Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Early Vedic Age
Uploaded by
Asdf zxcvOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Early Vedic Age
Uploaded by
Asdf zxcvCopyright:
Available Formats
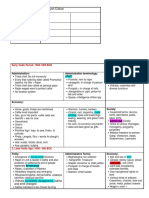
After Harappan age came vedic age
Vedic age is divided into 2.
a) Early vedic age[ 1500BC—1000BC]
b) Later Vedic age[1000—600BC]
Early Vedic age [1500 – 1000BC]
Rigveda [ mandals from 2 to 7 were written during this time
They lived in Saptsindhu area[ present day eastern Afghanistan + Punjab + west UP]
Main crop was barley
Main Gods
[Indra, varun, Agni]
Pushan: The god of jungle paths, herdsmen, and cattle
Soma God
Savitri – > Gayatri Mantra [ in the third mandal of rid veda is for her]
Cow was their main wealth..because they were tribal people with cattle rearing as their main
occupation.
There were no Taxes….However if you wanted, you could give bali [gifts] to the chief
Chief = Leader of clan/tribe
His main job was to protect the cows of the tribe, therefore he was called Gopati [protector of
cows]
Gomat = Richest person = person with most number of cows
Gavisthi = “battle fought for cows”
Gopati’s office was not hereditary and he was selected by the men of the tribe[jana]
Caste system was present, but wasn’t hereditary. You could change your caste by changing
your occupation.
The society was patriarchal in nature, though the women had important positions in the
society since they were educated and had access to the assembly.
Girls were free to choose their life partners. There are no instances of child marriage, sati, or
purdah in the Rig Veda and widow remarriage was allowed.
The ‘battle of ten kings’(dasharajna): between the Sudas [ chief of Bharata tribe] and ten
other tribes like, Puru, Anu, and Druhyu.
Sabha : assembly for elites only
Samiti : assembly for all
In 1000 BC, iron was discovered: it changed everything, Now they could make iron tools for
clearing forests….and marks the beginning of Later vedic age
You might also like
- History Capsule by StudyIQDocument68 pagesHistory Capsule by StudyIQSurajit Das0% (1)
- Ancient IndiaDocument89 pagesAncient IndiaShringar MascarenhasNo ratings yet
- Ancient IndiaDocument22 pagesAncient IndiaAman BansalNo ratings yet
- PDF 20220601 214410 0000Document19 pagesPDF 20220601 214410 0000MufeenNo ratings yet
- Vedic AgeDocument8 pagesVedic AgeRamita Udayashankar100% (2)
- Untouchables: My Family's Triumphant Journey Out of the Caste System in Modern IndiaFrom EverandUntouchables: My Family's Triumphant Journey Out of the Caste System in Modern IndiaRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (28)
- Vedic Age - Early Vedic Period (Aryan Age) - NotesDocument16 pagesVedic Age - Early Vedic Period (Aryan Age) - NotesAquib Irshad100% (1)
- History of India: A brief introduction about Indian History ( all periods)From EverandHistory of India: A brief introduction about Indian History ( all periods)No ratings yet
- Vedic Age NotesDocument11 pagesVedic Age NotesTanya TandonNo ratings yet
- History of Pakistan 18102022 014709pmDocument92 pagesHistory of Pakistan 18102022 014709pmIHDJsjnNo ratings yet
- Carnatic MusicDocument2 pagesCarnatic MusicAsdf zxcvNo ratings yet
- A Life with Wildlife: From Princely India to the PresentFrom EverandA Life with Wildlife: From Princely India to the PresentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The History of Pat I DarsDocument53 pagesThe History of Pat I DarsShilpan PatelNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Ghaziabad Vasundhara: NTSC Ancient India Topic-Early Vedic AgesDocument2 pagesDelhi Public School Ghaziabad Vasundhara: NTSC Ancient India Topic-Early Vedic AgesKanupriya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- 003 Vedic PeriodDocument29 pages003 Vedic Periodt4h56nkq9pNo ratings yet
- Vedic Age (1500-600bc) : Present Name Ancient Name Indus Jhelum Chenab Beas Raavi Sutlej SaraswatiDocument8 pagesVedic Age (1500-600bc) : Present Name Ancient Name Indus Jhelum Chenab Beas Raavi Sutlej SaraswatiDinesh KattaNo ratings yet
- Ancient History of IndiaDocument21 pagesAncient History of IndiaAnu JosephNo ratings yet
- Vedic PeriodDocument25 pagesVedic PeriodSomnath ParbatNo ratings yet
- Vedic PeriodDocument11 pagesVedic PeriodSakshi GourNo ratings yet
- Vedic PeriodDocument16 pagesVedic PeriodSomnath ParbatNo ratings yet
- Aryan Culture 1. Cattle Rearing (Horse) 2. War Chariots: Early Vedic Period: 1500-1000 BCEDocument6 pagesAryan Culture 1. Cattle Rearing (Horse) 2. War Chariots: Early Vedic Period: 1500-1000 BCErahulNo ratings yet
- History Our Past-IDocument15 pagesHistory Our Past-IshashankniecNo ratings yet
- AH Research PaperDocument9 pagesAH Research Paperv sahithiNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 2 CompleteDocument26 pagesNotes Chapter 2 CompleteWamiq TariqNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 GSDocument84 pagesGrade 6 GSNithish BalasubramoniamNo ratings yet
- History Notes: Early and Post Vedic AgeDocument8 pagesHistory Notes: Early and Post Vedic AgeIRAM QayyumNo ratings yet
- SSC History CapsuleDocument39 pagesSSC History Capsulegauravkakkar28100% (1)
- HIS - 2 - Vedic Age, Heterodox Sects, Rise of Empires - 1Document95 pagesHIS - 2 - Vedic Age, Heterodox Sects, Rise of Empires - 1RaashmiNo ratings yet
- History Capsule SSC 2014Document20 pagesHistory Capsule SSC 2014mkiriti0% (1)
- History Capsule DsDocument39 pagesHistory Capsule DsChicko ChioNo ratings yet
- Saidai TNPSC NotesDocument42 pagesSaidai TNPSC Notesshardha100% (3)
- Ancient History Part 2Document14 pagesAncient History Part 2vishalbharati10230No ratings yet
- Ancient India HistoryDocument15 pagesAncient India HistoryAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- History Ch.2 Class 9Document16 pagesHistory Ch.2 Class 9Shivangi SinghNo ratings yet
- History of India: Ancient India Pre-Historic PeriodDocument89 pagesHistory of India: Ancient India Pre-Historic Periods saravanaNo ratings yet
- Erly India The Chalcolithic, Megalithic, Iron AgeDocument9 pagesErly India The Chalcolithic, Megalithic, Iron AgeVinita UgaonkarNo ratings yet
- History: Section - D: General AwarenessDocument24 pagesHistory: Section - D: General AwarenessLeslie MorganNo ratings yet
- Later Vedic CultureDocument4 pagesLater Vedic CultureBhat ShahidNo ratings yet
- Eng 159 Arabian LitDocument6 pagesEng 159 Arabian Litjywhl maeNo ratings yet
- Early Vedic Age: By-Manish ShrivastavaDocument14 pagesEarly Vedic Age: By-Manish ShrivastavaMayank DwivediNo ratings yet
- India PresentsDocument104 pagesIndia PresentsbEbecloeweNo ratings yet
- Vedic Period: The Aryans: by Tarun GoyalDocument28 pagesVedic Period: The Aryans: by Tarun GoyalErVinay ChouhanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Notes Vedic CivilizationDocument3 pagesNCERT Notes Vedic CivilizationAnand Jha100% (1)
- Ch-2 The Vedic PeriodDocument4 pagesCh-2 The Vedic PeriodSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Ancient History NCERT Important TopicsDocument7 pagesAncient History NCERT Important Topicsbikash2601No ratings yet
- Budhism 12thDocument42 pagesBudhism 12thSangeetha PriyaaNo ratings yet
- History of The Vedic PeriodDocument9 pagesHistory of The Vedic PeriodKirti PalNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian History - Vedic Civilization: VedasDocument8 pagesAncient Indian History - Vedic Civilization: Vedasshalini priyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Early Societies in South AsiaDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Early Societies in South Asiaapi-264416360No ratings yet
- Hindu and Tribal Folklore in AssamDocument10 pagesHindu and Tribal Folklore in AssamFlorencia FrutillaNo ratings yet
- History NotesDocument55 pagesHistory NotesAMAN BHARDWAJNo ratings yet
- Ancient India: A Glimpse of Indias' Glorious Ancient PastFrom EverandAncient India: A Glimpse of Indias' Glorious Ancient PastNo ratings yet
- Single Use Plastics: Ban On SupDocument12 pagesSingle Use Plastics: Ban On SupAsdf zxcvNo ratings yet
- Hindustani MusicDocument4 pagesHindustani MusicAsdf zxcv100% (1)
- Science & Technology: Current Affairs-2021Document14 pagesScience & Technology: Current Affairs-2021Asdf zxcvNo ratings yet
- Dhyeya IAS Geography Economic Geography Industrial Regions of The World Class Notes by Sanjeev Sharma Sir PDF in HindiDocument7 pagesDhyeya IAS Geography Economic Geography Industrial Regions of The World Class Notes by Sanjeev Sharma Sir PDF in HindiAsdf zxcvNo ratings yet
- Dhyeya IAS Geography Economic Geography Industrial Regions of The World Class Notes by Sanjeev Sharma Sir PDF in HindiDocument7 pagesDhyeya IAS Geography Economic Geography Industrial Regions of The World Class Notes by Sanjeev Sharma Sir PDF in HindiAsdf zxcvNo ratings yet
- Challenge and Strategy: Rethinking India's Foreign PolicyDocument14 pagesChallenge and Strategy: Rethinking India's Foreign PolicyAsdf zxcvNo ratings yet
- Majid Hussain Chapter 1 Latest EditionDocument29 pagesMajid Hussain Chapter 1 Latest EditionAsdf zxcvNo ratings yet
- Himalayas and Its Strategic Challenges To India: September 2020Document9 pagesHimalayas and Its Strategic Challenges To India: September 2020Asdf zxcvNo ratings yet