Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 17 - Money Growth and Inflation
Uploaded by
Mai TrucOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 17 - Money Growth and Inflation
Uploaded by
Mai TrucCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 17: MONEY GROWTH AND INFLATION
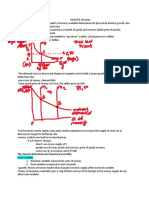
1. In the long run, money supply and money demand are brought into equilibrium by
the overall level of prices.
2. If the price level is above the equilibrium level, people will want to hold more
money than the Fed has created, so the price level must fall to balance supply and
demand.
3. If the price level is below the equilibrium level, people will want to hold less money
than the Fed has created, and the price level must rise to balance supply and
demand.
4. At the equilibrium price level, the quantity of money that people want to hold
exactly balances the quantity of money supplied by the Fed.
5. The supply curve is vertical because the Fed has fixed the quantity of money
available.
6. The demand curve for money is downward sloping, indicating that when the value
of money is low (and the price level is high), people demand a larger quantity of it to
buy goods and services.
7. At the equilibrium, the quantity of money demanded balances the quantity of
money supplied. This equilibrium of money supply and money demand determines
the value of money and the price level.
8. Increase in the money supply
9. Money in liquid form: A liquid asset is a reference to cash on hand or an asset that
can be readily converted to cash
10. Quantity of money demanded:
+ Negatively related to the value of money
+ Positively related to the P, other things equal.
W
11. Real wage= (W: nominal wage= price of labour e.g: $15/h; P: price level= price of
P
goods and services e.g: $5/unit of output)
P ×Y
12. Velocity formula: V = ↔ V × M =P× Y ( p × y=nominal GDP ¿
M
P: price level
Y: real GDP
M: money supply
V: velocity
13. Hyperinflation (siêu lạm phát): happen when inflation exceeding 50% per month
14. Excessive growth in the money supply always cause hyperinflation
15. The inflation tax= revenue the gorvenment raises by creating money
16. Fisher effect: in long run result:
+ Higher inflation rate
+ Higher nominal interest rate
17. Tax distortions:
+ Inflation makes nominal income grow faster than real income
+ Taxes are based on nominal income, and some are not adjusted for inflation.
+ Inflation causes people to pay more taxes even when their real incomes don’t
increase
18. Interest income = deposit x nominal interest rate
You might also like
- Quiz+5 SolutionDocument4 pagesQuiz+5 SolutionM Saqib ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Demand For MoneyDocument13 pagesCh. 4 Demand For Moneycoldpassion100% (1)
- Inflation: Chapter FourDocument17 pagesInflation: Chapter Fourrabia liaqatNo ratings yet
- Econ 161 SQMand PDocument4 pagesEcon 161 SQMand PSZNo ratings yet
- ECON 102 Chapter 17 Short AnswersDocument4 pagesECON 102 Chapter 17 Short AnswersĐưc Thiện ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Money Growth & Inflation (Ch:17 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryDocument18 pagesMoney Growth & Inflation (Ch:17 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryKaziRafiNo ratings yet
- Money and Inflation: Questions For ReviewDocument6 pagesMoney and Inflation: Questions For ReviewErjon SkordhaNo ratings yet
- Money-Growth NotesDocument27 pagesMoney-Growth NotesPrincess CentinalesNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Macroeconomics (Ecn 2215) : Money and Inflation Lecture Notes by Charles M. Banda Notes Extracted From MankiwDocument25 pagesIntermediate Macroeconomics (Ecn 2215) : Money and Inflation Lecture Notes by Charles M. Banda Notes Extracted From MankiwYande ZuluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document7 pagesChapter 25Tasnim SghairNo ratings yet
- Seigniorage:: Interest Rate. If I Denotes The Nominal Interest Rate, R The Real Interest Rate, and P The Rate ofDocument2 pagesSeigniorage:: Interest Rate. If I Denotes The Nominal Interest Rate, R The Real Interest Rate, and P The Rate ofSadi MohaiminulNo ratings yet
- Money, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates (Lecture 7)Document8 pagesMoney, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates (Lecture 7)nihadsamir2002No ratings yet
- Inflation: Its Causes, Effects, and Social Costs: Questions For ReviewDocument5 pagesInflation: Its Causes, Effects, and Social Costs: Questions For ReviewAbdul wahabNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - MONEY AND INFLATION IN THE LONG RUN (What Determines The Long Run Rate of Inflation?) Money and Inflation: What Is Money?Document4 pagesCHAPTER 7 - MONEY AND INFLATION IN THE LONG RUN (What Determines The Long Run Rate of Inflation?) Money and Inflation: What Is Money?Kotryna RudelytėNo ratings yet
- 1CH 22 Demand For MoneybaruDocument37 pages1CH 22 Demand For MoneybaruDika GalihNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document2 pagesChapter 13RomelEsperaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Inflation. Its Causes, Effects, and Social CostsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Inflation. Its Causes, Effects, and Social CostsJoana Marie Calderon0% (1)
- Chapter 17 V1Document14 pagesChapter 17 V1Minhaj TariqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document47 pagesChapter 3vanhuyennguyen2003No ratings yet
- MACRO 5.2 LecDocument5 pagesMACRO 5.2 LecАдамNo ratings yet
- Chap 17: Money Growth and Inflation I. The Classical Theory of Inflation 1. The Level of Prices and The Value of MoneyDocument4 pagesChap 17: Money Growth and Inflation I. The Classical Theory of Inflation 1. The Level of Prices and The Value of MoneyTrần Ngọc Châu GiangNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics CH 7Document32 pagesMacroeconomics CH 7karim kobeissiNo ratings yet
- Quantity Theory of MoneyDocument25 pagesQuantity Theory of MoneyNuurNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Money and InflationDocument5 pagesThe Relationship Between Money and InflationMussa AthanasNo ratings yet
- Money Interest Rates and Exchange RatesDocument44 pagesMoney Interest Rates and Exchange RatesSaim GöküşNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 3Document15 pagesLecture Notes 3Eris HotiNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy: Based On "Macroeconomics" by Dornbusch and Fischer and "Elements of Economics" by TullaoDocument12 pagesMonetary Policy: Based On "Macroeconomics" by Dornbusch and Fischer and "Elements of Economics" by TullaoDiane UyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Final NewDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Final NewRaghu RaamNo ratings yet
- INFLATIONDocument5 pagesINFLATIONPitel O'shoppeNo ratings yet
- Mba 022Document10 pagesMba 022Hezekia KiruiNo ratings yet
- Keynesian Money Demand Theory: Traditional ViewDocument52 pagesKeynesian Money Demand Theory: Traditional ViewALINo ratings yet
- MONEYDocument18 pagesMONEYGodfrey RushabureNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document5 pagesChapter 22Lili MártaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 (Demand For Money)Document71 pagesCh3 (Demand For Money)Rezuanul RafiNo ratings yet
- Money, Interest Rates, and Exchange RatesDocument9 pagesMoney, Interest Rates, and Exchange RatesKhushi RastogiNo ratings yet
- Econ 28Document2 pagesEcon 28Paige BurgosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document5 pagesChapter 21Mohammad SaifullahNo ratings yet
- Quantity Theory of MoneyDocument10 pagesQuantity Theory of Moneyrabia liaqatNo ratings yet
- Quantity Theory of MoneyDocument9 pagesQuantity Theory of Moneyrabia liaqatNo ratings yet
- Money Growth and Inflation: The Classical Theory of InflationDocument5 pagesMoney Growth and Inflation: The Classical Theory of InflationIzzahNo ratings yet
- Unit5 MoneyDocument34 pagesUnit5 Moneytempacc9322No ratings yet
- Lecture 03 Notes - Spring 2009 PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 03 Notes - Spring 2009 PDF6doitNo ratings yet
- 7 M&I Part2 07Document20 pages7 M&I Part2 07aadritadam2004No ratings yet
- Krugman PPT c14 RevDocument44 pagesKrugman PPT c14 RevMahr Saad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Quantity Theory of MoneyDocument12 pagesQuantity Theory of MoneyNuurNo ratings yet
- 2 - Money Demand TheoriesDocument8 pages2 - Money Demand Theoriesmajmmallikarachchi.mallikarachchiNo ratings yet
- Presented by Amir KhanDocument47 pagesPresented by Amir KhanSyed Arham MurtazaNo ratings yet
- ECN 111 Chapter 13 Lecture Notes: 13.1. Money and The Interest RateDocument3 pagesECN 111 Chapter 13 Lecture Notes: 13.1. Money and The Interest RatemustafaNo ratings yet
- Mac 24 - Lec 8Document51 pagesMac 24 - Lec 8Nguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- How Is The General Price Level Determined? Why Does Price Level Change? Classical or Pre-Keynesian Economists Answered AllDocument8 pagesHow Is The General Price Level Determined? Why Does Price Level Change? Classical or Pre-Keynesian Economists Answered AllpriyankabgNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5: Inflation: Its Causes, Effects, and Social CostsDocument19 pagesChapter-5: Inflation: Its Causes, Effects, and Social CostsAfiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 9Th Edition Mankiw Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesMacroeconomics 9Th Edition Mankiw Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjane.hardage449100% (11)
- Macroeconomics 9th Edition Mankiw Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesMacroeconomics 9th Edition Mankiw Solutions Manual 1tinacunninghamadtcegyrxz100% (28)
- Money and InflationDocument9 pagesMoney and InflationAkshat SolankiNo ratings yet
- Sale of Government Bonds CB Sells Bonds To The Public and Gets Cash in Return SucksDocument55 pagesSale of Government Bonds CB Sells Bonds To The Public and Gets Cash in Return SucksDora IskandarNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicsDocument40 pagesFinancial Markets: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicskatecwsNo ratings yet
- Economic Module 18Document3 pagesEconomic Module 18PatrickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Summary - Group 6Document10 pagesChapter 5 Summary - Group 6Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Demand For Money Is The Desired Holding of Financial Assets in The Form of MoneyDocument8 pagesThe Demand For Money Is The Desired Holding of Financial Assets in The Form of MoneyFathima FarnasNo ratings yet