Professional Documents
Culture Documents
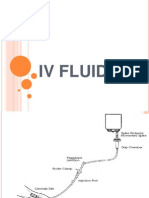
F&E - IV Solutions
Uploaded by
mark OrpillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F&E - IV Solutions
Uploaded by
mark OrpillaCopyright:
Available Formats
F&L Quick Notes: IV Solutions
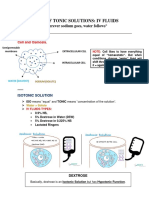
Isotonic solutions
• Definition: when solutions on both sides of a selectively permeable membrane have
established equilibrium or are equal in concentration, they are isotonic.
• Human blood is isotonic thus very little osmosis occurs since isotonic solutions have
the same osmolality as body fluids & thus increase extracellular fluid volume.
Memory Trick:
• Iso-tonic Solutions
• I-so-Perfect (no fluid shift, “I’m so perfect” perfect balance)
• List of fluids:
• 0.9% sódio, chloride (normal saline)
• 5% dextrose in water (DWS)
• 5% dextrose in 0.225% saline (DSW/ 1/4 NS)
• Lactated Ringer’s (LR)
Hypotonic solutions
• Definition: when a solution contains a lower concentration of solute than another
more concentrated solution, then it is a hypotonic solution.
• These solutions have lower osmolality than body fluids.
• They cause the movement of water into cells by osmosis, swelling the cells like a BIG
fat hippo, and therefore should be administered slowly to prevent cellular edema
Memory Trick:
• HypO - tonic
• HippO - tonic = fluid swells the cell like a big hippo
• List of fluids:
• 0.45% sodium chloride (1/2 NS)
• 0.225% sodium chloride (1/4 NS)
• 0.33% sodium chloride (1.3 NS)
Hypertonic solutions
• Definition: when a solution contains a higher concentration of solutes than
another less concentrated solution, then it is a hypertonic solution.
• These solutions have higher osmolality than body fluids
• They cause the movement of water outside the cells by osmosis, making the
cells skinny like a hyper person.
Memory Trick:
• Hyper - tonic
• Hyper person = very skinny cells like a hyper person is skinny
• List of fluids:
• 3% sodium chloride (3% NS)
• 5% sodium chloride (5% NS)
• 10% dextrose in water (D10W)
• 5% dextrose in 0.9% sodium chloride (D5W/NS)
• 5% dextrose in 0.45% sodium chloride (D5W/ 1/2 NS)
• 5% dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s (D5LR)
You might also like
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Hypotonic Hypertonic Isotonic Solutions UsesDocument9 pagesHypotonic Hypertonic Isotonic Solutions UsesImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument15 pagesREPORTMacen OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Programs: Lactated Ringers (Also Known As LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL)Document5 pagesNursing Programs: Lactated Ringers (Also Known As LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL)KiaBlancheTahud100% (1)
- Iv Fluids and Solutions With Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument33 pagesIv Fluids and Solutions With Nursing ResponsibilitiesJennie JalemNo ratings yet
- Types of FluidDocument8 pagesTypes of FluidMohammed A RajabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 NDHDocument3 pagesLecture 1 NDHTricia Jane OpinaldoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1Document25 pagesPharmacology 1Gul NazNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids TheoryDocument13 pagesIV Fluids TheoryFRESY TRI SUGIANTONo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument11 pagesIv FluidsDianna Rose BelenNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Different Types of IV FluidsDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of IV FluidsnicoleNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes: April Love Rivera-Oja, RN-MANDocument56 pagesFluids & Electrolytes: April Love Rivera-Oja, RN-MANAdelin MeroNo ratings yet
- 1IV FluidDocument31 pages1IV FluidManeesha KhalseNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology IV FluidDocument44 pagesPharmacology IV FluidmelaniNo ratings yet
- Types of IV FluidsDocument6 pagesTypes of IV Fluidsharrisburrrg100% (1)
- Parenteral Fluid Therapy: Types of Intravenous SolutionDocument18 pagesParenteral Fluid Therapy: Types of Intravenous SolutionKathleen Joy Costales Magtanong100% (1)
- IV Infusion SolutionDocument8 pagesIV Infusion SolutionmohammedNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1 PH and Buffers and #2Document23 pagesExperiment #1 PH and Buffers and #2Poker Face--No ratings yet
- Refreshing " Fluid Therapy"Document28 pagesRefreshing " Fluid Therapy"Bangun Cholifa nusantaraNo ratings yet
- 1 Water Its Properties PDFDocument27 pages1 Water Its Properties PDFAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Iv SolutionsDocument12 pagesIv SolutionsRinalyn BalderramaNo ratings yet
- V Solutions May Come in Different FormsDocument4 pagesV Solutions May Come in Different FormsJhade RelletaNo ratings yet
- What Are IV FluidsDocument5 pagesWhat Are IV FluidsRegine Mae Encinada100% (1)
- What Are IV FluidsDocument7 pagesWhat Are IV FluidsKATHLEEN MARIE MONTA�ONo ratings yet
- Types of SolutionDocument3 pagesTypes of SolutionfwarqueenNo ratings yet
- SAS 9 Parenteral TherapyDocument41 pagesSAS 9 Parenteral Therapyjenet soleilNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids and Solutions GuideDocument16 pagesIV Fluids and Solutions GuideMostafa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Isotonic, HypotDocument4 pagesIsotonic, HypotSannyjale BaldozaNo ratings yet
- 5% Dextrose in Water-A Carbohydrate Solution That: Key TermsDocument3 pages5% Dextrose in Water-A Carbohydrate Solution That: Key Termsamoosh_amani725No ratings yet
- 5 Lim - Types of IV FluidsDocument16 pages5 Lim - Types of IV FluidsSamantha Ishi LimNo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument92 pagesIv Fluidsakish4u86% (7)
- IV Fluids and Solutions Guide & Cheat Sheet (2023 Update) - NurseslabsDocument16 pagesIV Fluids and Solutions Guide & Cheat Sheet (2023 Update) - NurseslabsKc Mea Paran BorjaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 WaterDocument34 pagesChap 2 WaterGlidilyn Castillo BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument6 pagesIv FluidsCrishara PalomoNo ratings yet
- Types of SolutionDocument10 pagesTypes of Solutionhady920No ratings yet
- IV Fluid TherapyDocument2 pagesIV Fluid TherapylisalynnleeNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesFluids and Electrolytespaulzilicous.artNo ratings yet
- Intravenous FluidsDocument3 pagesIntravenous FluidsVivian Beth A. NaragNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy: Part o NeDocument68 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy: Part o NeMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Fluids Electrolytes Acid BaseDocument66 pagesFluids Electrolytes Acid Basechristianjoygallos9No ratings yet
- BIO 103 Lecture 4Document20 pagesBIO 103 Lecture 4Demi RoseNo ratings yet
- TonicityDocument6 pagesTonicitypavelbdsNo ratings yet
- Three Main Types of IVF: Isotonic Fluids Hypotonic Fluids Hypertonic FluidsDocument9 pagesThree Main Types of IVF: Isotonic Fluids Hypotonic Fluids Hypertonic FluidsIrina Luciana DumitriuNo ratings yet
- Aquino, Christian Jufers G. BSN3-NCA2: IsotonicDocument2 pagesAquino, Christian Jufers G. BSN3-NCA2: IsotonicJuf's Aquino IINo ratings yet
- Parenteral Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesParenteral Fluids and ElectrolytesJuliene Hannah FloresNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Therapy SeminarDocument29 pagesIV Fluid Therapy Seminarعمر احمد شاكرNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument24 pagesFluid and ElectrolyteVelpulakavyasree SonuNo ratings yet
- Types of Tonic SolutionsDocument3 pagesTypes of Tonic SolutionsKolimlim, Marienne SD.No ratings yet
- Fluid Management in ICUDocument37 pagesFluid Management in ICUمحمد قاسمNo ratings yet
- Dialysis NotesDocument9 pagesDialysis NotesJAYGONNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 SolutionsDocument81 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 SolutionsLol lolNo ratings yet
- IV SolutionsDocument8 pagesIV SolutionsAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Ivfluidtherapytypesindicationsdosescalculation 130123090523 Phpapp01Document68 pagesIvfluidtherapytypesindicationsdosescalculation 130123090523 Phpapp01rainNo ratings yet
- STM 0077Document185 pagesSTM 0077TroyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of IV FluidsDocument10 pagesDifferent Types of IV FluidsMarinill SolimanNo ratings yet
- Maternal Skills ReviewerDocument4 pagesMaternal Skills ReviewerLorel Faith ToradaNo ratings yet
- IV Infusion Preparations Fluid and Electrolytes: DR Anita JanadriDocument22 pagesIV Infusion Preparations Fluid and Electrolytes: DR Anita JanadriMohamed RasoolNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument38 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesJulia ManaloNo ratings yet
- IV FluidDocument49 pagesIV Fluidibrahimadnan040No ratings yet
- Self InflictedDocument4 pagesSelf Inflictedmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document2 pagesGroup 1mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Orpilla RNDocument2 pagesOrpilla RNmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Part 1 & 2Document35 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Part 1 & 2mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Toazinfo-Codes-I-Pr 9066fcd56131407b5641838bcf30c 230309 211145Document134 pagesToazinfo-Codes-I-Pr 9066fcd56131407b5641838bcf30c 230309 211145mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Checklist MS 1 and 2Document40 pagesChecklist MS 1 and 2mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 4TH QuarterDocument14 pagesGrade 8 4TH Quartermark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- SIR BORNIE E E N T POST TEST EditedDocument12 pagesSIR BORNIE E E N T POST TEST EditedHarvey T. Dato-onNo ratings yet
- Civil Registration Service Appointment SlipDocument1 pageCivil Registration Service Appointment Slipmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 4. Orpilla Jomark CDocument11 pagesCase Scenario 4. Orpilla Jomark Cmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- NCP GordonsPhysical AssessmentDocument12 pagesNCP GordonsPhysical Assessmentmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Funda ReviewDocument13 pagesDiagnostic Exam Funda Reviewmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 Post Test (CHN 1)Document11 pagesPhase 2 Post Test (CHN 1)Rosebel LaguraNo ratings yet
- M Vanguardia-McnpDocument11 pagesM Vanguardia-Mcnpmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The Heartmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- BSN 4b CasesDocument5 pagesBSN 4b Casesmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Application of Awards For GraduationDocument7 pagesApplication of Awards For Graduationmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- M Vanguardia-McnpDocument11 pagesM Vanguardia-Mcnpmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- G3 Schizo Psychiatric WardDocument18 pagesG3 Schizo Psychiatric Wardmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- PRC FORMS New Format 3Document5 pagesPRC FORMS New Format 3mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goalmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- OBOBDocument25 pagesOBOBmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Application Form: Customer InformationDocument2 pagesApplication Form: Customer Informationmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Subjective: IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Subjective: Independentmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjectives: Short-Term GoalDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjectives: Short-Term Goalmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 ChecklistsDocument14 pagesNCM 116 Checklistsmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Schizophrenia 1Document40 pagesGroup 1 Schizophrenia 1mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- NCMH Case StudyDocument34 pagesNCMH Case Studymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Notes 220728 202034Document9 pagesNotes 220728 202034mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Comm Letter Infromed Consent QuestionnaireCV 1Document14 pagesComm Letter Infromed Consent QuestionnaireCV 1mark OrpillaNo ratings yet