Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Building Information Modelling (Bim) Implementation 05
Uploaded by
Doi NaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Building Information Modelling (Bim) Implementation 05
Uploaded by
Doi NaCopyright:
Available Formats
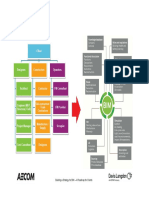
Figure 8: Shows the coded communication between the procurement manager, sub-contractor and the site
manager for the procurement and installation of the window frames
Through the action research stages, learning was increased tremendously and better shared understanding about
BIM was established. After witnessing the benefits through the piloting activities, forward lean thinking led to
how further efficiencies could be gained, which had particular focus on people factor of BIM implementation
while considering the technology and process factors. Therefore, in order to increase staff skills, training
programmes were undertaken in parallel with the piloting projects, which include i) training inside and outside
the organization for JMA and its stakeholders, ii) informing the users about the improvements and changes in a
timely manner via presentations, demonstrations and exhibitions. Overall, four areas of training were organised
and conducted. These are: 1) Basic Operation Skills, 2) JMA modelling standards, 3) JMA methodology of
model construction, 4) How to work with external parties. However, in all cases there was an effort to relate the
learning, back to the specific type of projects undertaken at JMA
4.4. Evaluation Stage: Project Review and Key Findings
It became obvious that BIM can open the door to many possibilities. For example, working with 3D models
facilitates the generation of 3D visuals, 3D printing and linking with virtual environments. Part of improving the
companywide capabilities is maintaining the BIM dialogue. Hence, BIM knowledge and best practice is
disseminated around the practice. Currently the BIM enabled process and procedures were documented as a
guide for the JMA staff on how best to use the BIM authoring tool, BIM object library addressing building types
and components and the knowledge database.
ITcon Vol. 17 (2012), Arayici, pg. 88
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- BICP Global BIM StudyDocument1 pageBICP Global BIM StudyDoi NaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Building A Strategy For BimDocument1 pageBuilding A Strategy For BimDoi NaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Europe: Table 1 - Rapidly Evolving National Digital ProgrammesDocument1 pageEurope: Table 1 - Rapidly Evolving National Digital ProgrammesDoi NaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- BSI - PAS - 1192 - 2 - 2013 Paj 32Document1 pageBSI - PAS - 1192 - 2 - 2013 Paj 32Doi NaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Building Information Modelling (Bim) Implementation 01Document1 pageBuilding Information Modelling (Bim) Implementation 01Doi NaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Building Information Modelling (Bim) Implementation 02Document1 pageBuilding Information Modelling (Bim) Implementation 02Doi NaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Educational Simulation in Construction Project Financial Risks ManagementDocument14 pagesEducational Simulation in Construction Project Financial Risks ManagementDoi NaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Sport NEW: Scriitorul Richard Bach Cartea Pescarusul Jonatan LivingstonDocument6 pagesSport NEW: Scriitorul Richard Bach Cartea Pescarusul Jonatan LivingstonDoi NaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)