Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study Outline
Case Study Outline
Uploaded by
Medardo BombitaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study Outline
Case Study Outline
Uploaded by
Medardo BombitaCopyright:
Available Formats
CASE STUDY
Suggested Outline in Solving Business Cases
1. Time Context
2. Viewpoint
3. Central Problem
4. Statement of Objectives
a. Must Objectives
b. Want Objectives
5. Areas of Consideration
a. External Environment
i. Threats
ii. Opportunities
b. Internal Environment
i. Strengths
ii. Weakness
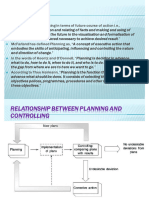
6. Alternative Courses of Action 5.0 Areas of Consideration
7. Final Decision When the student has determined what he considers to be the
8. Detailed Action Plan central problem and has stated his objectives, he must proceed to
organize the facts around the possible causes of the central
Outline Details problem or malady.
1.0 Time Context This requires the separation of the unimportant areas from the
Specify the time context (month and year) if case facts are explicit significant and the irrelevant from the relevant.
about it. The external environment must be assessed for opportunities and
The time context should tell us when the problem was observed threats. Likewise, the internal environment must be looked into for
which required the necessity of an action. strengths and weakness.
A business problem will have different solutions, under different
political and economic environments. 6.0 Alternative Courses of Action
Alternatives are collections of the best ways of meeting the
2.0 Viewpoint individual objectives.
In solving a business problem, the student must specify the In some cases, the alternatives are clear. In others, the student
viewpoint he is taking. must invent alternatives appropriate to the problem at hand.
Given a business problem the President of a company will most And student must not remain content with predetermined
likely have a different approach or solution from those of other alternatives. He must strive for new and better solutions.
company officers, or from those of a consultant. Alternatives must be mutually exclusive. Take each alternative and
It is preferred that the student take the viewpoint of the final measure it individually against each of the must and want
decision maker of the functional area concerned. objectives, separately. Discard an alternative that fails to perform
what a must objective requires.
3.0 Central Problem Alternatives that satisfy all must objectives must be evaluated
A problem is a deviation or an imbalance between what “should further against the want objectives. The advantages and
be” and what “actually is” happening. Thihs imbalance is caused disadvantages or the pros and cons of each alternative must be
by a change of one kind or another. A problem could be answered clearly stated, if this is done well, the choice of the best alternative
by the question, “What is wrong that needs correcting?” would be easier.
A business case may contain a variety of issues or problems from The student must first make a tentative choice of the alternative
the trivial to the significant, from the irrelevant to the relevant. which seems best to him.
The student should focus his attention on the key or central Assess the possible adverse consequences of the alternative
problem which will eventually result in the elimination of other decision.
peripheral problems. Look for promising areas where trouble could occur if the decision
is implemented.
4.0 Statement of Objectives For each prospective serious trouble area, the student should set
Objectives are specifications by which to develop alternative up corresponding preventive and contingency actions.
courses of action. These must be realistic, achievable, and If prospective serious trouble areas could not be prevented, review
whenever possible, quantifiable. other alternatives for final action.
These are statements or functions to be performed or fulfilled b y
the course of action. 7.0 Final Decision
The student must now make a final decision. He must be decisive.
4.1 Must Objectives He must not evade making a final choice of the alternative which
These objectives set the limits that cannot be violated by any seems best to him.
alternative course of action. In action, or a status quo position is no decision.
These objectives are of absolute importance to the success of the
decision and the survival of the organization. 8.0 Detailed Action Plan
These objectives are absolute importance of the success of the Make a detailed action plan to insure the success of the decision.
decision, and the survival of the organization. The actions and strategies to be taken must consider the problems
and objectives stated earlier in the case with the end of view of
4.2 Want Objectives solving the problems. And achieving the objectives.
These objectives do not set absolute limits but express relative The plan of action must show:
desirability. a) The activities
They are of relative importance to the success of the decision but b) Timetables of programs
less than absolute. c) Action officers responsible for implementing the plan
d) The budget
DR. EMERSON G. CABUDOL
egcabudol@ceu.edu.ph
You might also like
- 7 Effective Steps To Solve Case StudyDocument2 pages7 Effective Steps To Solve Case Studyalejandra riveraNo ratings yet
- PROJECT REPORT ON Entrepreneurship in INDIADocument36 pagesPROJECT REPORT ON Entrepreneurship in INDIApchhina77% (30)
- Meat Shop Business Plan FinalDocument21 pagesMeat Shop Business Plan FinalJenirose Racaza75% (4)
- Philippine Christian University: What Is A Case Study?Document2 pagesPhilippine Christian University: What Is A Case Study?KD MVNo ratings yet
- Analyzing A Case StudyDocument3 pagesAnalyzing A Case Studysukumaran321100% (1)
- Case Analysis - PLM FormatDocument3 pagesCase Analysis - PLM FormatCeasar Estrada50% (2)
- 2.revised. RISK MNGT PLAN and Case Analysis TEMPLATE Midterm Final Output 2Document8 pages2.revised. RISK MNGT PLAN and Case Analysis TEMPLATE Midterm Final Output 2Princess SalazarNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Business CasesDocument17 pagesAnalyzing Business CasesYsaiah John GallegoNo ratings yet
- How To Do Case-AnalysisDocument25 pagesHow To Do Case-AnalysisAlexandria De LucaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument11 pagesCase StudyGing Castillano-LumsodNo ratings yet
- ERROL Case Analysis Quick GuideDocument2 pagesERROL Case Analysis Quick GuideDarren Sean NavaNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument5 pagesCasePurushothaman KesavanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledMomon GalaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis in ActionDocument23 pagesStrategic Analysis in ActionFreddierick JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Org&mngt - Week 7-8Document13 pagesQ1 - Org&mngt - Week 7-8Charlene EsparciaNo ratings yet
- BES 8 Module 2 Decision MakingDocument13 pagesBES 8 Module 2 Decision MakingEric John CruzNo ratings yet
- DMN U1 Act2 Decision-Making ProcessDocument11 pagesDMN U1 Act2 Decision-Making Processrecalestructuras7No ratings yet
- MGT523 SPR (A) DL AY21-22 RequirementDocument7 pagesMGT523 SPR (A) DL AY21-22 RequirementAbdullahNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 SWA1 For Google ClassroomDocument10 pagesMODULE 3 SWA1 For Google ClassroomGian ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Case Study Standard Format2Document2 pagesCase Study Standard Format2Arnel PableoNo ratings yet
- 7 Effective Steps To Solve Case StudyDocument2 pages7 Effective Steps To Solve Case StudySachin Kumar SakriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Guidelines in Analyzing Business Case StudyDocument5 pagesLesson 8 Guidelines in Analyzing Business Case StudyMilene BasanalNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument1 pageProblem SolvingTelleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Decision MakingDocument18 pagesLesson 2 Decision MakingjustmecedrickNo ratings yet
- Final Notes GR 12 2024 Creative Thinking and Probelem SolvingDocument12 pagesFinal Notes GR 12 2024 Creative Thinking and Probelem SolvingmasellosbNo ratings yet
- Unit II FMEDocument41 pagesUnit II FME210801059No ratings yet
- Chapter FiveDocument9 pagesChapter FiveAbreham KassaNo ratings yet
- Bpac-101: Perspectives On Public AdministrationDocument15 pagesBpac-101: Perspectives On Public AdministrationDiksha UniyalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2:: Quantitative Decision MakingDocument20 pagesLesson 2:: Quantitative Decision MakingRitzh Aguirre CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management Canadian 8Th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesFundamentals of Management Canadian 8Th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFyvonne.simmons102100% (13)
- Fundamentals of Management Canadian 8th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesFundamentals of Management Canadian 8th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual 1paulwoodpiszdfckxy100% (26)
- Module 2 CMPMDocument10 pagesModule 2 CMPMHerwinn Ruiz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document12 pagesModule 1student07No ratings yet
- Problem Solving Lecture No. 1Document8 pagesProblem Solving Lecture No. 1nychopogiNo ratings yet
- YOUTH International University: Assignment 1: Design and Deliver Training ProgrammeDocument14 pagesYOUTH International University: Assignment 1: Design and Deliver Training ProgrammeZwe Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- Decission Making1Document11 pagesDecission Making1Bassam AlqadasiNo ratings yet
- CH-3 MGT IntDocument6 pagesCH-3 MGT IntwubeNo ratings yet
- Lessons in Problem SolvingDocument17 pagesLessons in Problem SolvingAllan Melvin ComiaNo ratings yet
- Int MGT Ch3 DMDocument5 pagesInt MGT Ch3 DMÆbeni DaniNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Copy 2024 Grade 12 Notes On Creative Thinking - Problem SolvingDocument9 pagesTeacher's Copy 2024 Grade 12 Notes On Creative Thinking - Problem Solvingkitumeleng395No ratings yet
- 7 Effective Steps To Solve Case StudyDocument3 pages7 Effective Steps To Solve Case StudyRajat KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP SUBJECT MODULE 4th WeekDocument7 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIP SUBJECT MODULE 4th WeekJackNo ratings yet
- 4IR 1 Jan Jun2020 Week11Document6 pages4IR 1 Jan Jun2020 Week11BonginkosiNo ratings yet
- STUDENT NOTES mgmt11 - Im07Document8 pagesSTUDENT NOTES mgmt11 - Im07Amir ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Decision Making Meaningand Definition 1. What Is Decision Making?Document2 pagesChapter Two Decision Making Meaningand Definition 1. What Is Decision Making?wubeNo ratings yet
- Optimization ProblemsDocument39 pagesOptimization ProblemsIbrahim El SharNo ratings yet
- QM Week 10 TOOLS FOR IMPROVING QDocument8 pagesQM Week 10 TOOLS FOR IMPROVING QEdrizz RizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Chapter FourDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Management Chapter Fourbiko ademNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DECISION MAKINGDocument9 pagesChapter 2 DECISION MAKINGMark lord bongatNo ratings yet
- The Following Steps May Be Taken To Make Planning EffectiveDocument3 pagesThe Following Steps May Be Taken To Make Planning EffectiveAkhilesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Analysis TemplateDocument4 pagesCase Study Analysis TemplateBlessie Ysavyll SaballeNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To The Module and Creative Decision MakingDocument25 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To The Module and Creative Decision MakingAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document6 pagesCase Study 1Libya ArabNo ratings yet
- Philippine Christian University: Case Study OutlineDocument3 pagesPhilippine Christian University: Case Study OutlineFred Nazareno CerezoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Project Life CycleDocument93 pagesLesson 1 - Project Life CycleHodo AbdilahiNo ratings yet
- MGT Lecture06Document4 pagesMGT Lecture06Sulman HaiderNo ratings yet
- Management Theory Chapter 4Document31 pagesManagement Theory Chapter 4AddiNo ratings yet
- Q1 W7 Mod7 PlanningTechniqueToolsDocument4 pagesQ1 W7 Mod7 PlanningTechniqueToolsCharlene EsparciaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis of Business CasesDocument36 pagesScientific Analysis of Business CasesJeff Lim100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Decision MakingDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Decision MakingEthio P100% (1)
- Bana Midterm ReviewerDocument2 pagesBana Midterm ReviewerNikko RosalesNo ratings yet
- Inf CRM Contact Center Digital ServicesDocument48 pagesInf CRM Contact Center Digital Servicesagung rizqie AdhiNo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationDocument11 pagesAccounting EquationAbhishek BaliarsinghNo ratings yet
- ABC Analysis - The Complete GuideDocument8 pagesABC Analysis - The Complete GuideraheemNo ratings yet
- Organizati On Management: MAS PracticeDocument31 pagesOrganizati On Management: MAS PracticeChristian AribasNo ratings yet
- Positioning A Long Island BankDocument8 pagesPositioning A Long Island BankChirag MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Chandan Itr 2form Downloaded 20-21Document33 pagesChandan Itr 2form Downloaded 20-21Ameet ChandanNo ratings yet
- Form 2A Lakatan ConsolidatedDocument17 pagesForm 2A Lakatan ConsolidatedDerwin DomiderNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesHomework 1 Solutionjingshu zhang100% (1)
- EPGP IIMK CSR Aaerospace IndustryDocument27 pagesEPGP IIMK CSR Aaerospace IndustryBarathy ArvindNo ratings yet
- Safe Express RELATIONSHIP FORMDocument3 pagesSafe Express RELATIONSHIP FORMfru basumataryNo ratings yet
- Marketing 04Document24 pagesMarketing 04Hammad NaqviNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Trends During COVID-19 Pandemic: ArticleDocument5 pagesE-Commerce Trends During COVID-19 Pandemic: Articleluciano gomesNo ratings yet
- Report On Entry Strategy in The Packaged Food Industry (FMCG) in Bangladesh "Chocolate Heaven" Prepared ForDocument18 pagesReport On Entry Strategy in The Packaged Food Industry (FMCG) in Bangladesh "Chocolate Heaven" Prepared ForAvi Deb NathNo ratings yet
- Perry Belcher-AI Summit SalesletterDocument27 pagesPerry Belcher-AI Summit SalesletterAdrian Iacob100% (1)
- Occupational Health and Safety PolicyDocument2 pagesOccupational Health and Safety PolicyAshish Kothwal0% (1)
- Are Cloud (Virtual) Kitchens Profitable - Aadil Kazmi - MediumDocument9 pagesAre Cloud (Virtual) Kitchens Profitable - Aadil Kazmi - Mediumfatank0450% (2)
- Entrepreneurship Skills Assignment 1Document10 pagesEntrepreneurship Skills Assignment 1fabiolabeukesNo ratings yet
- PP Lec 2 Prod Plann & ControlDocument8 pagesPP Lec 2 Prod Plann & ControlHitesh BalwaniNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods: Project (Part 1)Document1 pageBusiness Research Methods: Project (Part 1)ssagr123No ratings yet
- Sonalika TractorsCompany ProfileDocument3 pagesSonalika TractorsCompany ProfileRahul SoroutNo ratings yet
- Startup Pitch Deck - EQUASDocument19 pagesStartup Pitch Deck - EQUASAlexey MorovNo ratings yet
- New Earth Mining: Ashutosh DashDocument16 pagesNew Earth Mining: Ashutosh DashSaurabh ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Consulting FrameworksDocument10 pagesConsulting Frameworkskhushi bansalNo ratings yet
- Organization Chart: © 2014 Holcim LTDDocument1 pageOrganization Chart: © 2014 Holcim LTDSoumik BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- HB1465Document6 pagesHB1465Madison HardcastleNo ratings yet
- Colorado VC Attendee ListDocument18 pagesColorado VC Attendee ListMozammil Rana100% (1)
- Hutchison Ports Brochure en September 2023 1Document7 pagesHutchison Ports Brochure en September 2023 1sawmyo2007No ratings yet
- Operations Management: William J. StevensonDocument30 pagesOperations Management: William J. StevensonTarkeshwar ThakurNo ratings yet