Professional Documents
Culture Documents
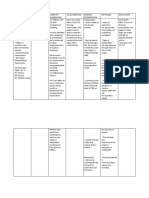
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
fei_santosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
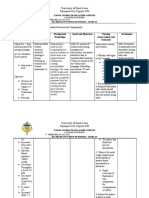
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
fei_santosCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
INTERVENTION
Subjective: Deficient Fluid After 2° of Monitor and -Tachycardia, After 2° of
“Kanina pa ako Volume Nursing record vital signs dypnea, or Nursing
dumudumi ng related Interventions, q 2° or as often hypotension Interventions,
malambot na to active fluid the patient fluid as necessary until may indicate the goal was
malambot” as volume loss. and blood stable. fluid volume met as the
verbalized by volume will deficit or patient’s fluid
the patient increase on its electrolyte and blood
level according imbalance volume increase
to its 1st up to normal as
Objective: appearance. evidenced by
( + ) sunken Measure intake - Low urine stable vital
eyeballs. and output q 1°. output and signs.
( + ) poor skin Record and high specific
turgor. report significant gravity
Pain scale of changes. Include indicates
8/10 urine, and stools. hyovolemia.
V/S as follow:
Assess skin -To check for
turgor and oral dehydration.
mucous
membranes q
2°.
Give oral/mouth -To avoid
care dehydrating
mucous
membranes
Don’t allow -To avoid
patient to sit or orthostatic
stand up quickly hypotension
as and possible
long as syncope.
circulation is
compromise
Administer and -To prevent
monitor further fluid
medications as loss.
ordered.
Acute Gastroenteritis is a catchall term for infection or irritation of the digestive tract, particularly the
stomach and intestine. It is frequently referred to as the stomach or intestinal flu, although the influenza
virus is not associated with this illness. Major symptoms include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and
abdominal cramps. These symptoms are sometimes also accompanied by fever and overall weakness.
Acute Gastroenteritis typically lasts about three days. Adults usually recover without problem, but
children, the elderly, and anyone with an underlying disease are more vulnerable to complications such
as dehydration.
Common symptoms:
Low grade fever to 100 F (37.7 C)
Nausea with or without vomiting
Mild-to-moderate diarrhea
Crampy painful abdominal bloating (The cramps may come in cycles, increasing in severity until
a loose bowel movement occurs and the pain resolves somewhat.)
More serious symptoms of acute gastroenteritis:
Blood in vomit or stool (Blood in vomit or stool is never normal and the affected individual
should call or a visit a health care practitioner.)
Vomiting more than 48 hours
Fever higher than 101 F (40 C)
Swollen abdomen or abdominal pain
Dehydration - weakness, lightheadedness, decreased urination, dry skin, dry mouth and lack of
sweat and tears are characteristic signs and symptoms.
You might also like
- NCP FluidDocument4 pagesNCP FluidSofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing SY 2015-2016Document2 pagesSt. Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing SY 2015-2016Sydelle GravadorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Peptic Ulcer DsDocument4 pagesNCP Peptic Ulcer Dsplug0650% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation Case: Amoebiasis Subjective:" Madalas Po AkongDocument47 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation Case: Amoebiasis Subjective:" Madalas Po AkongNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Defict Ms. HicksDocument8 pagesFluid Volume Defict Ms. HicksShenna RegaspiNo ratings yet
- Ricafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesRicafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaxine RicafortNo ratings yet
- Nursing - Care - Plan DRDocument5 pagesNursing - Care - Plan DRPrince TulauanNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Massive AscitesDocument12 pagesMassive Ascitesranitidin100% (1)
- NCP - DM - FatigueDocument12 pagesNCP - DM - FatigueJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanNo ratings yet
- Guinitaran, Christine Ann P. BSN 4 Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesGuinitaran, Christine Ann P. BSN 4 Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanGemmalene PaclebNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalDocument19 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalTin100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Nurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonDocument3 pagesNurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonMikaela Angeles NazarNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPNicole_Santos_6836No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis 1Document5 pagesNursing Diagnosis 1Kim TangoNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMargaret ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3Document2 pagesCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3JP2001No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- NCP J2Document1 pageNCP J2jade abarillaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Dengue FeverDocument21 pagesPresentation Dengue Feverpolarbear12121250% (2)
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennifer B. PascualNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk Fluid IntakeDocument1 pageNCP Risk Fluid IntakeShannon CabfitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis:: Interventions RationaleDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis:: Interventions RationaleKenji CadizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planmust dietNo ratings yet
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP Ca 3Document3 pagesNCP Ca 3Lalaine LocsinNo ratings yet
- Capacio Case#1 RevisedDocument4 pagesCapacio Case#1 RevisedLorenz CapacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsia-Eclampsia - Hellp SyndromeDocument23 pagesNursing Care Plans: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsia-Eclampsia - Hellp Syndromealmayasa2002No ratings yet
- DM ncp2Document1 pageDM ncp2Mark PabalanNo ratings yet
- NCP 3Document2 pagesNCP 3Cuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNCP - Activity IntolerancePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPAyla Mar100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan NCPDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (1)
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaNo ratings yet
- Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesExcess Fluid VolumeyuddNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- PD HandoutDocument6 pagesPD HandoutVanetNo ratings yet
- Borata Nursing Process RleDocument11 pagesBorata Nursing Process Rlefiel borataNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument5 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeCHRISTINE GRACE ELLONo ratings yet
- NCP TorresDocument7 pagesNCP TorresbabiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Ysun Espino100% (1)
- 17 Diarrhoea Paediatric - EMT - FinalDocument3 pages17 Diarrhoea Paediatric - EMT - FinalFebRianti RirinNo ratings yet
- Rowing PDFDocument8 pagesRowing PDFkullNo ratings yet
- Axillary MethodDocument5 pagesAxillary MethodJerica Jaz F. VergaraNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Activity ZoneDocument2 pagesActivity Zonetech timeNo ratings yet
- Receptor Pharmacology Cheat Sheet (4f6203b546fa5)Document5 pagesReceptor Pharmacology Cheat Sheet (4f6203b546fa5)sinthreckNo ratings yet
- Principles of Aerobic Exercise (I)Document45 pagesPrinciples of Aerobic Exercise (I)Martha ChaseNo ratings yet
- Cold Injuries and HypothermiaDocument34 pagesCold Injuries and HypothermiaRam Kirubakar ThangarajNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument74 pagesBiological Bases of BehaviorKylie AnneNo ratings yet
- ACLS Recerti Cation Exam Quiz: (/my-Account/)Document6 pagesACLS Recerti Cation Exam Quiz: (/my-Account/)andres novoaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsDocument12 pagesRespiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsAditya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Excretory SystemMariel Abatayo0% (1)
- Tutorial: MODULE: Musculoskeletal System IIDocument3 pagesTutorial: MODULE: Musculoskeletal System IIrishit20% (5)
- The Fitness Fatigue Model Revisited ImplicationsDocument10 pagesThe Fitness Fatigue Model Revisited ImplicationsLucas AvellanNo ratings yet
- Circulation 2 QPDocument10 pagesCirculation 2 QPAthenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewJayson SamonteNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument31 pagesBasic First AidMark Anthony MaquilingNo ratings yet
- Vieillard-Baron2018 Article DiagnosticWorkupEtiologiesAndMDocument17 pagesVieillard-Baron2018 Article DiagnosticWorkupEtiologiesAndMFranciscoNo ratings yet
- 2040 Full NotesDocument71 pages2040 Full NotesAthul DevadasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MIDocument14 pagesLesson Plan MIAnand Bhawna100% (1)
- Contoh Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageContoh Nursing Care PlanResmi LindaNo ratings yet
- OSCE Checklist Blood Pressure MeasurementDocument2 pagesOSCE Checklist Blood Pressure MeasurementRohullah QasimiNo ratings yet
- Biology IADocument15 pagesBiology IARNo ratings yet
- Coherence Analysis Between ECG and EEG SignalsDocument92 pagesCoherence Analysis Between ECG and EEG Signalspiyush_chawla18No ratings yet
- PEDocument11 pagesPEMary Joy QuilangNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - HandoutsDocument5 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - HandoutsKelly Trainor100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument42 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsKrakenzeN100% (1)
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument26 pagesTransport in Plants PDFMasOom Si ChuRail100% (2)
- Chronic Pain ManagementDocument44 pagesChronic Pain ManagementTomBramboNo ratings yet
- Esc Guidelines For The Management of Heart Failure (Autosaved)Document80 pagesEsc Guidelines For The Management of Heart Failure (Autosaved)Ahmad AlKhataybehNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3rd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd QuarterLyrMa NCNo ratings yet