Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Desktop Publishing (DTP) Notes
Desktop Publishing (DTP) Notes
Uploaded by
Mwangi CharlesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Desktop Publishing (DTP) Notes
Desktop Publishing (DTP) Notes
Uploaded by
Mwangi CharlesCopyright:
Available Formats
DESKTOP PUBLISHING (DTP) NOTES
Introduction
- Publishing is the process of producing publication like newspapers, cards, pamphlets, pictures, calendars
etc. that have special text, graphic layout and design.
- The traditional method of publishing involved drawing and writing manually on wooden or metallic boards.
The artwork was then painted with ink and pressed on papers to produce a printout. This was very tedious.
- Today the art of publishing has changed because of the advent of personal computers and smaller printers
that are able to print high quality text and graphics, even in an office or at home.
Desktop publishing (DTP)
- It refers to the process of producing publications like cards, newspapers etc. by designing their text and
graphic layout and inserting, editing, formatting and printing of text and graphical objects using a special
desktop publishing software installed on computers.
- The term desktop means that all the publishing process can now be done on a desk in the office or at home
using a personal computer.
- The difference between a desktop publisher and a word processor is that a desktop publisher software gives
the user more tools and control of the page layout, text manipulation and graphics design than a word
processor.
- However it is important to note that some word processors today have also been incorporated with text and
graphic formatting and editing tools. Hence a thin line exists between them and the desktop publishers. For
example one can design a full publication in Microsoft Word by using the available drawing and picture
tools, create columns etc.
Examples of DTP software include:
i. Adobe PageMaker
ii. Microsoft Publisher
iii. QuarkXpress
iv. Adobe InDesign
v. Ventura
vi. Serif PagePlus
vii. Apple Page 2
Purpose of desktop publishing software
DTP programs are very popular in publishing because they give the person designing publications a lot of control
on: -
a) Graphics design
- DTP allows different types of graphics to be incorporated into a publication e.g. photographs, illustrations,
texture, line drawing, cartoons.
b) Page layout design
- It involves placement and arrangement of text and graphics on the page to produce documents such as
newsletters, brochures, books etc.
- Consider the layout of a newspaper – it may consist of text, charts, graphics, photographs illustrations,
cartoons etc.
- Using desktop publisher, one can be able to design a page layout by setting consistent picture and object
locations, dividing page in a number of columns and creating layers.
- A layer can be viewed as the arrangement of objects on top of each other with the one on top being on the
first layer e.g. text can be on one layer while graphical objects on another. Therefore the text layer can be
manipulated separately from the graphical object layer. For example, text moves separate from the objects.
- Another example is that you make the graphical object layer transparent in order to make the text in a layer
behind the object visible.
- The different elements may be created using different packages e.g. graphics package – for illustrations,
spreadsheet package for charts, word processors for text.
c) Printing
- It involves proofing image setting, color separation (for productions), plate making and the actual printing.
- The final publication is usually printed on a typeset machine rather than a computer printer.
- DTP software in the printing process is to create the proofs and do the color separation.
- For the low volumes, the entire publication may be printed directly from the DTP package. It is too
expensive for high volume prints.
Advantages of DTP’s over Word processor
i. Every item on a page is contained in a frame and can be edited and formatted independently.
ii. Stories can be contained in a single frame or threaded between several frames.
iii. Frames need not flow in logical sequence e.g. a story on page one may be contained on page eight.
iv. Master page are used to set a common layout which may be repeated on several pages e.g. logo, page
number etc.
v. Publication can be printed in a form suitable for commercial printing e.g. using color separations.
AGHS © 2010 DESKTOP PUBLISHER NOTES COMPUTER STUDIES Page 1
vi. Wide range of templates is available e.g. brochures booklets, posters, business cards etc.
vii. Multiple stories from different authors can be handled with ease.
Types of DTP software
There are two broad categories of desktop publishing software namely graphic–based and layout-based DTPs.
1. Graphic-based: -
They are specifically developed to edit and format graphic objects such as those drawn by fine artists. Example of
graphic-based DTP software include: -
a. Adobe Photoshop
b. Adobe Illustrator
c. CorelDraw
This software have superior image handling capabilities like setting resolution, brightness, contrast, cropping and
filling images with all types of color. It is important to note that some graphic-based like CorelDraw and Illustrator
are also used for page layout design.
Graphics file formats include: -
Vector – EPS (Encapsulated Postscripts)
AI (Adobe Illustrator)
WMF (Window Metafile)
Bitmap – BMP (Bitmap)
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
JPG / JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Groups)
GIF (Graphic Interface Format)
NOTE:
Every software has a file extension for user files that are native to that program.
For example: -
Photoshop – psd
CorelDraw – cdr
Publisher – pub
Always save your graphics in the software default extension
2. Layout-based: -
They are specifically developed to create different page layout designs for text and pictures. For example the way
the front page of a newspaper is developed. It is difficult to achieve such without a good layout based DTP.
Examples of layout-based DTP software’s include:-
a. Adobe PageMaker.
b. Microsoft Publisher
c. InDesign.
The above types of DTP helps in producing publications such as newspapers, magazines, cards and booklets.
DESIGNING A PUBLICATION
- Publications vary in design and formatting. For example, a card has a design that is different from a
newspaper. It is possible to produce different types of such publications using a desktop publishing
software.
Examples of publication designed using DTP include: -
Cards: -
- These may be for weddings and other special occasions like graduations and congratulations, harambee
cards, postcards, greeting cards etc.
Certificates: -
- To show completion of courses and special events. These type of publications are very sensitive because
they must be designed to discourage any type of duplication or counterfeits.
Newspapers: -
- Have news targeting many people. They may have much text, graphic layouts and designs.
Books: -
- They are bulky publications with many pages bound together within the same publication.
Calendars: -
- Apart from showing dates, they are used by companies to advertise their products; hence most of them have
heavy catchy graphics.
Business cards: -
- Used to relay relevant company information within a small space. They should contain the company logo
and all contact information such as company and person’s names, telephone number, fax number, e-mail
address and postal address.
Journals: -
AGHS © 2010 DESKTOP PUBLISHER NOTES COMPUTER STUDIES Page 2
- They are publications written by experts for other experts in specific subject areas. They are published
regularly (monthly/longer) and contain articles usually documenting original research and experiments on
topics.
Flyers and Posters: -
- They are publications that relay information to a large number of people. They are usually hand delivered
to a post-box or person, stuck under windscreen wipers on cars, pinned onto doors or notice boards.
Newsletters
- They are publications similar to newspaper but are used for disseminating information to special interest
groups. They serve as a sales or public relations tool for some professionals.
Getting started with Adobe PageMaker
Currently Adobe PageMaker, CorelDraw and InDesign are the most commonly used commercial DTP software.
However beginners in DTP and students find it easier to use Microsoft Publisher since it inherits most of the features
of Microsoft Word.
Launching Adobe PageMaker 7.0
1. Click the Start button and then point to Programs
2. On the programs sidekick menu, point to Adobe group then select PageMaker
3. The PageMaker program starts and provides the Document set up dialog box. If the Document setup dialog
box is not displayed, then click File menu and select the New command.
4. In the Document Setup dialog box specify the publication setup options.
5. Click OK to apply the selected options. A publication window will be displayed.
Launching Microsoft Publisher 2007
i. Click the Start button and then point to Programs
ii. On the programs sidekick menu, point to Microsoft Office and then select Microsoft Office Publisher 2007.
iii. The Microsoft Publisher program starts with different publications displayed on the Ms Publisher window.
iv. Specify the type of publication you want to work on or you can select a blank publication. The blank
publication tab provides a number of blank templates that helps one to with the initial layout and page
orientation of the new publication.
The blank publication has the following features:
a. The pasteboard
b. The toolbox
c. Rulers
d. The printable area
e. Master pages
f. Control pallete
The pasteboard
- A paste board is a large blank area where you place text and graphical objects before arranging them neatly
on the printable work area enclosed with margins.
The printable area
- It is the area that looks like a page surrounded by margins on the pasteboard. Any object or text that is
placed on the printable area will be printed by the printer.
The toolbox
-
This is a set of buttons that contains various tools that you can use to create and manipulate your
publication.
Summary of the function of each tool
Tool Purpose
Pointer /Select objects Select, move and resize text blocks and graphical objects
Text box Type, select and edit text
Rotate Select and rotate objects
Insert table For inserting a table in a publication
Insert WordArt For inserting Wordart text
Ellipse Draw ellipses and circles
Ellipse frame Create a circular or oval placeholder for text and objects
Polygon frame Create a polygonal placeholder for text and graphics
Hand Scroll the page or to preview and test hyperlinks
Zoom Magnify or reduce an area of the page.
AutoShapes Used for drawing different shapes like lines, stars and banners, connectors, basic
shapes, block arrows and flowcharts etc.
Rectangle Draw squares and rectangles
Master Pages
AGHS © 2010 DESKTOP PUBLISHER NOTES COMPUTER STUDIES Page 3
- It is a publication page that contains the design and layout elements that you want to repeat on multiple
pages in your publication. These elements include headers, footers and layout guides.
- Every new publication starts with one master page by default and must always have at least one master
page.
- One advantage of using master pages for the common elements is that it gives your publication a more
consistent appearance. One can also create and update these elements in one place, instead of changing
them on each page where the design elements appear.
Rulers
- Each publication window can include horizontal and vertical rulers. They extend along the top and left
boarders of the window. One can display rulers when you need them and hide them when you want more
room on the screen to view a publication.
- The rulers must be visible to help the user to manually create ruler guides. Ruler guides are non-printable
lines or guides that ensure that text and graphical objects are in the required place.
Setting up margin guides
Margins guides are very important because they define the printable area publication.
To change margin settings:
On File menu, click Page setup
From the page setup dialog box at the top right:
a. Enter the values for Inside and Outside margins for a double sided document to accommodate binding for a
document that will be printed on both sides. For single sided pages, set the left and right margins.
b. Enter the value for the top and bottom margins.
c. Click Ok to the setup dialog box and effect the changes.
Saving the layout
When one completes setting up a publication layout, it is important for one to save before he/she starts entering text
and graphics.
Steps: -
a. When saving for the first time, from the File menu, click Save As or click the save button on the toolbar.
b. In the Save As dialog box, specify the name of the file and the storage location of the publication then click
Save button.
Displaying and hiding rulers
If the rulers are not displayed, click the View menu, then Rulers to display them. To hide the rulers, click the view
menu and then select Rulers.
Selecting ruler measurements
One can be able to set different measurements on both rulers. For example one can set the vertical ruler in
millimeters and the horizontal in inches.
Steps for setting measurements
Select Tools from the menu bar
From the pull down menu, select Options.
In the Options dialog box, select the measurement units i.e. inches, centimeters, picas, pixels, points etc. if
you are not familiar with some units, it is advisable you use millimeters or inches.
Manipulating text and graphical objects
To add text using text frame tool in Publisher
1. Click tool marked A on the tool box.
2. On an empty area on the pasteboard or printable area, drag to define the text block.
3. Type the text.
Resizing and moving text objects.
Text may not fit in the defined text frame. Publisher displays A… below the text frame.
To resize the text block both in PageMaker and Publisher: -
1. Click the text block using the pointer tool.
2. Position the pointer on the selection handle and drag to resize.
To move the text block in Publisher
1. Click the text block using the pointer tool.
2. Position the pointer tool on the object and hold down the left mouse button.
3. Drag the text object to a new position.
Importing text from a word processor
Other than typing text in Publisher one can also import text from a word processor file. To import text in Publisher: -
1. On the File menu, click Import Word Document
2. In the dialog box, select the file then click OK.
3. The text is pasted onto the printable area
AGHS © 2010 DESKTOP PUBLISHER NOTES COMPUTER STUDIES Page 4
Inserting graphical objects
One can import pictures and other graphical objects into a publisher document by linking or embedding.
To import an object in Publisher
On the Insert menu, point to Picture, click From File.
In the Insert picture dialog box, select the drive or folder where the file is located, click Insert.
Click the file then Insert.
To embed or link an object in Publisher:
On the Insert menu, click Object
In the dialog box displayed, click Create from file.
Click the Browse button to select the file you want to link or embedded.
To create a link, make sure that the link checkbox is checked √. For embedding leave the box unchecked.
Click OK.
Editing text and graphical objects
Deleting text and text objects
One may want to delete some text or an entire text object.
To delete text in Publisher:
Click the Text tool and highlight text.
Press Delete or Backspace key on the keyboard.
To delete a text object:
Click the Pointer tool then click the text frame
Press the Delete or Backspace key.
Copying and moving a block of text.
- Copying involves creating an exact copy of a word, sentence or paragraph in another place within the
document or in another document (duplicate).
- Moving involves removing a character, word or paragraph from one location to another place in the same
document or to another document (no duplicate).
To copy or move a block of text in Publisher:
Select the block of text.
On the Edit menu, click Copy or Cut
Click where you want to paste the text.
From Edit menu, click Paste.
Spelling and grammar checker.
- It is an inbuilt tool that helps the user to correct spelling errors and incorrect grammar structures. However,
the checker can only recognize errors of those words whose correct spelling is in its dictionary. A correctly
spelt word used wrongly cannot be detected hence the document should be proofread just before and after
printing.
To spell check a publication in Publisher:
On the Tools menu, point to Spelling, and then click Spelling.
In the Check spelling dialog box, mark Check all stories.
Replace or Ignore the misspelled words.
Click OK to close spelling check complete message box.
Find and Replace
Find helps one to search for a particular word in a document. It automatically locates the word or phrases of
interests.
If one wants to replace a word or phrase, use the replace option
To search for a particular word or phrase in Publisher:
On the Edit menu, click Replace, to display dialog box.
In the Find What box, type the word(s) to be searched.
In the Replace with box to type the word(s) to replace the found word(s)
Click Find Next or Replace/Replace All button.
Editing a publication layout
To edit a publication layout in PageMaker or Publisher
Switch to the master pages.
Make the necessary changes, and then switch back to foreground pages.
Editing graphical objects
Graphical objects are clip arts and pictures. One can edit object attributes such as size, position, color, brightness,
contrast etc.
To edit object attributes in Publisher.
Select the object
Display picture toolbar.
Adjust the required attributes.
AGHS © 2010 DESKTOP PUBLISHER NOTES COMPUTER STUDIES Page 5
FORMATTING A PUBLICATION
Formatting refers to applying special effects or attributes to the layout, text and graphical objects.
Text formatting
To format text in a Publisher:
Highlight the text to format
On the formatting toolbar, choose font style, sixe, and other attributes.
Superscript and Subscript
To format text to superscript or subscript
1. Highlight the text.
2. On the Format menu, select Font. From the Font dialog box mark the Superscript or Subscript.
3. In the dialog box click Superscript, and then Click OK.
Paragraph and page formatting
Paragraph formatting involves aligning text, indenting, adding column guides, inserting headers and footers.
Inserting column guides.
By default, a page is made up of one column.
To create more than one column in Publisher:
On the Arrange menu, click Layout Guides,
In the dialog box, enter the number of columns required, and then click OK.
Headers and Footers
- Headers are lines of text, page numbers or dates that appear at the top of every page.
- Footers are lines of text, page numbers or dates that appear at the bottom of every page.
To insert headers and footers in a Publisher:
Switch to master pages.
On the View menu, click Header and Footer
To insert page numbers, click Page Numbers from the Insert menu
To insert text, create a text frame then type in text.
Formatting graphical objects
Fill and stroke
- Filling refers to applying a solid color or patterns to a drawing, while stroke refers to line style.
To apply background and stroke in Publisher:
o Select the object
o On the Format menu, click AutoShape.
o In the Format AutoShape dialog box, select Fill and color properties, then click OK.
NB: To make the fill transparent, slide the transparency button or press Ctrl + T.
Rotating an object
To rotate an object in Publisher:
Select the object
Hold down Ctrl key and drag the green rotation handle.
Alternatively, on the Arrange menu, point to Rotate of Flip.
On the Dialog box select the option you want.
Rotate the handle in clockwise or anticlockwise direction.
Arranging objects
If an object is hidden by another, you need to rearrange them in order of priority.
To arrange objects in Publisher:
Select the object you wish to bring to the front or send to the back.
On Arrange menu from the Menu bar, point on Order from the resulting pull down menu.
Select an Arrange option from the list.
Cropping graphical objects
Cropping refers to hiding unwanted parts of a graphical object particularly in a picture.
To crop an object:
Select the object
On the picture toolbar, click the crop tool.
Position the cropping tool over placeholder on the object and drag inwards.
Grouping objects
- One can group objects by combining them, so that one can work with them as though they were a single
object. Grouped objects can be rotated, flipped, and re-sized as a single unit. One can also change the
attributes of all objects in a group at one time e.g. fill color.
- Grouping makes work easier when developing complex drawings. One can always ungroup a group of
objects any time you want and then ungroup them later.
To group objects in Publisher:
a. Hold down Shift key as you click each object.
AGHS © 2010 DESKTOP PUBLISHER NOTES COMPUTER STUDIES Page 6
b. Right click the selections, and then click Group.
c. Alternatively, hold down Shift or Ctrl key as you click each object.
d. Click Arrange menu from the menu bar, from the pull down menu select Group or Ungroup or Regroup.
NB: One can press Ctrl + Shift + G for grouping
Press Ctrl + Shift + G for ungrouping.
Wrapping text around an object
Picture and text objects can share the same space in different ways. In relation to the object, text can be placed
above, below, behind, around, on top or in spaces around the picture.
Select both object placed on the text frame.
On the Arrange menu, point on Text Wrapping.
Select the type of text wrapping you want to use for example; square, tight, through, top and bottom, none,
edit wrap points etc.
Alternatively, select both object placed on the text frame.
On Format menu, click Picture.
In the Dialog box, click Layout tab, then select a wrapping style.
Specify other wrapping options, and then click the OK button.
Working with tables
Tables are used to put information in columns, such as price lists, currency rates, table of contents for a newsletter
etc. A table looks different from a text frame as it contains cells and grid lines to mark the cell area.
Note:
Unlike the Word Processing tables, Publisher tables do not have the Field Calculate capability.
Creating a table
Select Table from the menu bar. From the pull down menu, select Insert and then Table.
Resize the table to the desired size.
To add text into your table, click the cell where you want to add text and start typing.
NB:
When the table is unlocked, the table cell expands to fit the text you type. When the table is locked, and one types
more text than the cell it can hold, the extra text will not be visible. To unlock the table, check the Grow to Fit Text
(see a tick to the left of the option) on the Table menu.
Merging/Splitting Cells in a Table
To merge cells, select the adjacent cells that you want to combine.
On the Table menu, select Merge Cells. The content of each cell will appear in the merged cell.
To split cells, select the cell, and on the Table menu, choose Split Cells.
Adding Boarders, Fills and Effects to a table.
Select the cells you want to change.
On the Format menu, click Table. The Format Table dialog box appears.
To add, remove or change a line border, select Line and choose the option you want, then click OK
To add colors or patterns to cells or entire table, select the cells/table, click the arrow next to the Colour
box and then select the options you want.
To make cells transparent, go to Fill, and move the Transparency slider to get the percentage of
transparency you want.
Deleting a table.
To delete a table select the table. Go to the Table menu and choose Delete. Choose Table.
Printing a publication: -
To print a publication in Publisher:
i. On the File menu, Click Print.
ii. Click Properties button to set print options.
iii. In Print Dialog box, click the Advanced Print settings.
iv. Click the separation tab.
v. In the Output list, click Separations to process cyan, magenta, yellow and black separately.
vi. Finally click Ok to start printing.
END OF TOPIC
AGHS © 2010 DESKTOP PUBLISHER NOTES COMPUTER STUDIES Page 7
You might also like
- How To Make Gold Methods For Transmutation of Silver To GoldDocument19 pagesHow To Make Gold Methods For Transmutation of Silver To Goldaaaa100% (5)
- Computer Basics PDFDocument17 pagesComputer Basics PDFTushar Rana100% (1)
- Computer Basics Basics2Document43 pagesComputer Basics Basics2tes100% (1)
- Terminology Mouse Clicks Menus File Extensions Hardware: Windows BasicsDocument7 pagesTerminology Mouse Clicks Menus File Extensions Hardware: Windows BasicsTimothy John SomcioNo ratings yet
- Switch and RouterDocument7 pagesSwitch and RouterIsmail Hossain RanaNo ratings yet
- Use An Enterprise Information SystemDocument7 pagesUse An Enterprise Information SystemMarshalee WillisNo ratings yet
- Hardware Function - CpuDocument42 pagesHardware Function - CpumyzalNo ratings yet
- Pseudo CodeDocument17 pagesPseudo CodekalladyNo ratings yet
- Data and Information: What Is A Computer?Document6 pagesData and Information: What Is A Computer?Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Wireline PCE PDFDocument56 pagesWireline PCE PDFMuhammad ShahrukhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Introduction To ComputingDocument16 pagesLecture 02 Introduction To ComputingHuzaifa QamashNo ratings yet
- Ms0750 Vanguard 3-Cylinder Ohv LC Gasoline Briggs & StrattonDocument132 pagesMs0750 Vanguard 3-Cylinder Ohv LC Gasoline Briggs & StrattonKenn Ferro80% (5)
- Energy Audit of Cooling Water SystemDocument39 pagesEnergy Audit of Cooling Water Systemmadan karkiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming LanguageDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Programming LanguageDr Narayana Swamy Ramaiah100% (1)
- 01 Computer LiteracyDocument19 pages01 Computer LiteracyGadi Fosta100% (1)
- Cve40001 Kho+lee+tan PVD Sem1 2015Document29 pagesCve40001 Kho+lee+tan PVD Sem1 2015alexheeNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Predictions and Risk Assessment in Oilfield Production SystemsDocument37 pagesCorrosion Predictions and Risk Assessment in Oilfield Production SystemsMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Storage Devices and Multimedia DevicesDocument25 pagesStorage Devices and Multimedia DevicesJoevertVillartaBentulanNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument37 pagesSoftwareAnjanette BautistaNo ratings yet
- All Rights Reserved: Ateneo Computer Science Center Ateneo de Davao UniversityDocument59 pagesAll Rights Reserved: Ateneo Computer Science Center Ateneo de Davao Universityapi-19939410No ratings yet
- Basics of ComputerDocument19 pagesBasics of Computerrahul upadhyayNo ratings yet
- HCI Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesHCI Lecture NotesGerald Valdez100% (1)
- Introduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanDocument83 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanSadhika KatiyarNo ratings yet
- CBSE - VI - Computer Studies - OpenShot Video EditorDocument23 pagesCBSE - VI - Computer Studies - OpenShot Video EditorAhaan DoshiNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Module 1 Week 1Document34 pagesQuarter 1 Module 1 Week 1minaNo ratings yet
- Android 01 Mobile Computing - DoneDocument57 pagesAndroid 01 Mobile Computing - DoneIT ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Tim 5245 13 003 Eng 110Document440 pagesTim 5245 13 003 Eng 110Scenic777No ratings yet
- Letter-Writing: Mail Merge Rubric: Category 4 3 2 1Document1 pageLetter-Writing: Mail Merge Rubric: Category 4 3 2 1Eduardo Talaman100% (1)
- AndroidDocument12 pagesAndroidSergio Darío LópezNo ratings yet
- CSC0100 Ch4-Using A Web BrowserDocument9 pagesCSC0100 Ch4-Using A Web BrowserWussan MalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DesktopPublishingDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - DesktopPublishingSreekanth RallapalliNo ratings yet
- Desktop Publishing Notes - Part IiDocument2 pagesDesktop Publishing Notes - Part IiDos SinNo ratings yet
- Computer Repair and MaintenanceDocument2 pagesComputer Repair and Maintenanceclinton koechNo ratings yet
- Course Notes - Unit 1 PDFDocument4 pagesCourse Notes - Unit 1 PDFMichael SkyersNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Understanding and Skills: Instructor: Doug Bloodworth EmailDocument61 pagesBasic Computer Understanding and Skills: Instructor: Doug Bloodworth EmailSohelNo ratings yet
- 01 CSA Assignment QuestionsDocument3 pages01 CSA Assignment QuestionsSurendran RmcNo ratings yet
- Translator Program PDFDocument3 pagesTranslator Program PDFCONSTANTINOS100% (1)
- Name: - Russell D'souza F.Y.BMS Roll No.: - 17 Introduction To Computers Submitted To: - Miss Vileena 2013-2014 SignDocument17 pagesName: - Russell D'souza F.Y.BMS Roll No.: - 17 Introduction To Computers Submitted To: - Miss Vileena 2013-2014 SignRussell D'souza100% (1)
- Handouts 07Document9 pagesHandouts 07ryan abanicoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksTanmoy C0% (1)
- 079 CMT pr-1Document8 pages079 CMT pr-1Aarunain PandavdraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Computer System (2) (1) - 1629266582Document61 pagesUnit 1 Computer System (2) (1) - 1629266582Nischal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- SS 1 COMPUTER STUDIES 3RD TERM Updated NoteDocument10 pagesSS 1 COMPUTER STUDIES 3RD TERM Updated NoteDAYONo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ComputerDocument3 pagesBasic Concepts of ComputerSunithaNo ratings yet
- Computer ConceptDocument9 pagesComputer ConceptChristelle Joy EusebioNo ratings yet
- Computer Lesson 1Document11 pagesComputer Lesson 1jenchulichaeng blinkueNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument4 pagesComputer HardwareEhnan J LamitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Hardware & SoftwareDocument42 pagesLesson 3: Hardware & SoftwareRosen LPNo ratings yet
- Computer System SoftwareDocument18 pagesComputer System SoftwareRoma Dela Cruz - CayaoNo ratings yet
- The Component of System UnitDocument52 pagesThe Component of System UnitgtNo ratings yet
- Computer Introduction: Diagram Showing Flow of Data in A ComputerDocument53 pagesComputer Introduction: Diagram Showing Flow of Data in A ComputerAnton OkothNo ratings yet
- Peripheral DevicesDocument22 pagesPeripheral DevicesHans Leo LatigayNo ratings yet
- Hard DiskDocument3 pagesHard DiskBILAL ZAFARNo ratings yet
- A Computer Maintenance and Repair A CompDocument15 pagesA Computer Maintenance and Repair A CompEphrem ChernetNo ratings yet
- BMM 111 Chapter 7 Computer Software NotesDocument62 pagesBMM 111 Chapter 7 Computer Software NotesGifted Renny.100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Basic of Operating SystemDocument45 pagesUnit 1 - Basic of Operating SystemTapan RanaNo ratings yet
- Dikshant International School: Project On Computer NetworkingDocument17 pagesDikshant International School: Project On Computer NetworkingkanchanfartiyalaihmNo ratings yet
- Core Hardware NotesDocument27 pagesCore Hardware NotesVishal100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Expansion BusDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Expansion Busapi-3750451100% (1)
- Computer PeripheralsDocument23 pagesComputer PeripheralsscribdNo ratings yet
- Modem TechnologyDocument25 pagesModem TechnologyPrajwal RaoNo ratings yet
- LENS-Basic Computer ConceptsDocument11 pagesLENS-Basic Computer ConceptsDani Jiel MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Multimedia Authoring ToolsDocument45 pagesChapter 01 - Multimedia Authoring Toolstopexsan100% (1)
- Module 2 - Reading5 - ChipsetDocument3 pagesModule 2 - Reading5 - ChipsetChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Computer System Expansion SlotsDocument5 pagesComputer System Expansion SlotsMary MillareNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Mail MergeDocument9 pagesPurpose: Mail MergeZain Tech TipsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Introduction To Programming and C++Document5 pagesLesson Plan - Introduction To Programming and C++Abhishek Singh0% (1)
- Network Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandNetwork Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tcas South Central RailwayDocument61 pagesTcas South Central RailwaySaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Respon KognitifDocument123 pagesRespon KognitifSyaeful GunawanNo ratings yet
- Strong Typing vs. Strong Testing: Bruce EckelDocument2 pagesStrong Typing vs. Strong Testing: Bruce EckelAlejandro RiosNo ratings yet
- Table of IonsDocument2 pagesTable of IonsLucia Jimenez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Manual ION8650Document104 pagesManual ION8650Manuel Lavado SilvaNo ratings yet
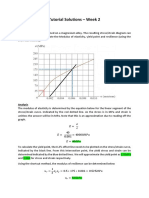
- Week 2 - Tutorial SolutionsDocument4 pagesWeek 2 - Tutorial SolutionsAsian JesusNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics and Animation Journal 1Document51 pagesComputer Graphics and Animation Journal 1templategamingffNo ratings yet
- One Mark in Visual Basic 6.0Document4 pagesOne Mark in Visual Basic 6.0vijayakumar2k9398367% (3)
- Ksksksks Sksksks KSKSKS: Sksks Ksks SKS KSDocument14 pagesKsksksks Sksksks KSKSKS: Sksks Ksks SKS KS박민규No ratings yet
- Lab Report: 1 Title: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesLab Report: 1 Title: ObjectiveRojot Saha100% (1)
- Remed SurveyDocument4 pagesRemed Surveysamantha sarahNo ratings yet
- Module 02 - Preliminary TestDocument43 pagesModule 02 - Preliminary TestTuan AnhNo ratings yet
- Problems SolutionsDocument23 pagesProblems SolutionsMukesh Kumar0% (1)
- New York: STATISTICS IN PRACTICE - CASE 1 - Data For Statistical Analysis Business WeekDocument3 pagesNew York: STATISTICS IN PRACTICE - CASE 1 - Data For Statistical Analysis Business WeekNikita ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Resistance Training Vs Static Stretching Effects.22Document8 pagesResistance Training Vs Static Stretching Effects.22Domenic MicheliNo ratings yet
- A6V10388515 - Ultrasonic Heat and Cooling Energy Meters UH50.. - enDocument54 pagesA6V10388515 - Ultrasonic Heat and Cooling Energy Meters UH50.. - enNestor RomeroNo ratings yet
- 820 User ManualDocument14 pages820 User ManualErick CastilloNo ratings yet
- Verilog Palnitkar Solutions Chapter 7 - 3Document11 pagesVerilog Palnitkar Solutions Chapter 7 - 3Aahnaf Mustafiz 1631698043No ratings yet
- LAYOUT OF THE PHYSICS LABORATORY REPORT Csec - PDF - Experiment - DensityDocument1 pageLAYOUT OF THE PHYSICS LABORATORY REPORT Csec - PDF - Experiment - DensityDavid DillonNo ratings yet
- مُثَلَّث: Maslas Meaning in EnglishDocument1 pageمُثَلَّث: Maslas Meaning in EnglishMr Asraf AllyNo ratings yet
- IJSTR TemplateDocument4 pagesIJSTR TemplateGiridhar ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter4 D E SDocument47 pages3 Chapter4 D E SMarah MalaNo ratings yet