Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Excel Module Week 4 - Cost of Capital (20 Points) : Situation
Excel Module Week 4 - Cost of Capital (20 Points) : Situation
Uploaded by
w_fib0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesOriginal Title
WK_4_Excel_Module_Cost_of_Capital
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesExcel Module Week 4 - Cost of Capital (20 Points) : Situation
Excel Module Week 4 - Cost of Capital (20 Points) : Situation
Uploaded by
w_fibCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
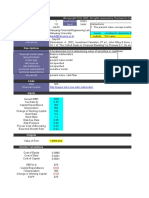
A B C D E F G
2 Excel Module Week 4 - Cost of Capital (20 points)
3 Situation
4
5
6 During the last few years, Jana Industries has been too constrained by the high cost of capital to make
7 many capital investments. Recently, though, capital costs have been declining, and the company has
8
decided to look seriously at a major expansion program that has been proposed by the marketing
department. Assume that you are an assistant to Leigh Jones, the financial vice president. Your first
9 task is to estimate Jana's cost of capital. Jones has provided you with the following data, which she
10 believes may be relevant to your task:
11
12 A. The firm's tax rate is 40% and its before tax cost of debt is 10%
13
14
B. The current price of Jana's 12% coupon, semiannual payment, noncallable bonds with 15 years remaining to
15 maturity is $1,153.72. Jana does not use short-term interest-bearing debt on a permanent basis. New bonds
16 would be privately placed with no flotation cost.
17
18 C. The current price of the firm’s 10%, $100 par value, quarterly dividend, perpetual preferred stock is $116.95.
19 Jana would incur flotation costs equal to 5% of the proceeds on a new issue.
20
21
D. Jana's common stock is currently selling at $50 per share. Its last dividend (D ) was $3.12, and dividends are
22 0
expected to grow at a constant rate of 5.8% in the foreseeable future. Jana's beta is 1.2, the yield on T-bonds is
23 5.6%, and the market risk premium is estimated to be 6%. For the own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental-risk-premium
24 approach, the firm uses a 3.2% judgmental risk premium.
25
26 E. Jana's target capital structure is 30% long-term debt, 10% preferred stock, and 60% common equity.
27
28 To structure the task, Leigh Jones has asked you to answer the following questions.
29
30 1. Explain what sources of capital should be included when you estimate Jana's weighted average cost
31 of capital (WACC)? (1 point)
32
33 WACC is the average return required by all of the firms investors, determined by the firm's capital structure, interest
34 rates, its risk and market's attitude towards the risk. The calculation includes common stock, long term debt, bonds
35 and preferred stock. WACC is primarily used for some long term capital investement decisions.
36
37
38 As a source, Jana can use the WACC equation:
39 WACC= ((E/V) x Re) + ((D/V) x Rd x (1-Tc))
40 Re= cost of equity,Rd = cost of debt, E = market value of the firm's equity, D = market value of the firm's debt, V=E+D=2
41 Tc = Corporate tax rate
42
43
44 2. Explain whether the component costs be figured on a before-tax or an after-tax basis?
45 (1 point)
A B C D E F G
46 The component costs should be done on an after-tax basis. Dividents are paid on reinvestments made with after-tax
47 dollars, therefore all calculations of cash flow and rates of return should be done on an after-tax basis.
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55 3. Explain whether the costs be historical (embedded) costs or new (marginal) costs & WHY?
56 (HINT: "costs" refer to cost of capital, cost of preferred stock, and cost of common equity (1 point)
57
58 The costs should be new marginal rather than historical. It is due to capital costs primarily used in making decisions
59 that require raising new capital.
60
61
62
63
64 4. What is the before and after tax cost of debt? (2 points)
65
66 COST OF DEBT, rd
67
68 Before Tax Cost of Debt = B-T rd = 6(1-0.10)=6(0.9)= 5.4%
69
70 After Tax Cost of Debt = A-T rd = ( 1 - Tax Rate) x (B-Trd)
71 6(1-0.40)=6(0.6)= 3.6%
72
73
74
75 5. What is the firm's cost of preferred stock? (2 points)
76
77 Explain and calculate the firm's cost of preferred stock
78 Firms use preferred stock as part of their financing mix. A company takes care of full cost since the preferred
79 dividends are not tax deductible. Nowadays many firms have a sinking fund which would limit its life. Firms try to pay
80 their preferred dividends and if that would to fail, common stock payouts would not be met, failure to raise additional
81 funds in the capital markets and in some cases stockholders could take control of the firm.
82
83
84
85
86 Pref. Dividend $10.00
87 Pref. Price (Pps) $116.95
88 Flotation costs (F) 5%
89
90 rps = Pref. Dividend ÷ Pps(1 – F)
91 10/((116.95(1-5) = 8.93%
A B C D E F G
92
93
94
95 COST OF EQUITY (INTERNAL), rs
96 6. What are the two primary ways companies raise common equity? (1 point)
97
98 Two primary ways the companies rainse common equity are by retaining earningd and by issuing new commn stock.
99
100
101
102
103
104
105 7. Why is there a cost associated with reinvested earnings? (1 point)
106
107 While the earnings are reinvested, the stockholders would receive the funds in order to reinvest in other securities.
108 The firm then should earn on its reinvested earnings as stockholders earn on alternative investements of
109 equivalent risk.
110
111
112
113
114
115
116 8. Jana doesn’t plan to issue new shares of common stock. Using the CAPM approach, what is Jana's
117 estimated cost of equity? (2 points)
118
119 The CAPM Approach
120 rs = Risk-free rate + (Market risk premium) (Beta)
121 rs = rRF + (RPM) bi (Note: RPM is the expected return on the market minus the risk-free rate.)
122
123 PROBLEM
124
125 Assuming the risk-free rate (i.e., the current yield on a long-term Treasury bond) equals 5.6%, the
126 expected market risk premium is 6%, and the firm's beta is 1.2, what is the company's cost of equity
127 from internal funds?
128
129 Risk-free rate (rRF) 5.6%
130 Expected market risk premium (RPM 6%
131 Beta (bi) 1.2
132 Cost of Equity (rs) ???
133
134 rs = rRF + (RPM) x (bi) = CAPM formula
135 rs = 0.056 + (0.06)1.2 = 12.8%
136
A B C D E F G
137 rs = Cost of Equity
138
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Lecture 4 Leveraged Buyouts 1Document34 pagesLecture 4 Leveraged Buyouts 1w_fibNo ratings yet
- Multifamily Acquisition ModelDocument4 pagesMultifamily Acquisition Modelw_fibNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- (SWMS-01) Loading, Unloading and ShiftingDocument5 pages(SWMS-01) Loading, Unloading and ShiftingPRATEEK SINGH100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Introduction To Business Combinations and The Conceptual FrameworkDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Business Combinations and The Conceptual Frameworkw_fibNo ratings yet
- Credit Swiss Pitch BookDocument39 pagesCredit Swiss Pitch Bookw_fibNo ratings yet
- 1.FV Function Excel Template 1Document6 pages1.FV Function Excel Template 1w_fibNo ratings yet
- Bridgewater ReportDocument12 pagesBridgewater Reportw_fibNo ratings yet
- Dupont DPC LBO AssignmentDocument3 pagesDupont DPC LBO Assignmentw_fibNo ratings yet
- The Real Estate Development Process: Lot and Unit Assumptions - Bateman ApartmentsDocument7 pagesThe Real Estate Development Process: Lot and Unit Assumptions - Bateman Apartmentsw_fibNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey Standard Elements: Message Title StickerDocument19 pagesMckinsey Standard Elements: Message Title Stickerw_fibNo ratings yet
- Private Equity and Venture Capital Management: DR Shane Lavagna-SlaterDocument36 pagesPrivate Equity and Venture Capital Management: DR Shane Lavagna-Slaterw_fibNo ratings yet
- 2GO Excel Calculation 1Document60 pages2GO Excel Calculation 1w_fibNo ratings yet
- Business Communication NotesDocument214 pagesBusiness Communication NotesAnonymous xpdTqv100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Mes For Dummies 10662 PDFDocument52 pagesMes For Dummies 10662 PDFSamanthaPereraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 and 7 Project Finance Model 1Document61 pagesLecture 6 and 7 Project Finance Model 1w_fibNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Key Partners Key Activities Value Proposition Relationship Customer GroupsDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Key Partners Key Activities Value Proposition Relationship Customer Groupsw_fibNo ratings yet
- Analyst TrainingDocument162 pagesAnalyst Trainingw_fibNo ratings yet
- Systeme - Io ReviewDocument7 pagesSysteme - Io ReviewVinayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Venture CapitalDocument40 pagesLecture 2 Venture Capitalw_fib100% (1)
- IRR Approach - To Assess Which One Is Better Investment AlternativeDocument5 pagesIRR Approach - To Assess Which One Is Better Investment Alternativew_fibNo ratings yet
- WACC Formula Excel Template: Visit: EmailDocument3 pagesWACC Formula Excel Template: Visit: Emailw_fib100% (1)
- Go To Market Strategy - Advanced Techniques and Tools For Selling More Products To More Customers More Profitably PDFDocument309 pagesGo To Market Strategy - Advanced Techniques and Tools For Selling More Products To More Customers More Profitably PDFanshumanNo ratings yet
- GP Concept Note-Harshita KaarthikayaDocument13 pagesGP Concept Note-Harshita KaarthikayakaarthikayaNo ratings yet
- 3.NPER Function Excel Template 1Document9 pages3.NPER Function Excel Template 1w_fibNo ratings yet
- Discounted Cash Flow Model: Leesb@hanyang - Ac.krDocument2 pagesDiscounted Cash Flow Model: Leesb@hanyang - Ac.krw_fibNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Business Model Canvas IIDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Business Model Canvas IIw_fibNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Beroni Group: Managing General Partners-Limited Partner RelationshipsDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Beroni Group: Managing General Partners-Limited Partner Relationshipsw_fib100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Business Model CanvasDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Business Model Canvasw_fibNo ratings yet
- Private Capital Investing: Private Equity - Private DebtDocument20 pagesPrivate Capital Investing: Private Equity - Private Debtw_fibNo ratings yet
- Assumptions:: Simple LBO Model - Key Drivers and Rules of ThumbDocument2 pagesAssumptions:: Simple LBO Model - Key Drivers and Rules of Thumbw_fibNo ratings yet
- Project Title: Financial Modeling and Analysis of 50 Flats Housing Project in Gurgaon, Haryana INDocument13 pagesProject Title: Financial Modeling and Analysis of 50 Flats Housing Project in Gurgaon, Haryana INw_fibNo ratings yet
- Revision Points 2 - AudiencesDocument5 pagesRevision Points 2 - AudiencesYashodhaNo ratings yet
- Rac Group: Now, We Also Have Extension Sales and Service Office atDocument12 pagesRac Group: Now, We Also Have Extension Sales and Service Office atShruti SangmuleNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Industrial Policy 2009-14: Department of Industries and CommerceDocument54 pagesKarnataka Industrial Policy 2009-14: Department of Industries and CommerceAnonymous gwWpeCiZNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Project Report INE3004 - 2021-2022Document23 pagesE-Commerce Project Report INE3004 - 2021-2022Nguyễn Hoàng TrườngNo ratings yet
- Societal MarketingDocument7 pagesSocietal Marketingraje.jk86% (14)
- Prelim BibliographyDocument12 pagesPrelim BibliographyCai TeeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Brief History of The IndustryDocument46 pages1.1 Brief History of The IndustryTomy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Magazine - May 2023Document52 pagesControl Engineering Magazine - May 2023bladimir moraNo ratings yet
- Baseline-Narrative ReportDocument15 pagesBaseline-Narrative ReportlightsonsNo ratings yet
- Labor Midterm Case DigestDocument20 pagesLabor Midterm Case DigestLen-Len CobsilenNo ratings yet
- 20 January 2022 (Thursday)Document4 pages20 January 2022 (Thursday)谦谦君子No ratings yet
- Alonzo Greene Updated Resume 1Document3 pagesAlonzo Greene Updated Resume 1Alonzo GreeneNo ratings yet
- Role Model of My Life - Bhushan GharalDocument10 pagesRole Model of My Life - Bhushan GharalBhushan GharalNo ratings yet
- K ShanmugamDocument7 pagesK ShanmugamShankker KumarNo ratings yet
- Ural Development in India " .": Target Based ApproachDocument35 pagesUral Development in India " .": Target Based ApproachAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Using Database Partitioning With Oracle E-Business Suite (Doc ID 554539.1)Document39 pagesUsing Database Partitioning With Oracle E-Business Suite (Doc ID 554539.1)casiusclipNo ratings yet
- CF Question Paper t2Document3 pagesCF Question Paper t2KUSHI JAINNo ratings yet
- Megaskindustrialcorporation: 1 Floor, Philpremiere BLDG., 10 Niog Road, Niog Iii, Bacoor City, Cavite 4102Document2 pagesMegaskindustrialcorporation: 1 Floor, Philpremiere BLDG., 10 Niog Road, Niog Iii, Bacoor City, Cavite 4102Darwin BendecioNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Talent Acquisition Process of Standard Chartered Bank LTDDocument50 pagesRecruitment and Talent Acquisition Process of Standard Chartered Bank LTDSadia SultanaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Copywriting Sample Instructions - v2 - BilingualDocument6 pages1 - Copywriting Sample Instructions - v2 - Bilingualmarcus204No ratings yet
- Competitive Strategy Within Engineering Management (2533)Document7 pagesCompetitive Strategy Within Engineering Management (2533)Sai PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Polaris Case DecisionshetDocument3 pagesPolaris Case DecisionshetPaul JohnNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Muhs NashikDocument7 pagesDissertation Muhs NashikCollegePapersForSaleCanada100% (1)
- Contracts VoucherDocument52 pagesContracts VoucherExan PurchasingNo ratings yet