Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment No. 2 MTH 432A: Introduction To Sampling Theory 2021
Uploaded by
Krishna Pratap MallOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment No. 2 MTH 432A: Introduction To Sampling Theory 2021
Uploaded by
Krishna Pratap MallCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment No.
2
MTH 432A: Introduction to Sampling Theory 2021
The following data give the geographical area (in acres) under paddy for 58 villages. Draw a sample
of eight villages using SRSWOR and SRSWR, find an estimate of average area per village under
paddy, an estimate of its variance and its 95% confidence interval. Execute it in R Software.
98, 270, 79, 273, 130, 158, 116, 194, 41, 33, 78, 56, 58, 19, 64, 81, 141, 58, 29, 46, 93, 127,
114, 88, 108, 58, 47, 69, 44, 56, 102, 102, 187, 161, 179, 76, 137, 179, 76, 137, 127, 104, 117,
170, 210, 101, 222, 223, 96, 114, 318, 272, 155, 292, 240, 201, 261, 189
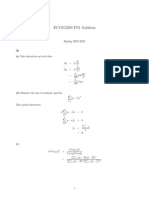
(1) Draw a random sample of size 10 using R statistical software from
(i) Binominal population with parameter 12 and 0.25.
(ii) Poisson distribution with parameter 5.2
(iii) Normal distribution with mean 3.5 and variance 5.75
(iv) bivariate normal population with parameters (15.7, 42. 8, 9.2 2 , 11.7 2 , 0.79)
and compute sample mean and sample variance. Try to observe the difference by drawing
samples several times with the same as well as different populations. Increase the sample size
and observe the differences in the results.
(2) Consider a normal population N (5,2 2 ). Draw 5, 15, 30, 50, 100, 500 and 1000 samples of
size 5 using R Software. Compute E ( y ) , E ( s 2 ) and make density plots for each case. Repeat
the above process for sample sizes 15, 30, 100 and 1000. Present all the results suitably.
Prepare superimposed graphs.
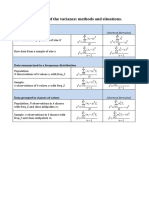
(3) Let ( X i , Yi ) be the values with respect to the two random variables X and Y respectively
n n
N N
associated with the unit label i, i=1,2,…,n. If Xˆ =
n
Xi ,
i =1
Yˆ =
n
Y ,
i =1
i
1 N N 2 ( N − n)
S xy = i
N − 1 i =1
( X − X )(Yi − Y ) under SRSWOR, then Cov ( ˆ
X , Yˆ ) =
Nn
S xy
(4) Consider the setup of SRSWOR with sampling units {U1 , U 2 , U 3}, N=3, n=2 and consider the
estimator
Yˆ * = 1 + 2 if sample space s = {U1 ,U 2 },
Y Y
2 2
Y 2Y
= 1 + 3 if sample space s = {U1 ,U 3},
2 3
Y Y
= 2 + 3 if sample space s = {U 2 , U 3}.
2 3
Show that E (Yˆ * ) = Y and V (Yˆ * ) V (Y ) if Y (3Y − 3Y − Y ) 0
3 2 1 3
(6) Let ( X i , Yi ) be the values with respect to the two random variables X and Y respectively
1 N
associated with the unit label i, i=1,2,...,N . If S xy = ( X i − X N )(Yi − YN ) and
N − 1 i =1
1 n 1 N
1 n
sxy =
n − 1 i =1
( X i − X n )(Yi − Yn ) where X N =
N
X
i =1
i and X n = X i , then prove that
n i =1
under simple random sampling E ( sxy ) = S xy .
You might also like
- Random Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101From EverandRandom Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101No ratings yet
- Class 23Document7 pagesClass 23Smruti RanjanNo ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Sums and Means - Practice Problems: Pierre Brochu Department of Economics University of OttawaDocument6 pagesSums and Means - Practice Problems: Pierre Brochu Department of Economics University of Ottawa42度鱼No ratings yet
- Synthetic Estimators Using AuxiliarDocument14 pagesSynthetic Estimators Using AuxiliarShamsNo ratings yet
- Stat 400, Section 6.1b Point Estimates of Mean and VarianceDocument3 pagesStat 400, Section 6.1b Point Estimates of Mean and VarianceDRizky Aziz SyaifudinNo ratings yet
- Almost Unbiased Exponential Estimator For The Finite Population MeanDocument14 pagesAlmost Unbiased Exponential Estimator For The Finite Population MeanScience DirectNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Least Squares Linear Regression Review: Week 4Document10 pagesOrdinary Least Squares Linear Regression Review: Week 4Lalji ChandraNo ratings yet
- Topic 2a Theory of EstimationDocument12 pagesTopic 2a Theory of EstimationKimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Continuous Time Financial MathematicsDocument55 pagesIntroduction to Continuous Time Financial MathematicsmorganNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Notes Part 1Document23 pagesStatistics and Probability Notes Part 1ISIMBI OrnellaNo ratings yet
- Sample Statistics ExplainedDocument13 pagesSample Statistics Explainedpurbita boseNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis with Dummy VariablesDocument98 pagesRegression Analysis with Dummy Variables邱致翔No ratings yet
- Ratio and Product Methods of Estimation: Y X Y X Y XDocument23 pagesRatio and Product Methods of Estimation: Y X Y X Y XPrateek NaikNo ratings yet
- Variance EstimationDocument2 pagesVariance EstimationMalkin DivyaNo ratings yet
- Correlation AnalysisDocument27 pagesCorrelation AnalysisShuvoNo ratings yet
- ETF2100 intro econometrics review statsDocument7 pagesETF2100 intro econometrics review statsFira SyawaliaNo ratings yet
- Econometrics | Stochastic RegressorsDocument13 pagesEconometrics | Stochastic RegressorsAbdullah KhatibNo ratings yet
- STATS Shortcut FormulaDocument3 pagesSTATS Shortcut Formulajeet sighNo ratings yet
- ST102 Exercise 1 solutions optimizedDocument4 pagesST102 Exercise 1 solutions optimizedJiang HNo ratings yet
- Stimation: StatisticDocument46 pagesStimation: Statisticمحمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- 10-701/15-781 Machine Learning Mid-term Exam SolutionDocument12 pages10-701/15-781 Machine Learning Mid-term Exam SolutionProfessor, CSE Veltech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Tables and formulas for statistical conceptsDocument2 pagesTables and formulas for statistical conceptsAbdulla ShaheedNo ratings yet
- A Family of Median Based Estimators in Simple Random SamplingDocument11 pagesA Family of Median Based Estimators in Simple Random SamplingScience DirectNo ratings yet
- Econometria ResumoDocument19 pagesEconometria ResumorubiportelaNo ratings yet
- Linear Least Square Regression of A LineDocument27 pagesLinear Least Square Regression of A LinenationindiaNo ratings yet
- Stat231 Final Formula SheetDocument15 pagesStat231 Final Formula SheetVazylNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference Key ConceptsDocument38 pagesStatistical Inference Key ConceptsSRIDHAR RAMESHNo ratings yet
- What Is Regression?Document13 pagesWhat Is Regression?Mohammad Omar FaruqNo ratings yet
- ECMT1020 Formulas 2021Document9 pagesECMT1020 Formulas 2021Darius ZhuNo ratings yet
- MAS2020 Chapter 13 Simple Linear RegressionDocument32 pagesMAS2020 Chapter 13 Simple Linear RegressionHien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Empirical Study in Finite Correlation Coefficient in Two Phase EstimationDocument16 pagesEmpirical Study in Finite Correlation Coefficient in Two Phase EstimationScience DirectNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - The Multivariate Normal Distribution and Copulas - 2013 - SimulationDocument13 pagesChapter 6 - The Multivariate Normal Distribution and Copulas - 2013 - Simulation陳裕庭No ratings yet
- 1 Preliminaries: 1.1 MotivationDocument7 pages1 Preliminaries: 1.1 Motivationecd4282003No ratings yet
- dg1 hw4 SolutionsDocument8 pagesdg1 hw4 Solutionschristophercabezas93No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Haroon AfzalNo ratings yet
- Calculating variance and covariance: methods and formulasDocument3 pagesCalculating variance and covariance: methods and formulasGiorgia 1709No ratings yet
- Httpsmoodle - Hku.hkpluginfile - Php4357464mod Resourcecontent1PS120Solution - Pdfforcedownload 1Document9 pagesHttpsmoodle - Hku.hkpluginfile - Php4357464mod Resourcecontent1PS120Solution - Pdfforcedownload 1tszt49dwv4No ratings yet
- Ps 1Document6 pagesPs 1Jesus Enrique Miranda BlancoNo ratings yet
- Econometric Analysis On Efficiency of EstimatorDocument19 pagesEconometric Analysis On Efficiency of EstimatorScience DirectNo ratings yet
- MIT6 436JF08 Rec04Document3 pagesMIT6 436JF08 Rec04jarod_kyleNo ratings yet
- CRCT TD2Document5 pagesCRCT TD2abraham LincolnNo ratings yet
- Gauss-Markov theorem activity explainedDocument2 pagesGauss-Markov theorem activity explainedMarlon Quiñonez BallardoNo ratings yet
- ANOVA Test for Fabric StrengthDocument59 pagesANOVA Test for Fabric StrengthmadhavNo ratings yet
- 4 E GVQZ 7 TGC SW GDW KRR 0 GP HDAB US@F9 Pu:Ho R"ds Gwe N9 IoDocument1 page4 E GVQZ 7 TGC SW GDW KRR 0 GP HDAB US@F9 Pu:Ho R"ds Gwe N9 Ioheaan.lasaiNo ratings yet
- Stat Anal11Document11 pagesStat Anal11Erizelle Anne BrunoNo ratings yet
- Week1 PDFDocument22 pagesWeek1 PDFJohana Coen JanssenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics III(Prob&Stats)_unit 4 5Document122 pagesMathematics III(Prob&Stats)_unit 4 5Neha SultanpurkarNo ratings yet
- Wu6 HVR SxfMVA43CHj UFZf1B 2p # ) Vt1S) ) Bad ) ) VundefinedDocument1 pageWu6 HVR SxfMVA43CHj UFZf1B 2p # ) Vt1S) ) Bad ) ) Vundefinedheaan.lasaiNo ratings yet
- Almost Unbiased Ratio and Product Type Estimator of Finite Population Variance Using The Knowledge of Kurtosis of An Auxiliary Variable in Sample SurveysDocument12 pagesAlmost Unbiased Ratio and Product Type Estimator of Finite Population Variance Using The Knowledge of Kurtosis of An Auxiliary Variable in Sample SurveysScience DirectNo ratings yet
- Practice 2 Spring 2020 BISDocument3 pagesPractice 2 Spring 2020 BISAyoub OumousNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio 1Document1 pageFormula Rio 1Natercia RodriguesNo ratings yet
- FECO Note 2 - Simple Linear RegressionDocument7 pagesFECO Note 2 - Simple Linear RegressionChinh XuanNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Finance: An: David RuppertDocument46 pagesStatistics and Finance: An: David Ruppertmastanoob50% (2)
- STA 303 Lec 1Document5 pagesSTA 303 Lec 1kuriajames147No ratings yet
- Education and Research: UP School of Statistics Student CouncilDocument26 pagesEducation and Research: UP School of Statistics Student CouncilJohn Paul Lagunilla GitoNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Handout Session 2Document18 pagesEconometrics Handout Session 2piergiorgioscaliaNo ratings yet
- Notes For Use in The Statistics ExaminationDocument1 pageNotes For Use in The Statistics ExaminationsilentscreamsofloveNo ratings yet
- Geostatistics in Hydrology Krig PDFDocument25 pagesGeostatistics in Hydrology Krig PDFHamid KorNo ratings yet
- APA Chapter2 T21Document37 pagesAPA Chapter2 T21XxXavillitoxX 5No ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 MTH 432A: Introduction To Sampling Theory 2021Document1 pageAssignment No. 1 MTH 432A: Introduction To Sampling Theory 2021Krishna Pratap MallNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 3 MTH 432A: Introduction To Sampling Theory 2021Document2 pagesAssignment No. 3 MTH 432A: Introduction To Sampling Theory 2021Krishna Pratap MallNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Hons.) Mathematics - IV - None - 2019-2020 - 32351402 Riemann Integration and Series of Functions - Praveen Kumar - PXS - COREDocument2 pagesB.Sc. (Hons.) Mathematics - IV - None - 2019-2020 - 32351402 Riemann Integration and Series of Functions - Praveen Kumar - PXS - COREKrishna Pratap MallNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Hons.) Mathematics - IV - None - 2019-2020 - 32351402 Riemann Integration and Series of Functions - Praveen Kumar - x8 - COREDocument8 pagesB.Sc. (Hons.) Mathematics - IV - None - 2019-2020 - 32351402 Riemann Integration and Series of Functions - Praveen Kumar - x8 - COREKrishna Pratap MallNo ratings yet
- AECC Paper - Parth Singh - 1-1Document7 pagesAECC Paper - Parth Singh - 1-1Krishna Pratap MallNo ratings yet
- Examinations: Subject 106 Actuarial Mathematics 2Document8 pagesExaminations: Subject 106 Actuarial Mathematics 2Vishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Normal Approximation To The Binomial and PoissonDocument11 pagesNormal Approximation To The Binomial and PoissonJoshua BautistaNo ratings yet
- CCMA4001 Quantitative Analysis I v1 PDFDocument3 pagesCCMA4001 Quantitative Analysis I v1 PDFLau Wing ChanNo ratings yet
- ct62010 2013Document165 pagesct62010 2013Amit Poddar100% (2)
- Travel Demand and Traffic ForecastingDocument13 pagesTravel Demand and Traffic ForecastingNandar Wady AungNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Maths S2 - Poisson Distribution Topic QuestionsDocument49 pagesEdexcel Maths S2 - Poisson Distribution Topic QuestionsChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics in Business and Economics 5th Edition Doane Solutions Manual 1Document25 pagesApplied Statistics in Business and Economics 5th Edition Doane Solutions Manual 1michelle100% (35)
- Distribution Tables PDFDocument11 pagesDistribution Tables PDFWamilus Sadri CiagoNo ratings yet
- EPS - Chapter - 4 - Discrete Distributions - JNN - OKDocument56 pagesEPS - Chapter - 4 - Discrete Distributions - JNN - OKKelvin Ken WitsNo ratings yet
- Probability Exam Questions and Solutions for Understanding Basic ConceptsDocument103 pagesProbability Exam Questions and Solutions for Understanding Basic Conceptssound05No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1 - Applied Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet 1 - Applied Stochastic ProcessesSelvanarden KaveriNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International As A Level Mathematics Probability Statistics 2 Practice Book Cambridge International Z LibDocument85 pagesCambridge International As A Level Mathematics Probability Statistics 2 Practice Book Cambridge International Z LibSukanya DattaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Some Special Probability DistributionsDocument17 pagesUnit-2 Some Special Probability DistributionsSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Intensity Based ModelsDocument17 pagesLecture 3 - Intensity Based ModelsPARTHNo ratings yet
- StatSecondAssignment SummaryDocument5 pagesStatSecondAssignment SummaryFriona PoçariNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Elderly Mobility in Hong Kong Implications For Elderly-Friendly TransportDocument11 pagesDeterminants of Elderly Mobility in Hong Kong Implications For Elderly-Friendly TransportShan BasnayakeNo ratings yet
- PL Meyer PDFDocument382 pagesPL Meyer PDFDurga SivakumarNo ratings yet
- SJC F6 2011-12-06 M1 Half Yearly ExaminationDocument10 pagesSJC F6 2011-12-06 M1 Half Yearly ExaminationKelvin CheungNo ratings yet
- Discrete DistributionsDocument106 pagesDiscrete DistributionsAkshay PNo ratings yet
- Ruin Probability in A Threshold Insurance Risk Model: Isaac K. M. Kwan and Hailiang YangDocument9 pagesRuin Probability in A Threshold Insurance Risk Model: Isaac K. M. Kwan and Hailiang YangPetya ValchevaNo ratings yet
- Ams MCQ 17301Document11 pagesAms MCQ 17301Rupali Sardar100% (2)
- MABA5 ProbabilityDocument15 pagesMABA5 ProbabilityHarper DooNo ratings yet
- Haan C T Statistical Methods in Hydrology SolutionDocument24 pagesHaan C T Statistical Methods in Hydrology Solutiongizem duralNo ratings yet
- Ch5 - Questions & AnswersDocument5 pagesCh5 - Questions & Answersmaxentiuss75% (4)
- Iannis Xenakis - Musique StochastiqueDocument14 pagesIannis Xenakis - Musique StochastiquevillaandreNo ratings yet
- Edexcel S2 Cheat SheetDocument12 pagesEdexcel S2 Cheat Sheetsushdhake5009No ratings yet
- Chapter3 220928 093636Document70 pagesChapter3 220928 093636Bá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- Traffic Flow CharacteristicsDocument43 pagesTraffic Flow CharacteristicsjejomarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Discrete Probability Distributions Answer KeyDocument91 pagesChapter 06 Discrete Probability Distributions Answer KeyCOFFEE TOURNo ratings yet
- Asbestos Detection Limit Based On Counts: Standard Practice ForDocument11 pagesAsbestos Detection Limit Based On Counts: Standard Practice Formohammed karasnehNo ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)