Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CamScanner 2021-08-08 14.57
CamScanner 2021-08-08 14.57
Uploaded by
Ayuzawa Ken0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views8 pagesCamScanner 2021-08-08 14.57
CamScanner 2021-08-08 14.57
Uploaded by
Ayuzawa KenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
C
‘Trial Rosli Dhoby P2 2020
Section A [15 marks}
1. ‘The diagram below shows the Bor-Haber eyele for the formation of sodium fluoride.
S74 mot!
Na(s) + '4E\(2) ———*_ Nas)
+107 KI mot | sr U
Nate) Fie) 428 ks mor!
49613 mot"! |
Na‘) + F®)
2. The radius and charge of each of six ions are shown in the table.
[ton Y g we [x Y 2
[Redius(nm) [oa os joss joss joss | 0.5
‘The ionie solids JX, LY and MZ are of the same lattice type. What is the correct order of their lattice energies
placing the one with the most exothermic first?
A IX>LY>MZ
B JX>MZ>LY
© LY>MZ>IX
D MZ>JX>LY
@ rr diagram show the apparatus for an electrolytic experiment of cells 1, Il, and III connected in series. What
‘are the products formed at the anodes of each cell?
carton
80, Ca
Cell Cell Cell MI
A Mass of Cu increases Hp liberated > liberated.
B Mass of Cu increases > liberated Cl liberated
c Mass of Cu decreases > liberated. > liberated
D Mass of Cu decreases > liberated Cl liberated
4, Acdisproportionation reaction occurs when aspecies M' spon
reduction.
2M"(aq) > Maa) + MGS)
“The table below contains E~ data fo
tancously undergoes simult
copper and mercury species.
EAN
CuP(ag) + > Cu") +0.15
Cu'(aq) +" 7 Cuts) +052
He '(aq) +" > He") +0.91
Hg'(aq) +e — He +0.80
Using these data, whi
Both CuCl) and H(1) undergo disproportion:
Only Cu(1) undergoes disproportionation.
Only Hg() undergoes disproportionation.
Neither Cu(l) nor Hg(1) undergoes disproportionation.
ation.
paw
5, Use the data in the table below to answer this question.
‘ch one of the following can be predicted?
EP IV
‘MnO: (aq) + 8H (aq) + Se" —> Mn’*(aq) + 41200)
+ 1,52
C07 (aq) + H4H"(ag) + 6" > 2Cr°*(ag) + THRO)
+133
Fe*(aq) + & —> Fe*(aq)
+077
CPi(aq) +e CP*(aa)
-0Al
Zn**(aq) + 2e° — Zn(s)
= 0.76
‘The most powerful oxidising agent in the table is
Man?*(eq)
Zn(s)
MnO3(aq)
Zn**(aq)
wap
6. ‘The diagram shows how a property of
Na Mg Al Si >
A. Atomic radius
B. Electronegativity
C. First ionisation energy
D. Melting point
vvuain
dati N
ancous oxidation and ,
©
Period 3 elements varies across the period. What is the property?
isu wiul Val
W,
oxides of the elements are given in the table below.
Y and Z are clements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table. The physical and chemical properties of the
Oxide of element
w x
Y Zz
Physical state
Gas Solid
Solid Solid
Solubility in water
Soluble | Soluble
Insoluble | Insoluble
Acidity Basic Acidic | _Amphoteric
‘What could be elements W
w z
A cl Si
B Ss Al
c Na Al
D P Si
8. Which element has the highest first ionisation energy?
A. Aluminium
۩ B. Phosphorus
C. Silicon
D. Sulphur
9. The following table shows the lattice energy and the hydration energy of three sulphate salts X, Y and Z for
the three elements in Group 2 of the Periodic Table.
Sulphate salts Lattice energy/J mot! Hydration energy/kJ mot!
x -2489 -1650
Y -2374 1350
Zz “2484 =1480
Which of the following sulphate salts are arranged according to solubility in decreasing order?
AXZY
BX.Y,Z
@e y.zx
DZXY
10. The properties of three tetrachlorides of elements P, Q and R in Group 14 of the Periodic Table are as follow:
* The tetrachloride of P decomposes when heated and liberates chlorine gas.
© Aci
© Thereis
Which of the following shows the correct arrangement of the elements in order of increasing proton number?
AL QR P
B. P,R,Q
C. P,QR
D. R,QP
ic fumes are liberated when the tetrachloride of Q is added to water
}0 visible change when the tetrachloride of R is added to water.
vvual
cu wiur val
11. Which species is not produced by a redox reaction between solid sodium iodide and concentrated sulphurie\
acid?
A NaySOu
B ELS
ch
D SO»
12. Which statement about astatine is correct?
A. Astatine has a greater electronegativity than bromine
B_ Astatine is a better oxidising agent than bromine
CC Astatine has a greater boiling point than bromine
D_ Astatine has a greater first ionisation energy than bromine
13. The halogens are important chemicals in our daily lives. Which statement about Clz, Brz and Iz is tru
‘A. The halogens can act as both oxidising and reducing agents.
B. The strength of the van der Waals forces increases from Clz to I>.
C. Ch, Brz and Iz are formed when their respective halides react with concentrated H2SOs.
D. Ch, Brand I react vigorously with hydrogen gas in the presence of ultraviolet light.
14. Iron forms a complex ion with the formula (Fe(H2NCHsCH:NH2)2Ch]*. The systematic name of this complex
is
A. Dichlorodiethylenediamineiron(1) ion
B. Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)iron({1) ion
C. Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)iron(III) ion
D. Bis(ethylenediamine)dichloroiron({Il) ion
15,
Melting point/“C
a
—
The graph above shows the melting points of a few transition elements.
Why is the melting point of manganese low?
A. Its electrons are not ready to form metallic bonds
B. Manganese is a metalloid
C. The atoms are not closely packed in the metal lattice of manganese
D. There is a strong screening effect in the atoms of manganese
wiut ual
Section B [/5 marks}
Answer all questions in this section.
16. This question is about lattice energy
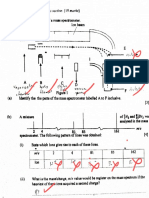
(a) Figure 1 shows a Born-Haber cycle for the formation of magnesium oxide.
Complete Figure I by writing the missing symbols on the appropriate energy levels. [3 marks]
Mg?*(a) + OF(9)
Energy
(6) Table 1 contains some thermodynamic data.
‘Enthalpy change /kJ mot!
Enthalpy of formation for magnesium oxide 602
Enthalpy of atomisation for magnesium +150
First ionisation energy for magnesium +736
Second ionisation energy for magnesium #1450
Enthalpy of atomisation for oxygen 4248
First electron affinity for oxygen 142
‘Second electron affinity for oxygen 4
Table 1
Calculate a value for the lattice energy of magnesium oxide [2 marks]
lattice energy:
vvainicu wit Udl
17. A student set up the cell shown in Figure2, \
fo
Copper. Copper
0.15 mol dav? ~1.0 mol dm?
CuSOs(aq) CuSO,(aq)
Figure 2
(a) The student recorded an initial voltage of +0.16 V at 25°C
(9 Explain how the salt bridge provides an electrical connection between the two solutions. [1 mark]
(i) The standard electrode potential for the Cu2*/Cu electrode is
Cu (aq) +2e—> Cus) B= 40.34 V
Calculate the electrode potential of the left-hand electrode in Figure2.
Electrode potential:
Gii)Both electrodes contain a strip of copper metal in a solution of aqueous Cu2* ions,
State why the lefi-hand electrode does not have an electrode potential of +0.34 V
(1 mark]
(iv) Give the cell diagram for the cell in Figure 2. Include all state symbols, [0 mark}
©
©) When the voltmeter is replaced by a bulb, the E° of the cell in Figure 2 decreases over time to 0,00 V
Suggest how the concentration of copper (Il) ions in the left-hand electrode changes when the bulb is
alight. Give one reason why the E of the cell decreases to 0,00 V [2 marks}
Change in concentration of copper (Il) ions in the left-hand electrode
Reason why the £ decreases to 0.00 V
vvuainicu wiul val
(6) Use data from Table 2 to identify the species that can be used to reduce VOz" ions to VO" in aqueous
solution
Table 2
Electrode half-equation ee/V
‘VO2*(aq)+ 2H"(aq) + e-->VO"(aq) + H20(!) +1.00
Vo™(aq) + 2H*(aq) + e->V"*(aq}+ H20(l) 40.34
Cla{aq) + 2e-2CI-(aq) 41.36
Fe?*(aq) + e->Fe**(aq) 40.77
Zn*(aq) + 2e"->2n(s) 0.76
@ Explain your answer. [2 marks]
Reagent
Explanation
(ii) Heating NHsVOs produces vanadium(V) oxide, water and one other product. Give an equation for the
reaction. {1 mark}
(iii) Venadium(V) oxide is the catalyst used in the manufacture of sulphur trioxide from SO2
Give one equation to show how this reaction occur. [1 mark]
veuainicu wiul Val
Section € [30 marks]
two questions in this section
rable with the following aspect
18. soe
{o) Explain the chemical characteristic of Group 14 elements in periodic T eel
(@ — Uydrolysis of tetrachloride -sguato st
. oa roxide of elements with +2 oxidation state
i) Acidcbase properties of ovide oa with Zoi eal aie
(Wit reference tothe stature and boning, expan Wh . eal
Poi is very unstable.
19
(@) Solution A contains the compound [Cu (OIC
{@ State the type of bonding between the oxygen and hy dro inthis compound. {1 mark]
(7 State why the chloride fons inthis compound are not cons dred to be ligand [1 mark]
(i excess of ammonia was aed toa sample of solution & 10 form solution B.
aoe onic equation forthe reaction that oecurs when solution A is converted into solution B and state
the colour of solution B. [2 marks]
{a Aqueous sodium carbonate was add to anther sample of station ‘Ato forma green solid C.
Identity the green solid C. [imark] ©
(a) Reagent D was aed fo another sample of solution A to form a yellow solution.
Coa engent D and write anionic equation forthe reation that occurs when the yellow solution is
formed from solution A. [2 marks]
Faplain wy colorimetry cannot be used to determine the concentration of solutions containing
[CaCI] In your answer, refer to the electron configuration ofthe metal fon. [2 marks}
(0) in an aqueous solution, Fe" jons act asa catalyst inthe reaetion between T-and S208 ions.
Give one reason why the reaction is slow in the absence of the cataly
Wate balanced equations to show how Fe" ions act as a catalyst for this reaction. [6 mad
20.
(a) Chlorine is used to decrease the numbers of microorganisms in water.
When chlorine is added to water, there is a redox reaction, as shown by the equation
Clot 120 2 HCIO+HCI
(i) Deduce the oxidation state of chlorine in HCIO and HCI [1 mark} |
(i) Give two hal-equations to show the oxidation and reduction processes that oceur in this red |
reaction,
(Gii)Chlorine is reacted with cold, aqueous sodium hydroxide in the manufacture of bleach.
“Give an equation for this reation between chlorine and sodium hydroxile [1 mark]
(iv) Potassium chlorate (VI, KCIO4, is used in fireworks. When potassium chlorate (VII) decompos
produces potassium chloride and oxygen. Give an equation for the decomposition of potassium
[2 marks]
chlorate (VII). Use the data in Table 3 to calculate the enthalpy change for this reaction. [2 marks]
Substance ‘OH i/ Wi mol?
KClOd(s) 434
Kcl(s) -436
(b) Radi a
(b) Radium, a radioactive clement, is
Periodic Table. Compare the thermal stability of radium
located below calcium in Group 2 of thi
plain your answer. [4 marks]
hydroxide with that of calcium hydroxide.
(c) When a 0.6284 g sample of a Group 2 hydroxi
; oup 2 hydroxide, formula M(OH)2.1120 is heated, it is dehydrat
the anhydrous hydroxide M(OH), losing 0.0594 g in the form of steam. Identify the metal _ “me
[5 marks]
|
Vvuainicu witrt val
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 5 6073425760494813727Document6 pages5 6073425760494813727Ayuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell ChemistryDocument8 pagesFuel Cell ChemistryAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell ChemistryDocument8 pagesFuel Cell ChemistryAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- English Muet ListeningDocument3 pagesEnglish Muet ListeningAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Gapped Text 1Document4 pagesGapped Text 1Ayuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STPM Experiment 7 Electrochemistry Faraday S Law Second TermDocument2 pagesChemistry STPM Experiment 7 Electrochemistry Faraday S Law Second TermAyuzawa Ken100% (1)
- Kegiatan Pinjaman Wang Secara Haram Berlaku Berleluasa Kerana Kegiatan Tersebut Mandapat Sambutan Daripada Orang RamaiDocument2 pagesKegiatan Pinjaman Wang Secara Haram Berlaku Berleluasa Kerana Kegiatan Tersebut Mandapat Sambutan Daripada Orang RamaiAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Reading Revision S2S2Document10 pagesReading Revision S2S2Ayuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Perbuatan Memenipulasi Bayi Dan Kanak Not FinishedDocument2 pagesPerbuatan Memenipulasi Bayi Dan Kanak Not FinishedAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Usaha Meningkatkan Mutu Sukan Negara Berhadapan Dengan Pelbagai MasalahDocument1 pageUsaha Meningkatkan Mutu Sukan Negara Berhadapan Dengan Pelbagai MasalahAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Program Orientasi T6 2020Document3 pagesProgram Orientasi T6 2020Ayuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Kestabilan Politik Di Negara Kita Menghadapi Pelbagai CabaranDocument2 pagesKestabilan Politik Di Negara Kita Menghadapi Pelbagai CabaranAyuzawa Ken50% (2)
- Malaysia Perlu Mengorak Langkah Ke Arah Pengunaan Tenaga LestariDocument1 pageMalaysia Perlu Mengorak Langkah Ke Arah Pengunaan Tenaga LestariAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Class: Section A: Working Quoted Appropriate. NameDocument7 pagesClass: Section A: Working Quoted Appropriate. NameAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- CN Ihe Uilipie-C Hoic R Shee: Sub-PartDocument7 pagesCN Ihe Uilipie-C Hoic R Shee: Sub-PartAyuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Edited - Adobe Scan 15 Dec 2020Document4 pagesEdited - Adobe Scan 15 Dec 2020Ayuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- Listening Questions S3SC2Document5 pagesListening Questions S3SC2Ayuzawa KenNo ratings yet
- SEM 1 Trial Sem 1 Set 12Document10 pagesSEM 1 Trial Sem 1 Set 12Ayuzawa KenNo ratings yet