Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure: Principles of Acounting - O' Level Notes
Uploaded by
JessyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure: Principles of Acounting - O' Level Notes
Uploaded by
JessyCopyright:
Available Formats
PRINCIPLES OF ACOUNTING - ‘O’ LEVEL NOTES
CAPITAL EXPENDITURE AND REVENUE EXPENDITURE
Capital expenditure is expenditure incurred to acquire non-current assets or adding value to existing
non –current assets.
Any other costs incurred to bring an asset into use are also classified as capital expenditure.
Included in such amounts should be spending on
acquiring fixed assets
bringing them into the business
legal costs of buying buildings
carriage inwards on machinery bought
any other cost needed to get a fixed asset ready for use
Revenue expenditure refers to expenses needed for the day-to-day running of the business.
Included under revenue expenditure for example are petrol costs for van, repairs to van, and
electricity costs of using machinery.
Exercise: Classify the following into capital and revenue expenditure.
1. New radio car
2. Fuel for motor vehicle
3. Computer repair costs
4. New air cooler system
5. Legal costs incurred on new asset
6. Carriage inwards on non current asset
7. Repainting of premises
If capital expenditure is incorrectly treated as revenue expenditure, net profit is reduced and the
value of non-current assets is understated.
If revenue expenditure is incorrectly treated as capital expenditure, net profit is increased and the
value of non-current assets is overstated.
It is important to note that expenditure can have a component of capital expenditure and revenue
expenditure. Such scenarios are referred to as joint expenditures. For example, wages of $20 000
might be ¾ revenue expenditure and ¼ capital expenditure. Therefore those wages need to be
treated accordingly.
1|Page
MUKWEPA STUDY CENTRE
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Cells Structure and Organisation 1Document36 pagesCells Structure and Organisation 1JessyNo ratings yet
- My Knight The LionessDocument221 pagesMy Knight The LionessJessy100% (1)
- Anything But A Happy GirlDocument144 pagesAnything But A Happy GirlJessyNo ratings yet
- 2019 WTS Financial MathsDocument35 pages2019 WTS Financial MathsJessyNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Notes Form 3 pdf-1Document54 pagesAgriculture Notes Form 3 pdf-1Jessy100% (1)
- Combined Science Notes: Chem Introduction: Sub-Atomic Particle Location Symbol Relative Mass ChargeDocument10 pagesCombined Science Notes: Chem Introduction: Sub-Atomic Particle Location Symbol Relative Mass ChargeJessyNo ratings yet
- Combined Science Notes: Germination: Germination Is The Process Whereby A Seed Becomes A SeedlingDocument4 pagesCombined Science Notes: Germination: Germination Is The Process Whereby A Seed Becomes A SeedlingJessyNo ratings yet
- Combined Science Notes: DiseasesDocument3 pagesCombined Science Notes: DiseasesJessyNo ratings yet
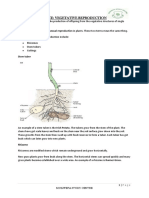
- Combined Science: Vegetative ReproductionDocument3 pagesCombined Science: Vegetative ReproductionJessyNo ratings yet
- Combined Science Notes: EcosystemsDocument3 pagesCombined Science Notes: EcosystemsJessyNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationJessyNo ratings yet
- It Was Forced SSN 1&2Document627 pagesIt Was Forced SSN 1&2Jessy50% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)