100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views10 pagesEnzyme Electrode
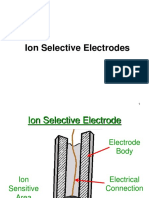
Enzyme electrodes work by immobilizing an enzyme like urease in a gel coating on an ion-selective electrode. Urease catalyzes the breakdown of urea into ammonium ions. A urea electrode dipped in a urea solution will allow urea to diffuse into the gel and be broken down by urease. The produced ammonium ions diffuse to the electrode surface and are detected, resulting in a potential reading proportional to the urea concentration. Enzyme electrodes can be used to measure analytes like urea, glucose, and ethanol through coupling selective enzyme reactions with amperometric electrode processes.
Uploaded by
Atheer abCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views10 pagesEnzyme Electrode
Enzyme electrodes work by immobilizing an enzyme like urease in a gel coating on an ion-selective electrode. Urease catalyzes the breakdown of urea into ammonium ions. A urea electrode dipped in a urea solution will allow urea to diffuse into the gel and be broken down by urease. The produced ammonium ions diffuse to the electrode surface and are detected, resulting in a potential reading proportional to the urea concentration. Enzyme electrodes can be used to measure analytes like urea, glucose, and ethanol through coupling selective enzyme reactions with amperometric electrode processes.
Uploaded by
Atheer abCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Enzyme Electrodes
- Classification of ISEs
- Enzyme Electrodes Overview
- Hydrolysis of Urea
- Measurement of Urea Hydrolysis
- Preparation of Enzyme Electrode
- Enzyme-Based Sensors
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Application of Enzyme Electrodes