Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Finance Assignment
Uploaded by
Pangambam Joshidas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views5 pagesA financial manager is responsible for monitoring the financial
health of an organization using financial reports. When things are going well,
they direct investment activities and develop plans that can help maintain and
improve the financial status of the company. When things are going badly, they
develop strategies to improve the company's finances not just in the short term
but in the long run as well. They often use their knowledge of a company's
finances to help advise executives on
Original Title
introduction to finance assignment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA financial manager is responsible for monitoring the financial
health of an organization using financial reports. When things are going well,
they direct investment activities and develop plans that can help maintain and
improve the financial status of the company. When things are going badly, they
develop strategies to improve the company's finances not just in the short term
but in the long run as well. They often use their knowledge of a company's
finances to help advise executives on
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views5 pagesIntroduction To Finance Assignment
Uploaded by
Pangambam JoshidasA financial manager is responsible for monitoring the financial
health of an organization using financial reports. When things are going well,
they direct investment activities and develop plans that can help maintain and
improve the financial status of the company. When things are going badly, they
develop strategies to improve the company's finances not just in the short term
but in the long run as well. They often use their knowledge of a company's
finances to help advise executives on
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Name – Pangambam Joshidas Singh
Section – C1902 Roll no – A19
Reg no – 11908073 Course code – CIV-225
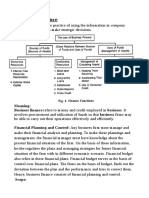
Q1 What a financial manager will do in order to maximize wealth
as well as profit to the organization?
Answer - A financial manager is responsible for monitoring the financial
health of an organization using financial reports. When things are going well,
they direct investment activities and develop plans that can help maintain and
improve the financial status of the company. When things are going badly, they
develop strategies to improve the company's finances not just in the short term
but in the long run as well. They often use their knowledge of a company's
finances to help advise executives on business decisions.
Wealth maximization is also called as value maximization or net present worth
maximization. This objective of Financial Management is universally
acceptable in all forms of business concern. It’s one of the modern approaches
that involve the latest innovations and improvement in the fields of business
operations. The term wealth means shareholders’ wealth, or the wealth of the
persons involved the business concern.
Capital investment decisions of a firm have a direct relation with wealth
maximization. All capital investment projects with an internal rate of return
(IRR) greater than cost of capital or having positive NPV or creates value for
the firm. These projects earn more than the ‘required rate of return’ of the firm.
In other words, these projects maximize the wealth of the shareholders because
they are earning more than what they can earn by investing themselves.
By analysing the projects with the methods of capital budgeting, we come to
know whether wealth will or won’t be created in a particular project. But what
is the real source of wealth creation? What is that characteristic of the project
which becomes the root cause of value creation?
The main aim of any form of business is to earn a profit. All the business entity
operates to earn the maximum amount of return in terms of profits. Profit
earning capacity is a measuring technique to evaluate the efficiency of the
concerned business. Profit Maximization is the traditional and narrow approach
that aims to maximize the profit for an organization.
Profit maximization is the traditional approach and the primary objective of
financial management. It implies that every decision relating to business is
evaluated in the light of profits. All the decisions with respect to new projects,
acquisition of assets, raising capital etc are studied for their impact on profits
and profitability. If the result of a decision is perceived to have a positive effect
on the profits, the decision is taken further for implementation.
Profit maximization ruled the traditional business mindset which has gone
through drastic changes. In the modern approach of business and financial
management, much higher importance is assigned to wealth maximization in
comparison of Profit Maximization vs. Wealth Maximization. The losing
importance of profit maximization is not baseless, and it is not only because it
ignores certain important areas such as risk, quality, and the time value of
money but also because of the superiority of wealth maximization as an
objective of the business or financial management.
Q2 How finance is interlinked with accounts. What will be the
effect if one fails?
Answer - Finance and Accounting are two separate disciples that often are
lumped together (as we obviously have done). At a high level, Finance is the
science of planning the distribution of a business assets. Accounting is the art
of the recording and reporting financial transactions. People tend to group
Finance and Accounting because both functions deal with the administration of
a business assets
Those who work in the financial department of a business are concerned
with planning the distribution of the business’ assets. This includes the
coordination of capital investments and debt backed investments for the purpose
of improving the value of the business. Those in Finance also plan the exit
strategy for the investors of the business, which is the way in which those that
invest in the business receive their financial reward. The financial goals and
objectives of the business are designed by the business’ Chief Financial Officer,
who is supported by people focused on Financial Analysis, Financial
Management, Budgeting, Purchasing, and Accounting.
Those who work in the accounting function of a business are concerned with
tracking and reporting the financial transactions of a business. Those in the
Accounting field are responsible for managing the general ledger, cash flow
management, collections, recognizing revenue, analysing profitability, reporting
earnings, managing debt, and of course paying taxes.
Accountant’s research and report the financial transactions and health of the
business using a standard set of rules and principles. Jobs in the Accounting
function include Financial Reporting Accountants, Auditors, Bookkeepers,
Accounts Receivable Clerks, Accounts Payable Clerks, Controllers, Treasurers,
and Tax Accountants. Typically, the entire accounting organization will report
into the Chief Financial Officer. Broadly speaking, Finance revolves around
planning future financial transactions while Accounting revolves around
reporting past financial transactions. While these are two separate functions that
require different skill sets, they do both revolve around the management of
assets; therefore, they are grouped together more often than not.
The sum of the last period’s closing cash balance plus this periods cash from
operations, investing, and financing is the closing cash balance on the balance
sheet. Financing activities mostly affect the balance sheet and cash from
finalizing, except for interest, which is shown on the income statement
Q3 Write a note on regulatory framework. What will
happen if we do not have these frameworks?
Answer - It refers to the control of commercial activities through system of
rules and norm. Direct involvement of government is not necessary. The
financial system in India is regulated by independent regulators in the field of
banking, insurance, capital market, commodities market, and pension funds.
However, Government of India plays a significant role in controlling the
financial system in India and influences the roles of such regulators at least to
some extent.
The following are five major financial regulatory bodies in India: - (We have
given links for these bodies. For more details about these you can click and visit
such websites)
(A) Statutory Bodies via parliamentary enactments:
1. Reserve Bank of India: Reserve Bank of India is the apex monetary
Institution of India. It is also called as the central bank of the country. The
Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935, in accordance with the
provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The Central Office of the
Reserve Bank was initially established in Calcutta but was permanently moved
to Mumbai in 1937. The Central Office is where the Governor sits and where
policies are formulated. Though originally privately owned, since
nationalization in 1949, the Reserve Bank is fully owned by the Government of
India.
It acts as the apex monetary authority of the country. The Central Office is
where the Governor sits and is where policies are formulated. Though originally
privately owned, since nationalization in 1949, the Reserve Bank is fully owned
by the Government of India.
The preamble of the reserve bank of India is as follows:
"...to regulate the issue of Bank Notes and keeping of reserves with a view to
securing monetary stability in India and generally to operate the currency and
credit system of the country to its advantage."
2. Securities and Exchange Board of India: SEBI Act, 1992: Securities and
Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was first established in the year 1988 as a non-
statutory body for regulating the securities market. It became an autonomous
body in 1992 and more powers were given through an ordinance. Since then, it
regulates the market through its independent powers.
3. The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority: The Insurance
Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) is a national agency of the
Government of India and is based in Hyderabad (Andhra Pradesh). It was
formed by an Act of Indian Parliament known as IRDA Act 1999, which was
amended in 2002 to incorporate some emerging requirements. Mission of IRDA
as stated in the act is "to protect the interests of the policyholders, to regulate,
promote and ensure orderly growth of the insurance industry and for matters
connected therewith or incidental thereto."
(B) Part of the Ministries of the Government of India:
4. Forward Markets Commission (FMC): Forward Markets Commission
(FMC) headquartered at Mumbai, is a regulatory authority which is overseen by
the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, Govt. of India.
It is a statutory body set up in 1953 under the Forward Contracts (Regulation)
Act, 1952 This Commission allows commodity trading in 22 exchanges in
India, out of which three are national level.
5. PERDA under the Finance Ministry: Pension Fund Regulatory and
Development Authority: PFRDA was established by Government of India on 23
August 2003. The Government has, through an executive order dated 10
October 2003, mandated PFRDA to act as a regulator for the pension sector.
The mandate of PFRDA is development and regulation of pension sector in
India.
You might also like
- AGL GasDocument3 pagesAGL Gasvu ducNo ratings yet
- Nature & Scope of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesNature & Scope of Financial ManagementGaganNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument18 pagesFinancial ManagementJohnykutty JosephNo ratings yet
- CB Insights Fintech Trends 2018Document118 pagesCB Insights Fintech Trends 2018DIana100% (1)
- Unit 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementPRIYA KUMARINo ratings yet
- SHS GenMath Q4 W3 4 PDFDocument22 pagesSHS GenMath Q4 W3 4 PDFJhie GacotNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finance and AccountingDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Finance and AccountingDr.Ashok Kumar PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Financial Management AssignmentDocument12 pagesFinancial Management AssignmentSoumya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Debt management ratios analysisDocument4 pagesDebt management ratios analysisJohn MuemaNo ratings yet
- Goals of Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesGoals of Financial ManagementAndrea Fernandes100% (9)
- Role of Finance ManagerDocument4 pagesRole of Finance ManagerphobosanddaimosNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ABM StrandDocument107 pagesBusiness Finance ABM StrandMiss Anonymous23No ratings yet
- Role of A Financial ManagerDocument13 pagesRole of A Financial ManagerpratibhaNo ratings yet
- 1) Explain The Objectives of Financial Management, Interphase Between Finance and Other FunctionsDocument6 pages1) Explain The Objectives of Financial Management, Interphase Between Finance and Other FunctionsGovendhan PNo ratings yet
- Importance of Financial Management ObjectivesDocument5 pagesImportance of Financial Management ObjectivesJohn Edward PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Fin ManDocument8 pagesFin ManCleoDolinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Financial ManagementPratham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management (TARUN PANT)Document13 pagesFinancial Management (TARUN PANT)Tarun PantNo ratings yet
- What Is The Purpose of Financial Management? Describe The Kinds of Activities That Financial Management Deals WithDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of Financial Management? Describe The Kinds of Activities That Financial Management Deals WithMary Joy BeltranNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Financial Statement AnalysisDocument83 pagesIntroduction to Financial Statement AnalysisNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction - Chapter 2 Industrial ProfileDocument74 pagesChapter 1 Introduction - Chapter 2 Industrial Profilebalki123No ratings yet
- Introduction to Financial Management ChapterDocument13 pagesIntroduction to Financial Management Chapterriajul islam jamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Group5Document8 pagesChapter1 Group5Shane Daphnie SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Topic 8Document26 pagesTopic 8Christine SantosNo ratings yet
- Importance of Finance:-: Chapter - 1Document102 pagesImportance of Finance:-: Chapter - 1VidyaNo ratings yet
- "Working Capital and Funds Efficiency": BBM" by Chandan. T.LDocument36 pages"Working Capital and Funds Efficiency": BBM" by Chandan. T.LmechanicalmadhuNo ratings yet
- 2017 Questions and Answers Module 1Document12 pages2017 Questions and Answers Module 1Pushpendra Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers For Essay QuestionsDocument12 pagesQuestions and Answers For Essay QuestionsPushpendra Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management in HBLDocument72 pagesInventory Management in HBLNareshkumar KoppalaNo ratings yet
- Financial ObjectivesDocument11 pagesFinancial ObjectivesLinda ZyongweNo ratings yet
- Financial Manager's Role in OrganizationsDocument10 pagesFinancial Manager's Role in OrganizationsZeleine Raine Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Explain The Objectives of Financial Management, Interphase Between Finance and Other FunctionsDocument12 pagesExplain The Objectives of Financial Management, Interphase Between Finance and Other FunctionsgangadharNo ratings yet
- Objectives and Scope of Financial ManagementDocument7 pagesObjectives and Scope of Financial ManagementMudassar KhalidNo ratings yet
- Assignment FinanceDocument6 pagesAssignment FinancejomarvaldezconabacaniNo ratings yet
- BSIS 2 Financial Management Week 3 4Document8 pagesBSIS 2 Financial Management Week 3 4Ace San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-26 at 7.44.54 PMDocument79 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-26 at 7.44.54 PMrishivardhan050No ratings yet
- Finance Viva Final SemesterDocument3 pagesFinance Viva Final SemesterSharfuddin ZishanNo ratings yet
- Functions of Finance Manager & How They Have Changed in Recent YearsDocument68 pagesFunctions of Finance Manager & How They Have Changed in Recent YearsSuzette NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of Kerala Gramin Bank Special Reference To Southern AreaDocument81 pagesFinancial Performance of Kerala Gramin Bank Special Reference To Southern AreaPriyanka Ramath100% (1)
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1Erika PiapiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 FM NotesDocument18 pagesModule 1 FM NotesDachu DarshanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance NotesDocument6 pagesBusiness Finance NotesAbdul Rauf RajperNo ratings yet
- Business Finance - Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument23 pagesBusiness Finance - Introduction To Financial ManagementAranda, Irian D.No ratings yet
- FM 1Document7 pagesFM 1Rohini rs nairNo ratings yet
- FM. Final ReportDocument37 pagesFM. Final ReportMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- CF Assignment 2Document7 pagesCF Assignment 2jannatNo ratings yet
- NOTES Abm11Document3 pagesNOTES Abm11Ina Vei AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Definition of Finance Goals of The Financial ManagerDocument14 pagesLesson 1 Definition of Finance Goals of The Financial ManagerJames Deo CruzNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document3 pagesDocument 3Mariwin MacandiliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Financial ManagementPasa YanNo ratings yet
- Mba Ii Sem Finacial ManagementDocument11 pagesMba Ii Sem Finacial ManagementningegowdaNo ratings yet
- Finance FunctionDocument25 pagesFinance FunctionKane0% (1)
- Financial Management CIA!Document10 pagesFinancial Management CIA!TEJASWI K NNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Business Finance ConceptsDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Business Finance Conceptsprasadnaidu00No ratings yet
- Q. Introduction, Meaning and Definition of Financial Management?Document8 pagesQ. Introduction, Meaning and Definition of Financial Management?Rizwana BegumNo ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument22 pagesCorporate Financeramakrishnan prNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document6 pagesLesson 1Chelsea Joy AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Overview and Key ConceptsDocument13 pagesFinancial Management Overview and Key ConceptssoleilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finance - Week 1Document20 pagesIntroduction To Finance - Week 1Jason DurdenNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To AccountingDocument3 pages1.introduction To AccountingAsm RayhanNo ratings yet
- Christine Joy M. Digno - BSA3 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesChristine Joy M. Digno - BSA3 Review QuestionsChristine DignoNo ratings yet
- The Elements Directly Related To The Measurement of Financial Position AreDocument8 pagesThe Elements Directly Related To The Measurement of Financial Position AreKim Patrice NavarraNo ratings yet
- Approved Guidelines On Operations of Electronic Payment Channels in NigeriaDocument48 pagesApproved Guidelines On Operations of Electronic Payment Channels in NigeriaBrute1989No ratings yet
- Kisan Credit Card Explained in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesKisan Credit Card Explained in 40 CharactersAshok RathodNo ratings yet
- List of Services Provided by IciciDocument3 pagesList of Services Provided by IciciNathan100% (1)
- Icpu Registration FormDocument1 pageIcpu Registration FormGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- TF 00000055Document3 pagesTF 00000055YustofiNo ratings yet
- Online Savings Account Statement: Goldman Sachs Bank USA PO Box 1978 Cranberry TWP., PA 16066Document5 pagesOnline Savings Account Statement: Goldman Sachs Bank USA PO Box 1978 Cranberry TWP., PA 16066Rapid FinanceNo ratings yet
- Ass Aud1Document4 pagesAss Aud1Taehyungiiee KimNo ratings yet
- NMC Self Declaration FormDocument12 pagesNMC Self Declaration Formजेनिश न्यौपानेNo ratings yet
- Statement of AccountDocument9 pagesStatement of AccountNeena kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Syndicated LoansDocument13 pagesLecture 4 - Syndicated LoansEmmanuel MwapeNo ratings yet
- Print Payment AdviceDocument13 pagesPrint Payment AdviceK Hyder Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Coinfloor Account Review FormDocument2 pagesCoinfloor Account Review FormAnonymous pUJV4kZNo ratings yet
- GIPS Compliance QuestionsDocument5 pagesGIPS Compliance QuestionsBảo TrâmNo ratings yet
- A Study On Project Report On Commercial BankDocument8 pagesA Study On Project Report On Commercial BankGAME SPOT TAMIZHANNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisDocument2 pagesFinancial Statements and Ratio AnalysisRyan MiguelNo ratings yet
- IMNU HimasnhuPatel Anand Rathi Internship ReportDocument57 pagesIMNU HimasnhuPatel Anand Rathi Internship ReportHimanshu Patel33% (3)
- Procedure of Account OpeningDocument11 pagesProcedure of Account OpeningSky WalkerNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AccountancyDocument28 pagesFundamentals of AccountancyCharity AmboyNo ratings yet
- Credit EDA Assignment PDFDocument40 pagesCredit EDA Assignment PDFAlisha AnandNo ratings yet
- PlumHQ Aims To Solve India's Missing Middle Puzzle in Digital InsuranceDocument9 pagesPlumHQ Aims To Solve India's Missing Middle Puzzle in Digital InsuranceShatir LaundaNo ratings yet
- B3MIN1009 Alternative Investments Overview of Sessions 2023-2024 FinalDocument7 pagesB3MIN1009 Alternative Investments Overview of Sessions 2023-2024 Finallilpumpdidnothingwrong dNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 ReviewerDocument33 pagesWEEK 1 ReviewerFebemay LindaNo ratings yet
- Easa Part 66 Exam Application FormDocument3 pagesEasa Part 66 Exam Application FormAzfar Omar50% (2)
- FinTech Certificate Course at Shaheed Sukhdev CollegeDocument6 pagesFinTech Certificate Course at Shaheed Sukhdev CollegeVanyaa Kansal100% (1)
- Ap 9201-2 SheDocument5 pagesAp 9201-2 SheShefannie PaynanteNo ratings yet