 01: The MicroscopeDocument21 pagesVeterinary Microscopic Anatomy (Histology) Lab: Lecture 01: The MicroscopeFor AstroNo ratings yet
- LPO / Low Power ObjectiveDocument2 pagesLPO / Low Power ObjectiveFor AstroNo ratings yet
- Cartilage and BoneDocument2 pagesCartilage and BoneFor AstroNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Anatomy and EmbryologyDocument77 pagesVeterinary Anatomy and EmbryologyFor AstroNo ratings yet
- Os Coxae: Pelvic Limb A. Os Coxae B. Femur C. D. Tarsals E. FDocument4 pagesOs Coxae: Pelvic Limb A. Os Coxae B. Femur C. D. Tarsals E. FFor AstroNo ratings yet
- SCAPULA /shoulder Blade/: Biceps Brachii MuscleDocument5 pagesSCAPULA /shoulder Blade/: Biceps Brachii MuscleFor AstroNo ratings yet