Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solution 1
Uploaded by
JoyeleyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solution 1
Uploaded by
JoyeleyCopyright:
Available Formats
Q) Forbidden energy gap of a semiconductor
a) Increases with temperature
b) decreases with temperature
c) slightly increase and then decrease with temperature
d) does not change with temperature
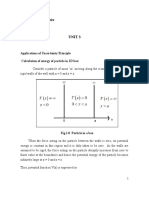
Hint: If N atoms are placed closed to one another, each of their energy level is under the influence of
other atoms their energy levels split into N close sub levels. Fig 1.1 and fig 1.2 depicts the following.
Here are some prerequisites(terms) we need to know before we attempt this question,
Energy band: It is a large number of energy levels closely spaced in a small energy range. These
energy bans arise when the inter atomic distance is reduced to a particular extent.
Types of energy bands
Conduction band: It is a lowest unfilled energy band next to valence band. It is to be noted that the
electrons from the valence band can move to conduction band
Valence band: The highest energy band filled with valence electrons.
Forbidden gap/band: the gap between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the
conduction band.
Fig 1.1
Fig 1.2
Speaking about the forbidden energy gap it can be mathematically represented as,
i.e. ∆𝐸𝑔= C.B (min) – V.B(max) …..eqn[1]
where - ∆𝐸𝑔 represents the forbidden energy gap,
- C.B (min) represents the minimum energy of the conduction band
- V.B(max) ) represents the maximum energy of the valence band.
If we see eqn 1 we can directly come to a conclusion that the energy gap reduces as the
electrons in the valence band gain thermal due to increase in temperature. This is a
mathematical approach.
But if we see this situation theoretically, the interatomic spacing increases when the
amplitude of vibration increase due to increase thermal energy. An increased interatomic
spacing decreases the potential seen by the electrons in the material and hence energy gap
is reduced. A better explanation to this is that splitting into N energy levels only takes place
when atoms are close to one another This extent of splitting gets reduced when the
substance is heated due to the amplitude of vibration of the atoms from their mean
2
𝑎𝑇
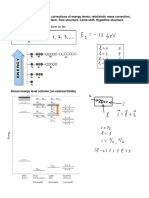
position. 𝐸𝑔 is given as a function of temperature i.e. 𝐸𝑔 (T)= 𝐸𝑔 (0) - 𝑇+𝐵 …..eqn (2)
Where a ,B and 𝐸𝑔 (0) are constant for a given semiconductor.
Here is a graph that represents the above equation (2)
NOTE:
1) The energy gap does not only change when there is a change in temperature, but it also
changes on application of compressive tensile stress or beating of the material.
2) No electrons are occupied in the forbidden gap and hence its name.
You might also like
- Falkner-Collapse Strength and Design of Submarine by D. FalknerDocument16 pagesFalkner-Collapse Strength and Design of Submarine by D. FalknerPiyush JainNo ratings yet
- Astm E2860Document18 pagesAstm E2860Ricardo Martins SilvaNo ratings yet
- Web Tapered Frame Design Based On AISC-ASD 9th, Appendix F Input Data & Design SummaryDocument3 pagesWeb Tapered Frame Design Based On AISC-ASD 9th, Appendix F Input Data & Design SummaryLivian TeddyNo ratings yet
- The Miller Park Crane Collapse DisasterDocument30 pagesThe Miller Park Crane Collapse DisasterAbdulrahman AlkhowaiterNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2-Final-March2021Document10 pagesLecture Notes 2-Final-March2021akshatha m sNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument12 pagesBand Theory of SolidsFitrianiNo ratings yet
- Solution 1 SemiconductorDocument2 pagesSolution 1 SemiconductorÂshútösh KumarNo ratings yet
- LAS Gen - Physics2Q1Week 4 For PrintingDocument6 pagesLAS Gen - Physics2Q1Week 4 For PrintingRae RedillasNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - MSCDocument22 pagesUnit 3 - MSCAndroid DotNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Theory and DevicesDocument105 pagesSemiconductor Theory and DevicesAnonymous AyCl4LNo ratings yet
- Langmuirchild Lab3Document27 pagesLangmuirchild Lab3chatriaayonNo ratings yet
- EE427 Answers June2007 PDFDocument21 pagesEE427 Answers June2007 PDFසම්පත් චන්ද්රරත්නNo ratings yet
- Physical and Biological Aspects of Nanoscience and NanotechnologyDocument44 pagesPhysical and Biological Aspects of Nanoscience and NanotechnologyEstudiante2346No ratings yet
- Module-4 FinalDocument18 pagesModule-4 FinalAbdulkhaliq NasherNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Part 2Document13 pagesUnit 1 - Part 2Kalpana Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- KT MV: Excitation Equilibrium: Boltzmann's EquationDocument4 pagesKT MV: Excitation Equilibrium: Boltzmann's EquationHema AnilkumarNo ratings yet
- Pre TR PDFDocument2 pagesPre TR PDFla anNo ratings yet
- PHY (UNIT 4) (NOTEs)Document27 pagesPHY (UNIT 4) (NOTEs)nileshpatil262004No ratings yet
- Physics Class XI, Part 2: Poisson's RatioDocument4 pagesPhysics Class XI, Part 2: Poisson's RatioQwertyNo ratings yet
- HallDocument29 pagesHallValen SanchezNo ratings yet
- KJHFDocument6 pagesKJHFHoàng Thu ThuỷNo ratings yet
- 5-Tillegg (Fra Kildefil 3) DosimetriDocument14 pages5-Tillegg (Fra Kildefil 3) DosimetriEsther León JorgeNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN MDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN McaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Lecture 07Document26 pagesLecture 07winnieNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Term Two - Solution Class 12thDocument30 pagesImportant Questions Term Two - Solution Class 12thGargi MishraNo ratings yet
- DielectricsDocument61 pagesDielectricsKanda VelanNo ratings yet
- Final HallDocument29 pagesFinal HallUnknownNo ratings yet
- EP - Unit 3 - Semiconductor PhysicsDocument33 pagesEP - Unit 3 - Semiconductor PhysicspukkokignoNo ratings yet
- Temu 1Document36 pagesTemu 1Farida UtamiNo ratings yet
- Bohr's Model, Energy Bands, Electrons and Holes: Dual Character of Material ParticlesDocument30 pagesBohr's Model, Energy Bands, Electrons and Holes: Dual Character of Material ParticlespurseyNo ratings yet
- Material Chapter TwoDocument9 pagesMaterial Chapter TwoTeshale AlemieNo ratings yet
- MIT8 044S13 ps11 PDFDocument9 pagesMIT8 044S13 ps11 PDF*83*22*No ratings yet
- Thermoelectric Effect Peltier Seebeck and Thomson: March 2020Document13 pagesThermoelectric Effect Peltier Seebeck and Thomson: March 2020sannintkdNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDocument28 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsYash Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 ATOMIC STRUCTURE: Electronic Configuration: C E HCDocument5 pagesTopic 12 ATOMIC STRUCTURE: Electronic Configuration: C E HCMoahmed Mahmoud IB15A 363KAGYNo ratings yet
- Lectures 2-3: Energy Levels of The Hydrogen Atom So FarDocument13 pagesLectures 2-3: Energy Levels of The Hydrogen Atom So FardwyphyNo ratings yet
- ThermoelectricDocument12 pagesThermoelectricRama Mahesa RajaNo ratings yet
- Physics 244 Notes Doped SemiconductorsDocument4 pagesPhysics 244 Notes Doped SemiconductorsChichia DollNo ratings yet
- Lectures 4Document19 pagesLectures 4mahmadidres095No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document14 pagesLecture 3mahmadidres095No ratings yet
- Lab 6 Stellar Temperatures and LuminosityDocument9 pagesLab 6 Stellar Temperatures and Luminositymei sya100% (1)
- ThermoelectricDocument13 pagesThermoelectricRama Mahesa RajaNo ratings yet
- APhO2015 Theo Sol1Document9 pagesAPhO2015 Theo Sol1AbhiNo ratings yet
- Conductivity of N and P Type Germanium: 3.1 ObjectiveDocument4 pagesConductivity of N and P Type Germanium: 3.1 ObjectiveSunil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phys 213 ExamDocument12 pagesPhys 213 ExamJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Electricity 7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDocument14 pagesChapter 7 Electricity 7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowvaaniNo ratings yet
- Energyband and Effective MassDocument37 pagesEnergyband and Effective MassMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument34 pagesElectric Chargeglaizamaeodinario5No ratings yet
- Diffuse Double LayerDocument16 pagesDiffuse Double LayerFelipe Cepeda SilvaNo ratings yet
- DoneDocument18 pagesDoner5g2k5b4nhNo ratings yet
- Zeeman EffectDocument10 pagesZeeman EffectSayyed SalmanNo ratings yet
- Free Electron Fermi GasDocument49 pagesFree Electron Fermi Gasqilastudy4No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: A Presentation OnDocument28 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: A Presentation OnPRE027No ratings yet
- Struktur Pita Dan Sifat Listrik Bahan (2015.10)Document38 pagesStruktur Pita Dan Sifat Listrik Bahan (2015.10)readhybsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and Electrode Electrolyte InterfaceDocument42 pagesElectrochemistry and Electrode Electrolyte InterfaceTanshin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance of SemiconductorsDocument7 pagesElectrical Resistance of Semiconductorssaturnsunflower54124No ratings yet
- ThermoelectricDocument13 pagesThermoelectricMurugesan VNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument20 pagesSemiconductormdtayyab212121No ratings yet
- Motion of EletronDocument2 pagesMotion of Eletronshank5No ratings yet
- Free Lect Ron ModelDocument6 pagesFree Lect Ron ModelŞahin AktaşNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2D Engineering ConstantsDocument20 pagesLecture 2D Engineering ConstantsHarish ShridharamurthyNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain GHL Relations Summary (From Lecture 5) : 1D, 2D, 3DDocument6 pagesStress-Strain GHL Relations Summary (From Lecture 5) : 1D, 2D, 3Dعمرو دراغمةNo ratings yet
- Design For Beams: Prepared By: Engr. Jo Ann C. CeledioDocument28 pagesDesign For Beams: Prepared By: Engr. Jo Ann C. CeledioMugiwara SparrowNo ratings yet
- Forces in BeamsDocument30 pagesForces in BeamsywakadeNo ratings yet
- Contact MechanicsDocument14 pagesContact Mechanicsalphading100% (2)
- ME8501 Metrology and MeasurementsDocument14 pagesME8501 Metrology and MeasurementsarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer DR - JamalDocument11 pagesHeat Transfer DR - JamalJuan David FlórezNo ratings yet
- Dws Info Plain Carbon Steel SlicklineDocument1 pageDws Info Plain Carbon Steel Slicklineerwin atmadjaNo ratings yet
- Abaqus TrainingDocument23 pagesAbaqus Trainingmikael bezerra cotias dos santosNo ratings yet
- Pressure VEsselDocument1 pagePressure VEsseltonyl1972No ratings yet
- Sentryglas: Sentryglas Elastic Properties (Sg5000)Document2 pagesSentryglas: Sentryglas Elastic Properties (Sg5000)Larry CastañedaNo ratings yet
- R7410303-Finite Element MethodsDocument4 pagesR7410303-Finite Element MethodssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ideal WorkDocument8 pagesIdeal WorkManjunatha Babu N.sNo ratings yet
- Steel PropertiesDocument2 pagesSteel PropertiesNurul AkmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Stresses and StrainsDocument25 pagesLecture 1 Stresses and Strainssamurai7_77No ratings yet
- Thermistor PracDocument7 pagesThermistor PracSekh AsifNo ratings yet
- Reitveld HighscoreDocument30 pagesReitveld HighscoreJosé M. Rivas Mercury100% (1)
- 507 39 Solutions-Instructor-manual Ch5 SM DRCSDocument35 pages507 39 Solutions-Instructor-manual Ch5 SM DRCSAniket WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Test Certificate: (BS EN 10204 Type 3.1)Document1 pageTest Certificate: (BS EN 10204 Type 3.1)Sachin NambiarNo ratings yet
- Article Welding DistortionDocument9 pagesArticle Welding DistortionAnonymous l5PQDDkNo ratings yet
- Pipe CalculationDocument10 pagesPipe CalculationTrishul Nath PallayNo ratings yet
- Influence of High Cutting SpeedsDocument114 pagesInfluence of High Cutting SpeedsNakarin X SumavongNo ratings yet
- MSC Structural Integrity Academic Year 2017-2018: College of Engineering, Design and Physical SciencesDocument14 pagesMSC Structural Integrity Academic Year 2017-2018: College of Engineering, Design and Physical Sciencesshafahat aliNo ratings yet
- Unloading and Reloading Stress Strain Model For Confined Concrete PDFDocument2 pagesUnloading and Reloading Stress Strain Model For Confined Concrete PDFagnayelNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy of The Concept of Load at A Distance in F.E.A. Codes (Basic Case Studies)Document20 pagesPedagogy of The Concept of Load at A Distance in F.E.A. Codes (Basic Case Studies)Henrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Self Healing MaterialDocument10 pagesSelf Healing MaterialwillypraviantoNo ratings yet