Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud
What If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud
Uploaded by
Minhh KhanggOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud
What If Fraud? Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud
Uploaded by
Minhh KhanggCopyright:
Available Formats
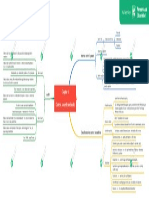
Can be channelled through the accounts in a number of ways
Company “A” wishes to record $100,000 in fictitious sales to a non-existing Fictious sales
customer. The initial accounting entry is debit (increase) accounts receivable and
credit (decrease) sales for $100,000
Failure to record all expenses accurately will inflate the reported profit figure Understanding expenses
Deliberate miscounting at inventory courts
Returns to suppliers may not be recorded Overvaluation of inventory
Deliveries to customers may be omitted from the books
Intentional misrepresentation
Cut- off dates
Manipulation of year-end events
Delaying the recording of pre-year-end purchases of goods not yet delivered can
achieve the same objective
Applying incorrect rates or inconsistent policies Manipulation of depreciation figures Distribute too much profits to shareholders
Write off aged receivables Irrecoverable debt policy may not be enforced Retained profits will be lower than believed
Overstated results
Investors making decisions based on inaccurate information
Incorrect decisions will be made
Members of payroll department miscalculate selected payslips Intentional misrepresentation Suppliers will extend credit without knowing the financial position of the company
External employees claiming overtime for hours which they did not really work Reduced to inverstors may be reduced unnecessary
Payroll fraud
The fraudster sets up a bank account in the bogus name and collects the extra cash Understated results The negative publicity can damage the business
themselves Systems for Legal consequences
Theft from petty cash What if fraud? detecting and
Lower profits
May easily go unnoticed Theft of cash prevent fraud
Small money taken at intervals Immediate financial implications Less cash or fewer asset Returns to shareholders are likely to fall
Employees may pilfer items of inventory Net asset position is weakened
Too insignificant to have any serious impact on results or long-term performance Theft of inventory Removal of funds or assets from a business
Ex: Employees taking office stationary Barings
Long-term effects on company performance
The theft of cash or checl receipts Reduction in working capital
Teeming and lading Must be an integral part of corporate strategy
Popular in the sales ledger area Priortising prevention
Key part of managing business risks in general
Bogus orders are set up, and goods are depatched on credit
Fictitious customers Emphasising ethics Ex: Having formal codes of ethics which employees are required to sign
The employee must have responsibilty for taking goods orders as well as the authority
to approve a new customer for credit Recruitment procedures Ex: Checking the information and referrences provided by applicants
Ex: a sale manager or director could reduce the price charged to a customer in
return for a cut of the saving Personnel controls
Collusion with customers
Ex: The employee suppress invoices or underrecord quantities of depatched goods Removal of funds or assets from a business Training and awareness
on delivery notes
Ex: Staff collude with suppliers, who issue invoices for larger quantities of goods than
Segregation of duties
were actually delivered
Paying for goods not received Implications
of fraud for Appropriate Ex: Seperate documents used to record sales order, despatch, delivery and invoice
Achieved by overdepreciating the relevant asset documentation sales
Disposal of assets to employees the
Ex: An employee arrange to buy a car as the company asset for personal use organisation Limitation controls
Quite difficult to prove
Bogus supply of goods and services Physical security Ex: Keeping tangible assets under lock and key
Ex: Senior staff falsely invoice the firm for the supply of consultancy services
Ailing companies may raid the pension fund and steal assets to use as collateral in
Authorisation policies Ex: Requiring written authorisation by a senior member of staff
obtaining loan finance Ex: Independent checks
Misuse of pension funds or other assets
Standard procedures
Company assets can be transferred to the fund at significant overvalueations Ex: Wages/payslips must be collected in person
Management teams will set budget and targets Ex: Access control
Meeting budgets/target performance measures Computer security
Ex: Emplyees siphon off and pocket any profits in excess of the target Ex: Segrgation of duties
Ex: Incorrect descriptions of items and use of compensating debits and credits
Manipulation of bank reconciliations and cash books
Fraudulent activities go undetected by make a reconciliation work frequently
You might also like
- Financial Statements Meaning and CharacteristicsDocument64 pagesFinancial Statements Meaning and CharacteristicsAbhishek Sinha100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Comparative Analysis of Financial Performance of Zomato: A Ratio Analysis ApproachDocument49 pagesProject Report ON Comparative Analysis of Financial Performance of Zomato: A Ratio Analysis Approachsudhanshu jeevtani100% (5)
- Trust DeedDocument11 pagesTrust Deednaastitvam100% (1)
- Business Analysis and Valuation 3 4Document23 pagesBusiness Analysis and Valuation 3 4Budi Yuda PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Tesla Report - A Detailed Financial Ratios AnalysisDocument18 pagesTesla Report - A Detailed Financial Ratios AnalysisKhubaib Malik100% (1)
- Finance Dossier FinalDocument90 pagesFinance Dossier FinalHarsh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For ManagerDocument202 pagesAccounting For ManagerKHAWAJA MUHAMMAD HUZAIFA100% (1)
- Kank CH 14v14Document20 pagesKank CH 14v14Nida NaseerNo ratings yet
- Korean Business Dictionary: American and Korean Business Terms for the Internet AgeFrom EverandKorean Business Dictionary: American and Korean Business Terms for the Internet AgeNo ratings yet
- Intermediatefinancialaccounting2018b PDFDocument583 pagesIntermediatefinancialaccounting2018b PDFNeil MarceloNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review: FABM 2: Recording Phase: Answer KeyDocument9 pagesPointers To Review: FABM 2: Recording Phase: Answer KeyMaria Janelle BlanzaNo ratings yet
- RICS Due Diligence Guidance NoteDocument24 pagesRICS Due Diligence Guidance NoteBagus Deddy Andri0% (1)
- Reading 18 - Evaluating Quality of Financial ReportsDocument10 pagesReading 18 - Evaluating Quality of Financial ReportsJuan MatiasNo ratings yet
- Revised Business and Profession - For StudentsDocument77 pagesRevised Business and Profession - For Studentsdevkinger1212No ratings yet
- Problems On Profit Prior To IncorporationDocument18 pagesProblems On Profit Prior To Incorporationcsneha0803No ratings yet
- Unit III Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary EcnomiesDocument6 pagesUnit III Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary EcnomiestjasonkiddNo ratings yet
- Business Income Sell Sheet 12.08Document2 pagesBusiness Income Sell Sheet 12.08Abdullah AljammalNo ratings yet
- 3 - Users of Accounting InformationDocument17 pages3 - Users of Accounting Informationdelacruz.kristinaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 - First HalfDocument24 pagesLec 8 - First HalfNidus PhrykeNo ratings yet
- Excess Earnings Time To GoDocument5 pagesExcess Earnings Time To GoAyan NoorNo ratings yet
- David Henry - Fuzzy NumbersDocument7 pagesDavid Henry - Fuzzy NumbersKarthikNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument9 pagesAccounting NotesJerusha ENo ratings yet
- AF W09 - Financial Statement Fraud - ENGDocument17 pagesAF W09 - Financial Statement Fraud - ENGjokitugasbro.idNo ratings yet
- 1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 11 Acc FinalDocument4 pages1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 11 Acc FinalsiyabongaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bookkeeping 1Document63 pagesIntroduction To Bookkeeping 1Mjhane Herrera BattungNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Module 12: Errors and Irregularities in The Transaction Cycles of The Business EntityDocument35 pagesGroup 4: Module 12: Errors and Irregularities in The Transaction Cycles of The Business EntityApril Joy ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementDocument2 pagesFinancial StatementJeftonNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledege in AccountingDocument6 pagesBasic Knowledege in AccountingJessa Mae tapicNo ratings yet
- End of Term RevisionDocument12 pagesEnd of Term Revisionamarashah182No ratings yet
- New IB BM Book (Dragged) 13Document1 pageNew IB BM Book (Dragged) 13celinejaaloukNo ratings yet
- Nfo Presentation DSP Quant FundDocument26 pagesNfo Presentation DSP Quant FundPrajit NairNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Doubtful AccountsDocument3 pagesEstimation of Doubtful AccountsClar AgramonNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Cycles and Analysis - Course PresentationDocument53 pagesCash Flow Cycles and Analysis - Course PresentationKoko BarakhianNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Financial ModelsDocument1 page7 Types of Financial Modelsofficial.waqaslatifNo ratings yet
- ACC 108 - Lecture 6Document40 pagesACC 108 - Lecture 6Shivati Singh KahlonNo ratings yet
- 9 CMA Rev. Cash Flow StatementDocument15 pages9 CMA Rev. Cash Flow StatementSakshiNo ratings yet
- Receivables: Accounts ReceivableDocument2 pagesReceivables: Accounts ReceivableKristalen ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Chapter 9: Accounts Receivable: Classification of ReceivablesDocument2 pagesFinancial Accounting Chapter 9: Accounts Receivable: Classification of ReceivablesMay Grethel Joy PeranteNo ratings yet
- Release Overview Financials 23B - V2.3Document28 pagesRelease Overview Financials 23B - V2.3davidjqNo ratings yet
- Rule-Based Investing According To Good Investing PrinciplesDocument26 pagesRule-Based Investing According To Good Investing Principlesrchawdhry123No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ABM1 - Q4 - LAS1 DRAFTDocument17 pagesFundamentals of ABM1 - Q4 - LAS1 DRAFTSitti Halima Amilbahar AdgesNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Module 12: Errors and Irregularities in The Transaction Cycles of The Business EntityDocument6 pagesGroup 4: Module 12: Errors and Irregularities in The Transaction Cycles of The Business EntityApril Joy ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Ghillyer6e PPT Ch02Document19 pagesGhillyer6e PPT Ch02Cuong VUongNo ratings yet
- Earnings ManagementDocument20 pagesEarnings ManagementSreehari R100% (1)
- Chapter 03 Solutions ManualDocument75 pagesChapter 03 Solutions ManualElio AseroNo ratings yet
- Theory Unit 2Document31 pagesTheory Unit 2Midhuha MumthazNo ratings yet
- Managing Investing Buying and Selling TaxationDocument4 pagesManaging Investing Buying and Selling Taxationwan erNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems - Contemporary View Integration of Quantitative and Qualitative DataDocument5 pagesAccounting Information Systems - Contemporary View Integration of Quantitative and Qualitative DataMichelleOgatisNo ratings yet
- Module 14Document3 pagesModule 14AstxilNo ratings yet
- Fixed Asset Controls and Reporting FinalDocument4 pagesFixed Asset Controls and Reporting FinalranjitNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Yona 1Document25 pagesFinal Exam Yona 1HazemNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 3 Current AssetDocument46 pagesPertemuan 3 Current AssetJason wibisonoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Essentials Chapter 1 SynthesisDocument3 pagesAccounting Essentials Chapter 1 SynthesisdaraNo ratings yet
- Analyzing AssetsDocument23 pagesAnalyzing AssetsSyed Muhammad Ali OmerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2:: Learning Objectives Key Learning PointsDocument1 pageUnit 2:: Learning Objectives Key Learning PointsSitakanta AcharyaNo ratings yet
- 03 Module ABM502Document9 pages03 Module ABM502Leodian Diadem MercurioNo ratings yet
- Dividends and Retained EarningsDocument1 pageDividends and Retained EarningsxxxNo ratings yet
- BT PPTs AllDocument213 pagesBT PPTs AllSanaiya JokhiNo ratings yet
- Abm 1-W6.M2.T1.L1Document6 pagesAbm 1-W6.M2.T1.L1mbiloloNo ratings yet
- ReceivablesDocument46 pagesReceivableswarsimaNo ratings yet
- Sector Matrices - Real Estate (Hospitality)Document124 pagesSector Matrices - Real Estate (Hospitality)Renneth Ena OdeNo ratings yet
- FABM2 (1st)Document3 pagesFABM2 (1st)7xnc4st2g8No ratings yet
- Notes 1: "Accounting Is The Language of Business."Document4 pagesNotes 1: "Accounting Is The Language of Business."Krissha GalonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document6 pagesChapter 15Joy RubioNo ratings yet
- Transactions Account Debited CreditedDocument8 pagesTransactions Account Debited CreditedH O P ENo ratings yet
- Borrelli Walsh - 20191111 - Due Diligence For Emerging Markets What WorksDocument3 pagesBorrelli Walsh - 20191111 - Due Diligence For Emerging Markets What WorksImroni PisesaNo ratings yet
- FTU Creative DevelopmentDocument2 pagesFTU Creative DevelopmentMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- THUEDocument5 pagesTHUEMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document1 pageChapter 6Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Social ResponsibilityDocument1 pageCorporate Governance and Social ResponsibilityMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- The Role of Accounting: Financial Accounting Vs Management AccountingDocument1 pageThe Role of Accounting: Financial Accounting Vs Management AccountingMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Indentifying and Preventing Fraud: Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud What If Fraud?Document1 pageIndentifying and Preventing Fraud: Systems For Detecting and Prevent Fraud What If Fraud?Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Technology: Has Separated Legal Personality From Its Owners (Shareholders)Document1 pageTechnology: Has Separated Legal Personality From Its Owners (Shareholders)Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Contractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersDocument1 pageContractual Relationship: Business Organisation StakeholdersMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Business Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Document1 pageBusiness Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Inflation: The Macroeconomic EnvironmentDocument1 pageInflation: The Macroeconomic EnvironmentMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- SHUBHANGI-TM2120309 Siyaram Silk Mills LimitedDocument13 pagesSHUBHANGI-TM2120309 Siyaram Silk Mills LimitedShubhangi KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam - Part 3: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesPractice Exam - Part 3: Multiple ChoiceAzeem TalibNo ratings yet
- Colegio de La Purisima Concepcion: School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas CityDocument5 pagesColegio de La Purisima Concepcion: School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas CityJhomel Domingo GalvezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Problem 7Document3 pagesChapter 7 Problem 7Pamela PerezNo ratings yet
- Sritex Corporate Report 2017Document52 pagesSritex Corporate Report 2017Fitri LestariNo ratings yet
- Self Storage 7Document13 pagesSelf Storage 7RobNo ratings yet
- CapmDocument3 pagesCapmTalha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Mountain Tourism in MontenegroDocument2 pagesMountain Tourism in MontenegroElena CosciucNo ratings yet
- Somya Amritanshu - Arcpa1206b - Q3 - Ay202223Document2 pagesSomya Amritanshu - Arcpa1206b - Q3 - Ay202223Sourabh PunshiNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Perspectives For 21st Century RefineriesDocument5 pagesHydrogen Perspectives For 21st Century Refineriesonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- MIS205 MMB NSU Lecture 1Document33 pagesMIS205 MMB NSU Lecture 1Shàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document19 pagesJurnal 1SekarNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Development of Ethiopia's Financial SectorDocument14 pagesThe Structure and Development of Ethiopia's Financial SectorWondaferahu Mulugeta86% (7)
- 아이엘츠 숙제Document2 pages아이엘츠 숙제agitongtong1No ratings yet
- Quantitative Ability Questions With SolutionsDocument135 pagesQuantitative Ability Questions With SolutionsRam KeserwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BecDocument11 pagesChapter 3 BecStephen ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Question CMA June 2019Document6 pagesQuestion CMA June 2019rumelrashid_seuNo ratings yet
- Investment in Associates (PAS 28) : Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsDocument6 pagesInvestment in Associates (PAS 28) : Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsMeg sharkNo ratings yet
- Finance & Accounts SectionDocument4 pagesFinance & Accounts SectionSheraz gondalNo ratings yet
- BetasDocument10 pagesBetasVilmaCastilloMNo ratings yet
- Profitability Analysis of Prism CementDocument60 pagesProfitability Analysis of Prism Cementvickram jainNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow ModelDocument7 pagesCircular Flow ModelshaheenNo ratings yet
- Iran Power Generation IndustryDocument162 pagesIran Power Generation IndustrysertackcdgNo ratings yet