Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stereochemistry Assignment #1 2018-2019 ANSWERS
Uploaded by
Zoe NorvilleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stereochemistry Assignment #1 2018-2019 ANSWERS
Uploaded by
Zoe NorvilleCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES - CAVE HILL CAMPUS SEMESTER 1, 2018-2019
CHEM2705 INTERMEDIATE ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Dr. J. BADENOCK
STEREOCHEMISTRY – ASSIGNMENT #1 ANSWERS
SUBMISSION DEADLINE: SEPTEMBER 25, 2018 BY 3:00 PM
TOTAL MARKS = 36 MARKS
1. i. The specific rotation of optically pure sucrose is 66.37° clockwise. What would be the
expected observed rotation for a solution of 1.08 g of sucrose in 100 mL of water
measured in a 400 mm polarimeter tube?
[] = observed
cxl
observed = [] x c x l
= + 66.37 x (1.08/100) x 4 dm
= + 2.87o
[3 marks]
ii. The specific rotation of (S)-glyceraldehyde is -8.7° and (R)-glyceraldehyde has a specific
rotation of +8.7°. What is the optical purity (% ee) and percentage composition of an
enantiomeric mixture of glyceraldehyde with a specific rotation of -7.2°?
% ee = []enantiomeric mixture x 100
[]pure enantiomer
% ee = 7.2 x 100 = 83% excess of the S enantiomer
8.7
Therefore %S enantiomer = 91.5%; %R enantiomer = 8.5%
[4 marks]
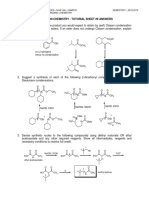
2. Consider compounds I and II below:
2
CHO H CHO
HO H R
H HO OH H 3 OH 1
= = 2
HO H HO H
OHC CH2OH 1 S
CH2OH CH2OH
3
I
2
CHO HO CHO
1 S H HO
HO 3 H HO H H
2 = = OH
HO S H H
1 OHC CH2OH
CH2OH CH2OH
3
II
i. Convert I into a Fischer projection.
ii. Convert II into a Newman projection.
iii. For both compounds, I and II, determine the configuration (R or S) for every chirality
center.
iv. Are I and II the same compound, enantiomers or diastereomers? DIASTEREOMERS.
[9 marks]
UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES - CAVE HILL CAMPUS SEMESTER 1, 2018-2019
CHEM2705 INTERMEDIATE ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Dr. J. BADENOCK
3. Draw Fischer projections for (2S,3R)-2,3-dibromohexane (label it as such) and all its
stereoisomers. Indicate from your structures.:
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
H Br Br H H Br Br H
H Br Br H Br H H Br
CH2CH2CH3 CH2CH2CH3 CH2CH2CH3 CH2CH2CH3
(2S, 3R) (2R, 3S) (2S, 3S) (2R, 3R)
A B C D
i. a threo compound – C OR D
ii. an erythro compound – A OR B
iii. a pair of enantiomers – A+B OR C+D
iv. a pair of diastereomers – A+C OR A+D OR B+C OR B+D
v. a pair of epimers – A+C (C-3) OR A+D (C-2) OR B+C (C-2) OR B+D (C-3)
Remember that only chiral centers should be shown as crosses in the projection.
[10 marks]
4. When III is treated with a strong base, only one elimination product is observed. Yet, when
IV is treated with a strong base, two elimination products are observed.
Explain these observations by drawing each compound in the chair conformation favoured
for elimination and showing the likely mechanism. Be sure to show the product(s) that result
in each case.
T Base
H
=
H H
B B Cl H H
H3C Cl
III
MECHANISM IS E2; ONLY ONE PROTON WITH NECESSARY
ANTI-PERIPLANAR RELATIONSHIP TO Cl LEAVING GROUP
B Base H Base
H
T H3C
Cl H H
B H Cl
IV
MECHANISM IS E2; TWO PROTONS WITH NECESSARY
ANTI-PERIPLANAR RELATIONSHIP TO Cl LEAVING GROUP
[10 marks]
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Carbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #8 2018-2019 AnswersDocument6 pagesCarbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #8 2018-2019 AnswersZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Stereochemistry Assignment #2 2018-2019 ANSWERSDocument3 pagesStereochemistry Assignment #2 2018-2019 ANSWERSZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Carbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #9 2018-2019 AnswersDocument9 pagesCarbonyl Chemistry Tutorial #9 2018-2019 AnswersZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Camp Week 3 Day 1Document12 pagesCamp Week 3 Day 1Zoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Aromatic Chemistry Assignment #3 2018-2019 ANSWERSDocument5 pagesAromatic Chemistry Assignment #3 2018-2019 ANSWERSZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Camp Week 3 Day 2Document13 pagesCamp Week 3 Day 2Zoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Topic: Zoology / Animals Thursday: Session 1: Introduction To Amphibians and Reptiles - 30 MinsDocument14 pagesTopic: Zoology / Animals Thursday: Session 1: Introduction To Amphibians and Reptiles - 30 MinsZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Fun ExperimentsDocument8 pagesFun ExperimentsZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Topic: Zoology / Animals Wednesday: Session 1: Introduction To Fish - 30 MinsDocument15 pagesTopic: Zoology / Animals Wednesday: Session 1: Introduction To Fish - 30 MinsZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Chemistry ExperimentsDocument10 pagesChemistry ExperimentsZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- CXC Chemistry - FundamentalsDocument20 pagesCXC Chemistry - FundamentalsZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Sigmazinc 158Document7 pagesSigmazinc 158JORGEALEXERNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Pharmaceutical Suspensions (The Suspension Theory)Document21 pagesPharmaceutical Suspensions (The Suspension Theory)Nickson DrabeNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Solution Manual For Essentials of General Organic and Biochemistry 3rd Edition Denise GuinnDocument17 pagesSolution Manual For Essentials of General Organic and Biochemistry 3rd Edition Denise GuinnCameronHerreracapt100% (39)
- Tds Imix 83 PolymerDocument2 pagesTds Imix 83 PolymerMukul SareenNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- GMW14872 - Cyclic Corrosion Laboratory TestDocument22 pagesGMW14872 - Cyclic Corrosion Laboratory TestZAPSENo ratings yet
- Jurnal Markus Tanpa NamaDocument8 pagesJurnal Markus Tanpa NamaMarkus Koko Nur BudiantoNo ratings yet
- Šoštarić 2018Document43 pagesŠoštarić 2018imran shaukatNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Iupac Nomenclature Rules 1Document1 pageIupac Nomenclature Rules 1CjES EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Chameleonic TextilesDocument1 pageChameleonic TextilesAhana BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Property and Microstructure Evaluation As A Function of Processing Parameters: Large HY-80 Steel Casting For A US Navy SubmarineDocument13 pagesProperty and Microstructure Evaluation As A Function of Processing Parameters: Large HY-80 Steel Casting For A US Navy SubmarineKay WhiteNo ratings yet
- Water Permeability Tests in A Borehole Using Open Systems (BS EN ISO 22282-2:2012)Document1 pageWater Permeability Tests in A Borehole Using Open Systems (BS EN ISO 22282-2:2012)m.askarNo ratings yet
- Prepared & Presented by Technical Service - PT. HEMPEL IndonesiaDocument32 pagesPrepared & Presented by Technical Service - PT. HEMPEL IndonesiavvpvarunNo ratings yet
- Tabel ASTM 53 PDFDocument32 pagesTabel ASTM 53 PDFsetiawan88% (52)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- ASTM D6209-98 Determination of Gaseous and Particulate Policyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient AirDocument14 pagesASTM D6209-98 Determination of Gaseous and Particulate Policyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient AirFredi Cari CarreraNo ratings yet
- CO2 Handbook IIARDocument190 pagesCO2 Handbook IIAROnofreHalberNo ratings yet
- Bio462 Exp 1Document5 pagesBio462 Exp 12023491958No ratings yet
- AINOMICRODocument13 pagesAINOMICROLast Juan StandingNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Preserving Archaeological Remains in Situ. Proceedings of The 4th International Conference by David GregoryDocument490 pagesPreserving Archaeological Remains in Situ. Proceedings of The 4th International Conference by David GregoryXinyu ZhNo ratings yet
- Chloetroulan - 03.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins - EssentialbiologyDocument7 pagesChloetroulan - 03.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins - EssentialbiologyChloe TroulanNo ratings yet
- Vitamin CDocument6 pagesVitamin CFrancis Adu-marfoNo ratings yet
- A. 2003. Grimsky, G. R. Spectrophotometric Determinaion of Protein ConcentrationDocument9 pagesA. 2003. Grimsky, G. R. Spectrophotometric Determinaion of Protein ConcentrationJorge Luis RomeroNo ratings yet
- Research Article Klebsiella Variicola Strain FH-1: Biodegradation of Atrazine by The NovelDocument13 pagesResearch Article Klebsiella Variicola Strain FH-1: Biodegradation of Atrazine by The NovelA AlagarasiNo ratings yet
- API 5L - 43rd and 44th Ed - Comparison r1Document68 pagesAPI 5L - 43rd and 44th Ed - Comparison r1gopidhan100% (1)
- Hypon at R em Ia: ST Epw Ise Appr Oach T o Diagn Osis: Ser U M Sodiu M 135 M M Ol/ LDocument1 pageHypon at R em Ia: ST Epw Ise Appr Oach T o Diagn Osis: Ser U M Sodiu M 135 M M Ol/ LMaría José GalvisNo ratings yet
- RVP Petroleo Con HTGC y HDADocument7 pagesRVP Petroleo Con HTGC y HDAGustav MolMedNo ratings yet
- Carbon NanomaterialDocument4 pagesCarbon NanomaterialAshish Dev (B21MT009)No ratings yet
- Tuffkote: Epigard Epoxy Finish Epigard HB MioDocument2 pagesTuffkote: Epigard Epoxy Finish Epigard HB MioSHATABDI- DELNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ADIP RefineryDocument2 pagesADIP RefineryVenkatesh Kumar RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Hydroscout Manual E34 Revision 3Document21 pagesHydroscout Manual E34 Revision 3Omar Ernesto EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Practical Techniques Booklet Qm1hekDocument49 pagesPractical Techniques Booklet Qm1hekzena Al-SarawanNo ratings yet