Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To OFDM
Uploaded by
Vimal RajOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To OFDM
Uploaded by
Vimal RajCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to OFDM - Orthogonal Frequency
Division Multiplexing
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a digital multi-carrier modulation
scheme that extends the concept of single subcarrier modulation by using multiple subcarriers
within the same single channel. Rather than transmit a high-rate stream of data with a single
subcarrier, OFDM makes use of a large number of closely spaced orthogonal subcarriers that
are transmitted in parallel. Each subcarrier is modulated with a conventional digital
modulation scheme (such as QPSK, 16QAM, etc.) at low symbol rate. However, the
combination of many subcarriers enables data rates similar to conventional single-carrier
modulation schemes within equivalent bandwidths.
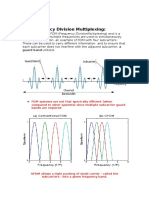
OFDM is based on the well-known technique of Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM). In FDM
different streams of information are mapped onto separate parallel frequency channels. Each
FDM channel is separated from the others by a frequency guard band to reduce interference
between adjacent channels.
The OFDM scheme differs from traditional FDM in the following interrelated ways:
1. Multiple carriers (called subcarriers) carry the information stream,
2. The subcarriers are orthogonal to each other, and
3. A guard interval is added to each symbol to minimize the channel delay spread and
intersymbol interference.
(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) A digital transmission technique
that uses a large number of carriers spaced apart at slightly different
frequencies. First promoted in the early 1990s for wireless LANs, OFDM is
used in many wireless applications including Wi-Fi, WiMAX, LTE, ultra-
wideband (UMB), as well as digital radio and TV broadcasting in Europe and
Japan. OFDM is also used in land-based ADSL Internet service (see DSL).
OFDM Uses Subcarriers
Although frequency division multiplexing (FDM) by itself implies multiple data
streams, OFDM carries only one data stream broken up into multiple signals.
Hundreds of carriers are used; each one a "subcarrier" for a single data
channel.
OFDM subcarriers can be modulated by any method, although QAM and
QPSK are typically used (see QAM and PSK). Coded OFDM (COFDM) adds
forward error correction. See OFDMA, carrier, bandwidth, CCK/OFDM and 8-
VSB.
What is OFDM
1.
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a very popular modulation scheme for wideband
digital communications used in applications such as wireless networking and digital television. It is a
frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) scheme in which a large number of closely-spaced orthogonal
subcarriers are modulated with the transmit data using conventional modulation schemes such as QAM
or PSK. Learn more in: Power Issues and Energy Scavenging in Mobile Wireless Ad-hoc and Sensor
Networks
2.
It is a digital modulation technique in which a single data stream is split into multiple parallel streams and
transmitted over narrow overlapping subcarriers. Learn more in: An Introduction to LiFi and Review of
Prototypes Designed on FPGA and Other Hardware
3.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing is a modulation technique for transmission over a frequency-
selective channel. OFDM divides the channel into multiple orthogonal frequencies, and each frequency
will use a subcarrier where data streams are transmitted. Because the concurrent subcarriers carry
different data streams, OFDM allows high spectral efficiency. Learn more in: Advances of Radio Interface
in WCDMA Systems
4.
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing is a technique that splits a wide frequency band into a number
of narrow frequency bands and inverse multiplexes data across the subchannels. Both 802.11a and the
forthcoming 802.11g standards are based on OFDM. Learn more in: Security and Privacy Approaches for
Wireless Local and Metropolitan Area Networks (LANs & MANs)
5.
A method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. Learn more in: Visible Light
Communication Numerous Applications
6.
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing. Learn more in: Mobile Network Architecture: 3GPP
Generations (UMTS, LTE, and Pre-5G)
7.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM / OFDMA) technology. This is a technique for
transmitting large amounts of digital data over a radio waves. OFDM works by splitting the radio signal
into multiple smaller sub-signals that are then transmitted simultaneously at different frequencies to the
receiver. Learn more in: The Diffusion of WiMax Technology: Hurdles and Opportunities
8.
A method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. Learn more in: Visible Light
Communication Numerous Applications
9.
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing. Learn more in: Mobile Telecom System Architectures—IMS
an Evolution Path Towards IP Convergence
Key features of OFDM
Multiple carriers (called subcarriers) carry the information stream.
The subcarriers are orthogonal to each other.
A guard interval is added to each symbol to minimize the channel delay spread
and intersymbol interference
Existing system:
These techniques are divided into two groups. These are signal scrambling techniques and signal
distortion techniques. The signal scrambling techniques are:
Signal Scrambling Techniques
(i)Block Coding
(ii) Selective Mapping Method(SLM)
(iii) Partial Transmit Sequence(PTS)
Disadvantages:
System suffers from high PAPR and ISI.
ICI occurs due to loss of Orthogonality
Requires time and frequency synchronization to get a low BER
The 5G mobile network promises to be faster and smarter and has lower latency and higher efficiency,
lower bandwidth issues compared to 4G.
You might also like
- An Introduction Tohf Software Defined RadioDocument77 pagesAn Introduction Tohf Software Defined Radiomario61mario100% (1)
- Atmosphere Propagation 234Document4 pagesAtmosphere Propagation 234Edi UnusicNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple AccessDocument10 pagesOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple AccessDarwinNo ratings yet
- Cell Availability TCH Availability CSSR S7Document21 pagesCell Availability TCH Availability CSSR S7RZNo ratings yet
- Channel Multiplexing, Bandwidth, Data Rate and Capacity: Nikola ZlatanovDocument8 pagesChannel Multiplexing, Bandwidth, Data Rate and Capacity: Nikola ZlatanovayadmanNo ratings yet
- Ofdm WorkingDocument16 pagesOfdm WorkingdinuarslanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsDocument36 pagesMultiple Input-Multiple Output Ofdm SystemsLoukya KuttiNo ratings yet
- MPCDocument17 pagesMPCBoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- OFDM Basics TutorialDocument3 pagesOFDM Basics Tutorialhisoni85No ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument48 pagesMultiplexingSamyuktaAdepu100% (1)
- Passive Intermodulation BasicsDocument2 pagesPassive Intermodulation BasicsRobb RobinsonNo ratings yet
- A Novel Implementation of OFDM Using FPGA: M.A. Mohamed, A.S. Samarah, M.I. Fath AllahDocument6 pagesA Novel Implementation of OFDM Using FPGA: M.A. Mohamed, A.S. Samarah, M.I. Fath Allahtsk4b7No ratings yet
- OFDM Basics TutorialDocument215 pagesOFDM Basics Tutorialtanujchawla30No ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS Handover Control Feature Guide - V8 5 - 201312 - 548013Document434 pagesZTE UMTS Handover Control Feature Guide - V8 5 - 201312 - 548013Đỗ Ngọc Tân100% (1)
- A Seminar Report: Department of Electronics & CommunicationsDocument7 pagesA Seminar Report: Department of Electronics & CommunicationsVipul PatelNo ratings yet
- A Review On OFDM: Concept, Scope & Its Applications: Manushree Bhardwaj, Arun Gangwar, Devendra SoniDocument5 pagesA Review On OFDM: Concept, Scope & Its Applications: Manushree Bhardwaj, Arun Gangwar, Devendra SonipankajmudgilNo ratings yet
- 8.assignment 3Document3 pages8.assignment 3HARIPRASATH ECENo ratings yet
- Wireless and CELLULAR COMMUNICATION (18EC81) Module-4Document37 pagesWireless and CELLULAR COMMUNICATION (18EC81) Module-4Vishwanath DesaigoudarNo ratings yet
- WCC Module-4 NotesDocument22 pagesWCC Module-4 NotesUday Kumar DNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 LTE NotesDocument60 pagesMODULE 1 LTE NotesKiran K Dhoni100% (1)
- LTE OFDM TechnologyDocument2 pagesLTE OFDM TechnologyVishwaNo ratings yet
- How, What Is Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) - 123Document7 pagesHow, What Is Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) - 123Quốc Đạt ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Project 121Document4 pagesProject 121Kishan NandakumarNo ratings yet
- Module 1-15ec81Document24 pagesModule 1-15ec81Asha JNo ratings yet
- Multicarrier Modulation With OFDM For 4G Networks: M.Gopu, Dr. Ritesh KhannaDocument4 pagesMulticarrier Modulation With OFDM For 4G Networks: M.Gopu, Dr. Ritesh KhannamalhiavtarsinghNo ratings yet
- OFDM Basics Tutorial: ReferencesDocument7 pagesOFDM Basics Tutorial: ReferencesDarwinNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document26 pagesModule 1Varshini NNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency-Division MultiplexingDocument12 pagesOrthogonal Frequency-Division MultiplexingfiraszekiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of LTE-1Document343 pagesFundamentals of LTE-1Karunadu StatusNo ratings yet
- Module 1 15ec81 WC LteDocument66 pagesModule 1 15ec81 WC LteVeeresh SoraturNo ratings yet
- Discrete Cosinetransform-Ii For Reduction in Peak To Average Power Ratio of Ofdm Signals Through - Law Companding TechniqueDocument14 pagesDiscrete Cosinetransform-Ii For Reduction in Peak To Average Power Ratio of Ofdm Signals Through - Law Companding TechniqueJohn BergNo ratings yet
- Module 4 WCCDocument32 pagesModule 4 WCCKali LinuxNo ratings yet
- Lte Ofdm TechnologyDocument2 pagesLte Ofdm Technologykapil singhNo ratings yet
- Wireless Cellular & LTE 4G Broadband: Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTEDocument22 pagesWireless Cellular & LTE 4G Broadband: Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTENavaneethNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTE: 1.4.1 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)Document39 pages1.4 Key Enabling Technologies and Features of LTE: 1.4.1 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)rohan gowdaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications: Some Recent Developments and Some On-Going ProjectsDocument35 pagesWireless Communications: Some Recent Developments and Some On-Going ProjectsSantosh P LaksmeshwarNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Active Constellation Extension Algorithm For Peak-To-Average Ratio Reduction in OfdmDocument11 pagesAdaptive Active Constellation Extension Algorithm For Peak-To-Average Ratio Reduction in Ofdmsurendiran123No ratings yet
- Module 1-15ec81Document25 pagesModule 1-15ec81PRANEETH DpvNo ratings yet
- Bapatla Women'S Engineering CollegeDocument78 pagesBapatla Women'S Engineering CollegeDavid Solomon Raju YellampalliNo ratings yet
- Outlines: 6.introduction To OFDM CommunicationDocument11 pagesOutlines: 6.introduction To OFDM CommunicationSelam TadeleNo ratings yet
- OFDMADocument7 pagesOFDMAAmgadNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Ofdm and Cdma Technique: Lalit Singh Garia, Amit Shah, Deepesh RawatDocument5 pagesComparative Study of Ofdm and Cdma Technique: Lalit Singh Garia, Amit Shah, Deepesh RawatInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- LTE Radio Interface Overview - ARIMASDocument2 pagesLTE Radio Interface Overview - ARIMASchooty80No ratings yet
- 4G Technology /OFDM:: What Is A Cyclic PrefixDocument8 pages4G Technology /OFDM:: What Is A Cyclic PrefixAzim WarNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (Ofdm) : Jss Academy of Technical EducationDocument16 pagesOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (Ofdm) : Jss Academy of Technical EducationRiya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Wireless GSM DocumDocument9 pagesWireless GSM DocumDaniel BelachewNo ratings yet
- Ofdm Basics For Wirless Communications: AbstractDocument11 pagesOfdm Basics For Wirless Communications: AbstractRaji SharmiNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document12 pagesGroup 2Tolu AyanaNo ratings yet
- Ofdm TutorialDocument4 pagesOfdm TutorialcriharshaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Cellular and LTE 4G BroadbandDocument26 pagesWireless Cellular and LTE 4G BroadbandSona Bhat100% (5)
- LTE OFDM, OFDMA-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesLTE OFDM, OFDMA-WPS OfficeEsam SamNo ratings yet
- LTE Networks Are Based On OFDMADocument8 pagesLTE Networks Are Based On OFDMAVicenteMarioHernándezGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Simulative Analysis of OFDMA System Under Pervasive EnvironmentDocument5 pagesSimulative Analysis of OFDMA System Under Pervasive EnvironmentliiNo ratings yet
- ACN Unit2Document10 pagesACN Unit2Smit prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Wireless NetworksDocument24 pagesUnit Ii Wireless NetworksSuganya CNo ratings yet
- Compare The Performance Analysis For FFT Based Mimo-Ofdm With DWT Based Mimo-OfdmDocument5 pagesCompare The Performance Analysis For FFT Based Mimo-Ofdm With DWT Based Mimo-Ofdmjagadeesh jagadeNo ratings yet
- Ijtra 140812Document3 pagesIjtra 140812Akshay Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Multiple Access TechniquesDocument30 pagesChapter 8 - Multiple Access TechniquesDr. Mudita JunejaNo ratings yet
- BookDocument26 pagesBookநாகராஜ் சுந்தரமகாலிங்கம்No ratings yet
- Information About CDMADocument8 pagesInformation About CDMANishabh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- WC <E 4G - 17EC81 - Module - 1 - Key Enablers For LTE FeatureDocument18 pagesWC <E 4G - 17EC81 - Module - 1 - Key Enablers For LTE FeatureJyothi MelinamaniNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Unit IIDocument28 pagesMobile Computing Unit IIAkash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple AccessDocument4 pagesOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Accessmohas92No ratings yet
- 4G and BeyondDocument32 pages4G and BeyondRico RindraNo ratings yet
- Raana Semicondutors PVT LTD: ARM 7-LPC2148 Development BoardDocument107 pagesRaana Semicondutors PVT LTD: ARM 7-LPC2148 Development BoardVimal RajNo ratings yet
- PTS-PAPR Reduction Technique For 5G Advanced Waveforms Using BFO AlgorithmDocument10 pagesPTS-PAPR Reduction Technique For 5G Advanced Waveforms Using BFO AlgorithmVimal RajNo ratings yet
- Power Measurement With Cadence EDA: Microelectronics Students Group December 31, 2009Document8 pagesPower Measurement With Cadence EDA: Microelectronics Students Group December 31, 2009Vimal RajNo ratings yet
- Starting Cadence and Library ManagementDocument7 pagesStarting Cadence and Library ManagementVimal RajNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing by Ramesh Babu PDFDocument303 pagesDigital Signal Processing by Ramesh Babu PDFVimal RajNo ratings yet
- Application Form: User IdDocument7 pagesApplication Form: User IdVimal RajNo ratings yet
- Anna University: Madras Institute of Technology CampusDocument4 pagesAnna University: Madras Institute of Technology CampusVimal RajNo ratings yet
- Power Efficient Cmos Full Adders With Reduced Transistor Count IJERTV3IS031276Document4 pagesPower Efficient Cmos Full Adders With Reduced Transistor Count IJERTV3IS031276Vimal RajNo ratings yet
- Svcet: 1. Addressing ModesDocument14 pagesSvcet: 1. Addressing ModesVimal Raj100% (1)
- 50992227FMJN - Digital Principles & System Design - Solution ManualDocument31 pages50992227FMJN - Digital Principles & System Design - Solution ManualVimal RajNo ratings yet
- PressedDocument222 pagesPressedVimal RajNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Different Image Segmentation Technique: ISO 9001:2008 CertifiedDocument6 pagesA Study On The Different Image Segmentation Technique: ISO 9001:2008 CertifiedVimal RajNo ratings yet
- Vlsi - Physical DesignDocument27 pagesVlsi - Physical DesignVimal RajNo ratings yet
- 833Document5 pages833Vimal RajNo ratings yet
- Using Signaltap Ii Embedded Logic Analyzers in Sopc Builder SystemsDocument21 pagesUsing Signaltap Ii Embedded Logic Analyzers in Sopc Builder SystemsVimal RajNo ratings yet
- BE MWE MaterialDocument81 pagesBE MWE Materialsravan_4510% (1)
- MADANAPALLE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY andDocument57 pagesMADANAPALLE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY andMylavarapu SriprithamNo ratings yet
- 99812556Document162 pages99812556stanpjames23090% (1)
- Chapter 5Document24 pagesChapter 5pkrsuresh2013No ratings yet
- 13cm PSK Transceiver For 1.2mbit/s Packet Radio Part-L: Tjaz 5,5JDocument30 pages13cm PSK Transceiver For 1.2mbit/s Packet Radio Part-L: Tjaz 5,5JΑΝΔΡΕΑΣ ΤΣΑΓΚΟΣNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Frequency ReuseDocument16 pagesExp 3 Frequency Reuse9185 KrisNo ratings yet
- 1131expt 03 MCC Be A SH21Document7 pages1131expt 03 MCC Be A SH21AlkaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Loop AntennasDocument26 pagesUnit 5 Loop AntennasTanay JoshiNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide For Using The HP 3586Document52 pagesPractical Guide For Using The HP 3586Richard MogfordNo ratings yet
- HAR177335Document4 pagesHAR177335gmahata555No ratings yet
- RV4PX310R-V2 Product SpecificationsDocument4 pagesRV4PX310R-V2 Product SpecificationsJuan carlosNo ratings yet
- Agilent-W1314A Datasheet 3Document16 pagesAgilent-W1314A Datasheet 3abhaykumar80No ratings yet
- CMC Unit-IDocument30 pagesCMC Unit-Iabhi1984_luckyNo ratings yet
- 3351601Document6 pages3351601Jayesh Savaliya0% (1)
- Question Paper Winter 2022Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Winter 2022harshy0816No ratings yet
- WCDMA Call Flow PDFDocument22 pagesWCDMA Call Flow PDFmaheshwankhedeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Spread SpectrumDocument26 pagesUNIT 4 Spread SpectrumSana BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Propagation Models PHDDocument6 pagesPropagation Models PHDHnd FinalNo ratings yet
- Yaesu SWL ModsDocument3 pagesYaesu SWL ModsrojorojilloNo ratings yet
- Report To GMSK Simulation PDFDocument20 pagesReport To GMSK Simulation PDFMoh MohNo ratings yet
- Example Logsrl TP Digital Repeater 20230816 Rev0Document53 pagesExample Logsrl TP Digital Repeater 20230816 Rev0danishmuizzuddin00No ratings yet
- V R Siddhartha Engineering College:: Vijayawada 17EC3701A: Antennas and Wave Propagation Questions Bank UNIT: I & II A.Y 2021-22Document2 pagesV R Siddhartha Engineering College:: Vijayawada 17EC3701A: Antennas and Wave Propagation Questions Bank UNIT: I & II A.Y 2021-22Narasimhareddy MmkNo ratings yet
- Mueller Massucci Antenna and Mobile Network Testing ChallengesDocument52 pagesMueller Massucci Antenna and Mobile Network Testing ChallengesGregory LevantNo ratings yet