Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability and Statistics: Integrated Math 1
Uploaded by
johnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability and Statistics: Integrated Math 1
Uploaded by
johnCopyright:
Available Formats
Integrated Math 1
Probability and Statistics
Farmington Public Schools
Grade 9
Mathematics
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 1
Table of Contents
Unit Summary
………………….….…………..page 3
Stage One: Standards
Stage One identifies the desired results of the unit including the broad understandings, the unit
outcome statement and essential questions that focus the unit, and the necessary knowledge and
skills.
The Understanding by Design Handbook, 1999
…………………………….... page 4-6
Stage Two: Assessment Package
Stage Two determines the acceptable evidence that students have acquired the understandings, knowledge
and skills identified in Stage One.
……………………………… page 7-8
Stage Three: Curriculum and Instruction
Stage Three helps teachers plan learning experiences and instruction that aligns with Stage One and
enables students to be successful in Stage two. Planning and lesson options are given, however teachers are
encouraged to customize this stage to their own students, maintaining alignment with Stages One and Two.
………………..……………… page 9-11
Appendices
….....………………………. page 12-57
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 2
Unit Summary
This unit on Statistics and Probability is taught in Integrated Math 1
after a unit on exponential patterns and before a unit on networks. This
unit will take approximately 5-6 weeks of class time.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 3
Stage One: Standards
Stage One identifies the desired results of the unit including the broad understandings, the unit outcome
statement and essential questions that focus the unit, and the necessary knowledge and skills.
The Understanding by Design Handbook, 1999
Essential Understandings and Content Standards
#7 Students will understand that people use basis concepts of probability
and statistics to meaningfully collect, organize, display and analyze data to
simulate events.
Students will:
a. (12th) estimate probabilities and predict outcomes
d. (12th) select appropriate measures of central tendency
g. (12th) use scatter plots and curve fitting techniques to interpolate
and extrapolate from data
i. (12th) use simulations to estimate probability
c. (8th) describe the shape of the data using range, outliers, and
measure of central tendency
d. (8th) select and construct appropriate graphs and measures of
central tendency for sets of data
Unit Outcome Statement
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 4
Consistently aligning all instruction with this statement will maintain focus in this unit.
Students will use statistics and probability concepts to make decisions about
real world situations using a sample. As a result of the statistics component
of this unit students will organize, display, and describe data using
appropriate statistical and graphical methods. As a result of the probability
component of this unit students will understand and apply the basic concepts
of probability using sample spaces, Venn diagrams and tree diagrams as well
as perform simulations.
Essential Questions
These questions help to focus the unit and guide inquiry.
• How reliable or useful are the statistical outcomes in decision making?
• How can data be described and interpreted?
• How can estimations of likelihood be made for random events?
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 5
Knowledge and Skills
The Knowledge and Skills section includes the key facts, concepts, principles, skills, and processes called for by
the content standards and needed by students to reach desired understandings.
The Understanding by Design Handbook, 1999
Knowledge
♦ Distinguish among mean, median and mode
♦ Define simple probability
♦ Describe a random event
♦ Understand the Law of Large Numbers and its relationship to probability
♦ Decide when to use a sample space, tree diagram, or Venn diagram
♦ How to construct and perform a simulation
♦ Determine the 5-number summary for data
♦ Identify the different graphical displays for data
o Stem and leaf
o Histogram
o Box plot
o Scatter plot
o Time plot
Skills/Processes
♦ Apply the Fundamental Counting Principle
♦ Calculate probabilities of an event by using a sample space, trees or Venn
diagram
♦ Calculate the 5-number summary
♦ Identify the shape of a distribution (skewed, symmetric, center)
♦ Perform an appropriate simulation for an event
♦ Construct the appropriate graphical displays for data
o Stem and leaf
o Histogram
o Box plot
o Scatter plot
o Time plot
Thinking Skills
♦ Recognizing intended meaning
♦ Making inferences
♦ Identifying appropriate evidence
♦ Recognizing fact vs. opinion
♦ Sorting/categorizing
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 6
Stage Two: Assessment Package
Stage Two determines the acceptable evidence that students have acquired the understandings, knowledge and
skills identified in Stage One.
Authentic Performance Task: Analyzing spending trends using Statistics
Goal: Students will analyze the spending habits of families in Farmington using the
grocery receipts. They will report their findings in a newspaper article.
using the data, graphs, measures of central tendency and probability values for
specific types of food items.
Role: You are a reporter for the Farmington Times Weekly newspaper. You have
been assigned the task of writing an article for the newspaper about the spending
habits of families in Farmington for publication in the local paper.
Audience: The editor of the newspaper and the readers of the newspaper article
Situation: With the emphasis on eating healthy and the new food pyramid, this
article will be to inform readers on the trends you see and make inferences about the
nutritional level of the diet of the families.
Product/Performance/Purpose: Using the receipts collected you will write an article
for the newspaper that will include the Who, What, When, Where and How of the
investigation. Within the article you will include:
• A categorical table of data including: dairy, produce, meat, grain, other foods,
and non-food purchases.
• Appropriate graphic for the data
• Measures of central tendency and range for total spent at the store as well as
for each category in the data table
• A time plot of (time shopped, $ spent) along with a linear regression analysis
• Comparison of food purchased to the food pyramid (attached)
• Percent saved using coupons
Standards & criteria for success: You will be assessed on:
o Mathematical accuracy including work
o Appropriate graphic with clear labels
o Proper use of mathematical terminology
o Clear conclusions drawn from the data analysis
o Neatness
Content standards addressed:
d. (12th) select appropriate measures of central tendency
g. (12th) use a scatter plots and curve fitting techniques to interpolate and
extrapolate from data
i. (12th) use simulations to estimate probability
c. (8th) describe the shape of the data using range, outliers, and measure of
central tendency
d. (8th) select and construct appropriate graphs and measures of central
tendency for sets of data
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 7
Tests, Quizzes, and Other Quick and Ongoing Checks for Understanding
Quick Quiz on stem and leaf plots (7d 8th grade)
Baseball Data stem and leaf assessment, students make a stem and leaf for both the
American and National League homerun data and compare and contrast their
findings. (7 c, 7d 8th grade)
Mean, Median, Mode progress check (7c 8th grade)
Teacher made progress check on choosing the appropriate measure of central
tendency (7d 12th grade)
Unit Test - Statistics (7d 12th grade, 7c, 7d 8th grade)
The focus on the test was on measures of central tendency, constructing and
interpreting graphs, the 5-number summary IQR.
Quiz on Simulations for a random event (7i 12th grade)
Probability progress check including sample space and probabilities (7a 12th grade)
Teacher made progress check on Venn diagrams (7a 12th grade)
Teacher made progress check on Fundamental Counting Principle (7a 12th grade)
Test on Probability (7a, 7i, 12th grade)
The focus of the test is on creating sample spaces, using tree and Venn diagrams for
probabilities and using the Fundamental Counting Principle to solve real world
problems
Projects, Reports, Etc.
Students will find two articles from the newspaper or magazine that incorporates
the use of statistics and /or probability. They will then write an analysis of the
appropriate use of statistics and/or probability in the decision making process of the
article. (7d 12th grade, 7c, 7d 8th grade)
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 8
Stage Three: Learning Experiences and Instruction
Stage Three helps teachers plan learning experiences and instruction that align with Stage One and enables
students to be successful in Stage Two.
Learning Experiences and Instruction
The learning experiences and instruction described in this section provide
teachers with one option for meeting the standards listed in Stage One. Teachers
are encouraged to design their own learning experiences and instruction,
tailored to the needs of their particular students
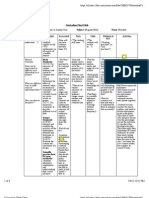
Middle Grades and High School
Guiding Questions Instructional Strategies Checking for
Understanding
Day 1-5 Picturing data
Given a data set, how can Think about this pg 2, given
you display it? a graph or table discuss with
class how it can be used to
make decisions. Lesson 2 pg 10 #5 checkpoint
EQ How can data be pg 11
described and interpreted? NOTE- U#L#I#=Unit,
Lesson. Investigation in text.
These are student-centered
investigation for groups of
two to four students.
Students instigate a
situation and develop a
problem solving strategy for
the concept in the title of the
investigation. Parts of the
investigations include a
student self-assessment of
the concept. After student-
centered discussion, the
teacher will bring the group
to an understanding of the
concept.
U1L1I2 Describing patterns National/American League
in data #2, 4 a-c pg. 9-10 worksheet
U1L2I1 Shapes of OYO pg 23
distributions # 1-4 pg 14-17 MORE pg 24-28 M1 O2 O5
U1L2I2 Producing plots with Quiz - Stem and Leaf
technology # 1, 3-5 pg 19-22
Hook: What does a picture of
data tell us about the
population?
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 9
Day 6-12 Measuring Data
Given a set of data, how can U1L2I3 Measures of center Lesson 3 pg 35-6 #5
you describe the center, #1, 2, 4a,b,g, 6 pg 31-6 Worksheet on Measures of
shape and spread? central tendency
MORE pg 38-44 M2, O1, O3,
R2
EQ How can data be Progress check - mean
described and interpreted? median mode
U1L3I1 The five number Lesson 1 pg 50 #7-9
summary#1-5 pg 48-9
U1L3I2 Picturing variability Lesson 2 pg 54 #5
#4 pg 53 one by hand, one on Worksheet - statistics
the calculator Worksheet Review of
histograms, 5# summary and
box plots
Hook: What does 'Average"
mean? What is the best way Authentic Assessment
to describe the center and
spread of a data set? Test Statistics
Dietary Change and
Cholesterol. Could be used
for review for test.
Days 13-17 Simulations
How do you use a simulation Probability Investigative Probability problem solving
to estimate probability? Spinner Task worksheet
Do simulation results always U7L1I1 How many children? OYO pg 490
equal theoretical #1-7 pg 484-8 MORE pg 491- 5 M1, M2,
probabilities? M3, O2, O5
Hook: Is it Fair? (spinners)
EQ How reliable or useful Why do we use simulations? Quiz
are the statistical outcomes
in decision-making? Teacher created-Students
research project of finding
newspaper or magazine
articles and analysis of the
appropriateness of the use of
statistics or probability.
Day 18- 25: Picturing Probability
How are diagrams used to Create a sample space for Calculate probabilities from
determine probability? rolling two dice including the this sample space
sum of the two dice.
Worksheet
Use a tree diagram to model Complete worksheet
random events. Worksheet
Progress check Tree/sample
How can you calculate the space
size of the sample space
without a diagram? Counting Theory worksheet Complete worksheet for
student create a sample homework
space for an event and
develop an arithmetic way of
answering the question.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 10
EQ How can estimations of Abby's Kennel Investigation Venn diagram worksheet
likelihood be made for to organize data using a
random events? Venn diagram.
CAPT question bank for
Hook: What is the probability and statistics
probability of rolling a sum
of seven on a pair of dice?
Test Probability
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 11
Appendices
Complete set of Essential understandings for your discipline
Any student work sheets
List of resources including texts, videos, field trips, web sites, etc.
Navigating through Probability in grades 9-12, NCTM
Navigating through Data Analysis in grades 9-12, NCTM
Contemporary Mathematics In Context, Course 1 A and B
Mathematics binder for Integrated Math 1 semester 1 and 2
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 12
Integrated Math I
Mean, Median & Mode Progress Check Name_______________________________
Find the mean, median and mode for the following set of data:
5 13 9 12 4 11 5 15 19 8
Mean__________ Median___________ Mode__________
Integrated Math I
Mean, Median & Mode Progress Check Name_______________________________
Find the mean, median and mode for the following set of data:
5 13 9 14 4 11 7 15 19 13
Mean__________ Median___________ Mode__________
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 13
Integrated Math I Name _________________________
Unit 1Test Date __________________________
1. A mathematics teacher, Mrs. Valdez, wanted to test how the use of a
calculator might affect her students’ scores on a test. On the day of
the test, the students who were selected to use calculators received
the following scores: 100, 55, 78, 66, 93, 73, 73, 65, 83, 72, and 57.
a) Make a stem and leaf plot.
b) Find the mean, median and mode (measures of center).
Mean __________ Median _____________ Mode _____________
c) If Mrs. Valdez has a student who was absent and takes a make up test, which
measure of center mentioned above will be the most affected if the student gets a
30? Why
2. On a test of eye-hand coordination, the number of seconds required to finish a task
involving fitting various shapes into corresponding holes is recorded. A group of 15
students in the second grade had the following number of seconds:
Coordination Scores in Seconds
83 76 90 58 66 44 86 66 61 59 50 53 61 64 73
a) Find the mean Mean _____________
b) Find the five number summary Minimum _____________
Q2 _____________
Median _____________
Q3 _____________
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 14
Maximum _____________
c) Find the IQR (Interquartile Range). Explain what the IQR means in terms of the
eye-hand coordination.
IQR ____________ Explanation:
3.
(insert a box plot for this question)
Using the box plot shown:
a) What does the “n = 20” mean?
b) How many scores are greater than 20?
c) What is the five number summary?
Minimum _____________
Q2 _____________
Median _____________
Q3 _____________
Maximum _____________
d) What is the range of the data?
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 15
4. Mr. Thomas has three Integrated Math 1 classes. Last week he gave a quiz with a
maximum of 10 points. The grades for each class are given in the table:
Per 1 8 7 9 8 6 7 8 7 6 6 8 8 6 6 7 6 4 9 7 7
Per 2 10 8 10 9 6 10 5 7 5 8 9 9 5 6 6 6 8 8 8 8
Per 3 8 9 9 8 5 9 9 8 8 7 8 9 9 7 6 5 2 9 7 9
a) Use the table to create a box plot for each of the classes and copy them below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
b) Which class has the largest interquartile range (IQR)?
c) Compare each class using the box plots. Are they similar? Different?
d) Which class would you say has the better scores? How did the box plots help
with your decision?
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 16
5. Based on the description below, construct a histogram:
The minimum score is between 20 and 29.
The maximum score is between 80 and 89.
Most of the scores were in the 40’s.
No one received quiz scores in the 50’s.
The graph is skewed to the right.
6. The histogram below shows the performance of a social studies class at Farmington
High School on a recent quiz. The quiz scores were grouped into intervals of size 5. A
score on the edge of a bar is counted in the bar on the right.
Describe the data shown in the histogram by using what you have learned in class and by
using your handout (Master 9a/9b). Be specific and thorough.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 17
Integrated Math 1 Name ______________________
Stats/Prob Authentic Assessment Date _____________
You are a reporter for the Farmington Times Weekly newspaper. You have been
assigned the task of writing an article for the newspaper about the spending habits
of families in Farmington for publication in the local paper. Your emphasis should be
on eating healthy and the new food pyramid. The article will be to inform readers on the trends
you see and make inferences about the nutritional level of the diet of the families.
Preliminary to writing the article you need to collect between 10 and 15 grocery store receipts for
family shopping trips. Before you write your article you will need to analyze the data on these
receipts and study the food pyramid provided. You should then check with the editor (teacher) to
make sure the data is usable for the article.
Using the analysis of the data collected you will write the article for the newspaper. The article
should include information about the data (Who, What, When, Where and How). Within the
article you will include:
• A categorical table of data including: dairy, produce, meat, grain, other foods, and non-
food purchases.
• Appropriate graphic for the data (at least one graph)
• An appropriate measure of central tendency and range for total spent at the store as well
as for each category in the data table
• A time plot of (time shopped, $ spent) along with a linear regression analysis (best fit)
• Comparison of distribution of food purchased in relationship to the guidelines in the
food pyramid (attached)
• Percent saved using coupons (if applicable)
Due date _______________________
Grade will be based on:
o Mathematical accuracy including work
o Appropriate graphic with clear labels
o Proper use of mathematical terminology
o Clear conclusions drawn from the data analysis
o How well you communicated the outcome of your work
o Neatness
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 18
Project Rubric
Meets expectations Partially correct Incorrect
Mathematical accuracy All mathematics is Some computational Missing computations or
computations shown and correct. errors present or not incorrect mathematics
included.
Appropriate graph Graphs used are Graphs used is not No graph included or an
appropriate for the data appropriate but correctly inappropriate graph was
and correctly drawn drawn, or is a correct used incorrectly
graph but
inappropriately drawn
Clear labels/scales All labels and scales are Some labels are missing Labels and scales are
accurate and on the or scale is incorrect missing
graph
Communication Mathematical Mathematical Mathematical
accuracy-vocabulary terminology is used terminology is generally terminology is used
correctly throughout the used correctly however incorrectly or not
paper there is consistent present.
incorrect use of some
concept.
Communication Clear and accurate Conclusions are unclear Conclusion are missing
conclusion clarity conclusions are given for the graphs or or inappropriate for the
based on the calculations graph or calculations
calculations and graphs
Overall neatness = 5 points
The IM1 team will develop scoring of this rubric when the assignment is given.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 19
QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (LZW) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (LZW) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 20
Integrated Math 1 Name ___________________
Unit 7 lesson 1 quiz A
1. Suppose a population control plan for Transville allows parents to have at most four children
each, and must stop having children when they have two girls. Explain how to use a coin to
simulate the experiment of having children until you have either two girls or four children.
2. Ross was exposed to a cold virus and now has a 50% chance of developing a cold on each of the
next 7 days. A simulation was run in which a fair coin was tossed.
H = develops a cold T = does not develop a cold
Each coin toss represents one day. So for example, TTH means that Ross developed a cold on the
third day, and TTTTTTT mean no cold for 7 days.
DATA
TTH TTTTTTH TH TH TH TTTH TH TTTH
TTTTH TTTTTH TH H TTH H H TTTTH
a. Complete the frequency table for the simulation:
Developed a cold Frequency
On day number
1 ________
2 ________
3 ________
4 ________
5 ________
6 ________
7 ________
b. Construct a histogram for the frequency table.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 21
c. Using the frequency table or histogram, estimate the average number of days it took Ross to develop a
cold.
d. Using the frequency table or histogram, estimate the percent of times that Ross will develop a cold
before the third day.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 22
Integrated Math 1 Name:________________________
TEST – Probability Date: ________________________
1. A bowl has several jelly beans in it, 4 red, 3 black, 2 green, 2 purple, and 1 orange.
If you choose one jelly bean,
a) What is the probability you will get a red one?
b) What is the probability you will get a purple or an orange one?
2. A bag holds blocks numbered 1 to 5. You draw one block out of the bag and then without
replacing it you draw a second block.
a) Produce a sample space for this situation.
b) What is the probability you will draw the same number twice?
c) What is the probability the second number will be odd?
d) If the first number is even, what is the probability the second number is odd?
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 23
3. Make a table for the arithmetic sums of rolling two dice.
a) What is the probability you will get a sum of 5?
b) What is the probability you will get an even number for a sum?
c) What is the probability that the sum will be greater than 9?
4. Make a tree that represents the tossing of a fair coin 3 times. List the sample space.
a) What is the size of the sample space?
b) What is the probability of getting 3 heads (in a row)?
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 24
c) What is the probability of getting 2 heads and 1 tail (in any order)?
5. Jenna has in her suitcase 4shirts and 3 pairs of jeans along with 2 pairs of shoes.
How many possible outfits does she have?
6. If you have some cards numbered 1 through 5. You draw one and then another after returning the first
one.
a) What is the probability of choosing a 9?
b) What is the probability of choosing 2 even cards?
7. Six friends (let’s call them A, B, C, D, E, and F) are going in pairs on a roller coaster.
a) What is the sample space for pairs of riders? (AB is the same as BA)
b) What is the probability of A and E riding together?
c) What is the probability of A and E not riding together?
8. Suppose a new population growth plan for China is proposed. Parents will be allowed to have at
most 3 children and must stop having children as soon as a boy is born. Explain how to simulate the
experiment of having children until you either have one boy or three children.
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 25
9. There are 49 people who own pets. 15 people own only dogs, 5 own cats and dogs only, and 3 own
cats, dogs and birds, and 4 own only a bird.
a. Draw a Venn diagram.
b. How many people own only cats?
c. How many pets are there?
In the game of “Shoot!,” three friends put out one or two fingers to find the sum.
If the sum of the three is odd, Mike gets 3 points.
If there are at least 2 numbers the same, Sue gets 2 points.
If all numbers are the same, Alice gets 14 points.
What is the probability of each of them winning?
Is this a fair game? Why or why not?
Beben, Lepi DRAFT: 06/30/2006 Farmington Public Schools 26
You might also like
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Document9 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- 180 Days of Math For Fifth Grade - Sanet.stDocument210 pages180 Days of Math For Fifth Grade - Sanet.stCrescent Cricket100% (2)
- Self-test on the COSO ERM frameworkDocument6 pagesSelf-test on the COSO ERM frameworkLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Data Collection and Organization: Study GuideDocument46 pagesData Collection and Organization: Study GuideAirah ColumnaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Income Statements EPS CalculationsDocument39 pagesUnderstanding Income Statements EPS CalculationsKeshav KaplushNo ratings yet
- Apstatssyllabus18 19Document3 pagesApstatssyllabus18 19api-286599245No ratings yet
- Sample Questions: General Information About The Nation's Report CardDocument49 pagesSample Questions: General Information About The Nation's Report CardswainanjanNo ratings yet
- Math Unit Plan - Grade 6Document19 pagesMath Unit Plan - Grade 6api-490524431No ratings yet
- Sample Questions: General Information About The Nation's Report CardDocument57 pagesSample Questions: General Information About The Nation's Report CardswainanjanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum AnalysisDocument16 pagesCurriculum Analysisapi-245616113No ratings yet
- Ccgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit1seDocument32 pagesCcgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit1seapi-239312188No ratings yet
- Curriculum Table Chart - RevisedDocument7 pagesCurriculum Table Chart - RevisedVartyYeremianNo ratings yet
- Step FinalDocument32 pagesStep Finalapi-448492086No ratings yet
- 2A Chapter 6 CA GuidelinesDocument1 page2A Chapter 6 CA Guidelineselenana710No ratings yet
- Unit Outline: MA5.2-1WM MA5.2-3WM MA5.2-15SP MALS-35SP MALS-36SP MALS-37SPDocument37 pagesUnit Outline: MA5.2-1WM MA5.2-3WM MA5.2-15SP MALS-35SP MALS-36SP MALS-37SPapi-408516407100% (1)
- Interpretingdata Grade6 Edf3021 Mathsassignment2Document5 pagesInterpretingdata Grade6 Edf3021 Mathsassignment2api-320610068No ratings yet
- Session F-2 - Statistics and Probability For Middle-School Math Te PDFDocument25 pagesSession F-2 - Statistics and Probability For Middle-School Math Te PDFFloravy Dimple Baisac ParantarNo ratings yet
- RC Tycoon Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesRC Tycoon Lesson Planapi-248223707No ratings yet
- Amy Corns - Connecting Scatter Plots and Correlation Coefficients ActivityDocument23 pagesAmy Corns - Connecting Scatter Plots and Correlation Coefficients ActivityRonvan AspillaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Sorico Math Unit 4 2 2013-2014Document3 pagesGrade 8 Sorico Math Unit 4 2 2013-2014api-233707670100% (1)
- 5-6 Data and ProbabilityDocument13 pages5-6 Data and ProbabilitymrkballNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics SyllabusDocument7 pagesProbability and Statistics Syllabusapi-470953927No ratings yet
- Stat. and Prob. Module 3Document24 pagesStat. and Prob. Module 3Catherine Joy MenesNo ratings yet
- Stats and Probability Unit UbdDocument54 pagesStats and Probability Unit Ubdapi-314438906100% (1)
- Ued 400 Stclair Payne Stage Three Math 5Document7 pagesUed 400 Stclair Payne Stage Three Math 5api-581039094No ratings yet
- Statistics Curr Map 2014-15Document8 pagesStatistics Curr Map 2014-15api-277145356No ratings yet
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide NovemberDocument56 pagesEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide Novemberapi-271033247No ratings yet
- Nemani Assignment 2b 5-Day Learning Map 1Document10 pagesNemani Assignment 2b 5-Day Learning Map 1api-464927954No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MasonmannixmorgankirkpatrickDocument18 pagesLesson Plan Masonmannixmorgankirkpatrickapi-585574749No ratings yet
- Drills A-Strategy-In-Improving-The-Numeracy-Skills-On-Operations of Integers-Of-Grade-8-StudentsDocument7 pagesDrills A-Strategy-In-Improving-The-Numeracy-Skills-On-Operations of Integers-Of-Grade-8-StudentsErliza PerezNo ratings yet
- New Normal Preparedness and The Academic Performance of StudentsDocument79 pagesNew Normal Preparedness and The Academic Performance of StudentsPrince GabatoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Learning Menu - Chloe Dunlop 2046935Document12 pagesAssignment 2 - Learning Menu - Chloe Dunlop 2046935api-428406493No ratings yet
- Stat. and Prob. Module 1Document20 pagesStat. and Prob. Module 1Catherine Joy Menes100% (1)
- Digital Unit PlanDocument5 pagesDigital Unit Planapi-259884525No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Document8 pagesLesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)api-324234986No ratings yet
- Edit 608 Keystone Unit and Classroom Tech Plan-Sondra Polan 2017Document13 pagesEdit 608 Keystone Unit and Classroom Tech Plan-Sondra Polan 2017api-399832630No ratings yet
- Math 9 Course Outline 2019-2020 1Document3 pagesMath 9 Course Outline 2019-2020 1api-264036251No ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument2 pagesData Analysisapi-162570032No ratings yet
- Sta 2023Document5 pagesSta 2023Chrystelle CharlierNo ratings yet
- Statslessonplanems480 HerringDocument15 pagesStatslessonplanems480 Herringapi-439439342No ratings yet
- Data Collection ProjectDocument3 pagesData Collection ProjectMsJacciNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesNormal Distribution Lesson Planapi-26632580075% (4)
- DateDocument3 pagesDateapi-237198864No ratings yet
- BCF204-Statistical Techniques With RDocument2 pagesBCF204-Statistical Techniques With RMo AadilNo ratings yet
- Unit Objective: Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesUnit Objective: Lesson Planapi-295559929No ratings yet
- Mean Mode RangeDocument16 pagesMean Mode RangePraise NehumambiNo ratings yet
- Last MDocument8 pagesLast Mgladen shelley billonesNo ratings yet
- Project1-1 2 InstructionaldesignDocument65 pagesProject1-1 2 Instructionaldesignapi-250634113No ratings yet
- Text Messaging Is Time Consuming! What Gives?Document18 pagesText Messaging Is Time Consuming! What Gives?Trisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Document5 pagesLesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)api-500841760No ratings yet
- Sample Questions: General Information About The Nation's Report CardDocument45 pagesSample Questions: General Information About The Nation's Report CardswainanjanNo ratings yet
- Mental Math Grade 6Document25 pagesMental Math Grade 6berman100No ratings yet
- Udl Lesson On BoxplotsDocument5 pagesUdl Lesson On Boxplotsapi-399832630No ratings yet
- Action Research Plan ComponentsDocument2 pagesAction Research Plan Componentsstrisko100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Regine MalanaNo ratings yet
- Sweat Shop MathDocument2 pagesSweat Shop Mathapi-272758838No ratings yet
- Hot Hot HotDocument5 pagesHot Hot Hotapi-289190212No ratings yet
- Final Examination Delafuente, JoelDocument5 pagesFinal Examination Delafuente, JoelMa. Jamie Lhen CoralesNo ratings yet
- Otl 579 Project PlanDocument21 pagesOtl 579 Project Planapi-543059557No ratings yet
- Curriculum Chart Table Generative Topic: Using Graphs To Analyze Data Subject: 8th Grade Math Name: MeredithDocument4 pagesCurriculum Chart Table Generative Topic: Using Graphs To Analyze Data Subject: 8th Grade Math Name: MeredithVartyYeremianNo ratings yet
- Amu GuideDocument94 pagesAmu Guideblue_cristal85No ratings yet
- PDF TestDocument1 pagePDF TestjohnNo ratings yet
- FS Deck Mounted Skylight Installation InstructionsDocument8 pagesFS Deck Mounted Skylight Installation InstructionsjohnNo ratings yet
- Hosting Your Own: Parent NightDocument7 pagesHosting Your Own: Parent NightjohnNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Parent Night 1Document47 pages8th Grade Parent Night 1johnNo ratings yet
- CMS 6th Grade Info Night 030917Document20 pagesCMS 6th Grade Info Night 030917johnNo ratings yet
- Science Fair Handbook 2019 High SchoolDocument12 pagesScience Fair Handbook 2019 High SchooljohnNo ratings yet
- Standard 12 - Probability and Statistics: K-12 OverviewDocument34 pagesStandard 12 - Probability and Statistics: K-12 OverviewAnju KamalaNo ratings yet
- Planning A Successful Parent Night: Plan AheadDocument1 pagePlanning A Successful Parent Night: Plan AheadjohnNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Ear Th's Upset Stomach?Document32 pagesEarthquakes and Volcanoes: Ear Th's Upset Stomach?RAJPUT BOYS 7777No ratings yet
- Lynbrook High School 1280 Johnson Avenue San Jose CA 95129 Stober FieldDocument1 pageLynbrook High School 1280 Johnson Avenue San Jose CA 95129 Stober FieldjohnNo ratings yet
- Volcano Experiment ActivityDocument2 pagesVolcano Experiment ActivityjohnNo ratings yet
- Science Fair Handbook 2019 High SchoolDocument12 pagesScience Fair Handbook 2019 High SchooljohnNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Ear Th's Upset Stomach?Document32 pagesEarthquakes and Volcanoes: Ear Th's Upset Stomach?RAJPUT BOYS 7777No ratings yet
- Volcano Experiment ActivityDocument2 pagesVolcano Experiment ActivityjohnNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation JANUARY 2021: February 2, 2021Document44 pagesInvestor Presentation JANUARY 2021: February 2, 2021johnNo ratings yet
- U.S. Department of The Interior U.S. Geological SurveyDocument7 pagesU.S. Department of The Interior U.S. Geological SurveyjohnNo ratings yet
- Stock Market Slides PDFDocument18 pagesStock Market Slides PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- OECD Blockchain PrimerDocument12 pagesOECD Blockchain PrimerThawatrath SiriworapaisanNo ratings yet
- Cupertino High SchoolDocument2 pagesCupertino High SchooljohnNo ratings yet
- WEF Getting Started Cryptocurrency 2021Document23 pagesWEF Getting Started Cryptocurrency 2021Jeff100% (1)
- Hubble Focus GalaxiesDocument45 pagesHubble Focus GalaxiesjohnNo ratings yet
- Waterforlife PDFDocument44 pagesWaterforlife PDFhaseebNo ratings yet
- 001 What Is BlockchainDocument105 pages001 What Is BlockchainjohnNo ratings yet
- Solana WhitepaperDocument32 pagesSolana Whitepapermorten44No ratings yet
- Overview of Business Innovations and Research Opportunities in Blockchain and Introduction To The Special IssueDocument7 pagesOverview of Business Innovations and Research Opportunities in Blockchain and Introduction To The Special IssuejohnNo ratings yet
- MULLIGAN Blockchain Brief OverviewDocument19 pagesMULLIGAN Blockchain Brief OverviewjohnNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology Overview: NISTIR 8202Document68 pagesBlockchain Technology Overview: NISTIR 8202Joel Eljo Enciso SaraviaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology, Bitcoin, and Ethereum: A Brief OverviewDocument8 pagesBlockchain Technology, Bitcoin, and Ethereum: A Brief OverviewjohnNo ratings yet
- HC InfoDocument1 pageHC InfojohnNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management HandoutDocument56 pagesCrisis Management HandoutdraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Chọn đáp án đúng:: Buổi 9: Động từ khuyết thiếu (Modal verb)Document6 pagesExercise 1: Chọn đáp án đúng:: Buổi 9: Động từ khuyết thiếu (Modal verb)Huyền HồNo ratings yet
- Analgesia SystemDocument7 pagesAnalgesia SystemMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- TEFL I Course Prepares Students to Teach EnglishDocument8 pagesTEFL I Course Prepares Students to Teach EnglishErma DomosNo ratings yet
- Bismillah Skripsi Herlina Rozaaaa-1Document57 pagesBismillah Skripsi Herlina Rozaaaa-1Saidi NetNo ratings yet
- 22m Fast Patrol Craft Features & SpecsDocument1 page22m Fast Patrol Craft Features & SpecsNico BossiNo ratings yet
- WordPress Introduction: CMS BasicsDocument21 pagesWordPress Introduction: CMS BasicsNgô Ngọc Hải phươngNo ratings yet
- SRV210 - 250TC Spare PartsDocument2 pagesSRV210 - 250TC Spare PartsEnzo SovittiNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument20 pagesHistoryAlexandru RomînuNo ratings yet
- Quickguide Students For CopyrightsDocument2 pagesQuickguide Students For Copyrightslordvorldomort100% (1)
- MF ISIN CodeDocument49 pagesMF ISIN CodeshriramNo ratings yet
- Texto en inglesDocument5 pagesTexto en inglesJesus Andres Lopez YañezNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is Gloss ?Document14 pages1) What Is Gloss ?AvadhutNo ratings yet
- Williamstown Cannabis Cultivation PlanDocument48 pagesWilliamstown Cannabis Cultivation PlanOltion JaupajNo ratings yet
- OTISLINE QuestionsDocument5 pagesOTISLINE QuestionsArvind Gupta100% (1)
- Staff Nurse HallticketDocument2 pagesStaff Nurse HallticketHiking DiaryNo ratings yet
- F5 GTM Concepts Guide v11Document209 pagesF5 GTM Concepts Guide v11Majnu SmNo ratings yet
- HackSpace - June 2021Document116 pagesHackSpace - June 2021Somnath100% (1)
- Lifeboat Equipment ListDocument1 pageLifeboat Equipment Listjosua albertNo ratings yet
- UFD/MMC/SD Controller Flash Support Limitation and Interconnection NoteDocument5 pagesUFD/MMC/SD Controller Flash Support Limitation and Interconnection Noteمہرؤآنہ آبہرآهہيہمہNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesWater TreatmentSantiago LarrazNo ratings yet
- Desantis, AlanDocument18 pagesDesantis, AlanOreillerNo ratings yet
- A Very Rare Type of NeuralgiaDocument2 pagesA Very Rare Type of NeuralgiarosaNo ratings yet
- MdmedichaoiceDocument324 pagesMdmedichaoicelancastd54No ratings yet
- Inv 069 1701757527Document1 pageInv 069 1701757527neetu9414576916No ratings yet
- Chemists 12-2023Document7 pagesChemists 12-2023PRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- Catanduanes State University: Page 1 of 12Document12 pagesCatanduanes State University: Page 1 of 12Jonah reiNo ratings yet
- Online test series analysis reportDocument17 pagesOnline test series analysis reportchetan kapoorNo ratings yet