Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4
Uploaded by
Chesca Alon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageprobability information
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentprobability information
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 page4
Uploaded by
Chesca Alonprobability information
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Module: Discrete Probability Distribution
Probability Distribution
A probability distribution is a function or rule that
assigns the value of a random variable to the
probability associated with these values. The
probability that the random variable X will equal x
as P(X=x) or simply P(x), where the uppercase
letter denoted by X represents the name of the
random variable. The lowercase counterpart
represents the value of the random variable.
Methods of Presenting Probability Distribution
Example 1. Consider the random experiment of
tossing 2 coins. Let X be the number of heads, then
construct the probability distribution of X using
tabular, graphical and formula form.
Solution:
There will be 4 possible outcomes in the sample
space since coin 1 can fall 2 ways and coin 2 can
also fall in 2 ways. Thus, 2(2) = 4
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of The Estimate 1 2Document5 pagesModel R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of The Estimate 1 2Chesca Alon100% (1)
- 2Document3 pages2Chesca AlonNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3Chesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Plyometric Pre-Test: Flexibility, Strength, Agility, Power and SpeedDocument15 pagesPlyometric Pre-Test: Flexibility, Strength, Agility, Power and SpeedChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Introduction To Cost Terms and ConceptsDocument52 pagesModule 2 Introduction To Cost Terms and ConceptsChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Computing Continuous Probabilities With ExcelDocument1 pageComputing Continuous Probabilities With ExcelChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Role of Probability Concepts in Business Decision-MakingDocument1 pageRole of Probability Concepts in Business Decision-MakingChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- EDITED Module 2 Lesson 1Document28 pagesEDITED Module 2 Lesson 1Chesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Variable and Absorption CostingDocument48 pagesModule 3 Variable and Absorption CostingChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Dicussion BSA13 Nov 21 2019 Partnership DissolutionDocument5 pagesDicussion BSA13 Nov 21 2019 Partnership DissolutionChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Fabric and DyeDocument1 pageFabric and DyeChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Form 1. Fitness TestDocument1 pageForm 1. Fitness TestChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Notes To Financial Statement Problem 3-1: Answer: D. All of These Can Be Considered A Purpose of The NotesDocument6 pagesNotes To Financial Statement Problem 3-1: Answer: D. All of These Can Be Considered A Purpose of The NotesChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- End of QuizDocument6 pagesEnd of QuizChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Submissions - B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 - DLSU-D College - GSDocument3 pagesSubmissions - B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 - DLSU-D College - GSChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT 2 - Part 2 of Obligations - B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 - DLSU-D College - GSDocument8 pagesSUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT 2 - Part 2 of Obligations - B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 - DLSU-D College - GSChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Alon-Contract-Objects Cause FormsDocument5 pagesAlon-Contract-Objects Cause FormsChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- ALON-ENABLING ASSESSMENT - Void or Inexistent Contracts - B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 - DLSU-D College - GSDocument5 pagesALON-ENABLING ASSESSMENT - Void or Inexistent Contracts - B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 - DLSU-D College - GSChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- ALON-Comprehensive Exam On ContractsDocument8 pagesALON-Comprehensive Exam On ContractsChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Partnership Accounting Quiz Submissions: Standalone AssessmentDocument5 pagesPartnership Accounting Quiz Submissions: Standalone AssessmentChesca Alon100% (1)
- ALON-CONTRACTS (2ND QUIZ) - 30 Over 30Document5 pagesALON-CONTRACTS (2ND QUIZ) - 30 Over 30Chesca AlonNo ratings yet
- ALON-CONTRACTS (1ST QUIZ) - 30 Over 30Document5 pagesALON-CONTRACTS (1ST QUIZ) - 30 Over 30Chesca AlonNo ratings yet
- End of Quiz: B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 Enabling Assessment: Voidable ContractsDocument3 pagesEnd of Quiz: B-BLAW211 Law On Obligations and Contracts BSA21 1S AY20-21 Enabling Assessment: Voidable ContractsChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Alon-Contract-Objects Cause FormsDocument5 pagesAlon-Contract-Objects Cause FormsChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Methods of Data PresentationDocument27 pagesLesson 2.1 Methods of Data PresentationChesca AlonNo ratings yet
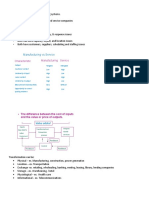
- Manufacturing Vs ServiceDocument2 pagesManufacturing Vs ServiceChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 MEASURES OF Central Tendency and LocationDocument24 pagesLesson 2.2 MEASURES OF Central Tendency and LocationChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3: Measures of DispersionDocument13 pagesLesson 2.3: Measures of DispersionChesca AlonNo ratings yet
- Drops, Dynamics, and DaisiesDocument7 pagesDrops, Dynamics, and DaisiesChesca AlonNo ratings yet