Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DoIP Faltblatt Softing
Uploaded by
Korkut ErdenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DoIP Faltblatt Softing
Uploaded by
Korkut ErdenCopyright:
Available Formats
DoIP
Diagnostic Communication over Internet Protocol
Automotive Data and Connectivity Where is DoIP applied? What is DoIP? Advantages of DoIP
Safety Accessibility Engineering Test Manufacturing Service
• Short and simple: “DoIP is the packaging of diagnostic messages Performant handling of huge data volumes
Internet
in Ethernet frames for communication of a diagnostic tester with a vehicle”
Connected
Office Driver Home Production Test After Sales Test
• DoIP is a standardized diagnostic transport protocol according to Time-saving at ECU Flash Programming
Specification
Why D oIP
ISO 13400
Road Test
• DoIP is used in combination with the standardized diagnostic protocol Cost-efficient because no VCI is necessary
Automotive Connected System Integration
Vehicle
UDS (ISO 14229-5: UDSonIP)
Infrastructure Devices Entertainment
Systems
Service & Functional Test, HiL • Services of UDSonIP are identical to UDSonCAN Simple integration to IT Infrastructure
Diagnostics
• DoIP with Ethernet 100 Base-TX instead of CAN enables substantial
System Development Supplementary to legislative CAN
Efficiency Environment • Vehicle inspection and repair
higher bandwidth Flexible use because of standardized communication
ECU Development
• Measurement reading • Vehicle access with DoIP is backwards compatible using discretionary
• Increasing interconnection of vehicles and their environment • Routing of data from internal pins of the existing diagnostic connector Integrated with other standards for vehicle diagnosis
• Driving assistance and infotainment systems cause huge data volume vehicle buses
• DoIP enables easy integration into various network structures,
• Increasing time for flash programming at production line and after-sales service • Online data streaming
• DoIP as a performant and flexible vehicle access • Flash programming even with WLAN Future-proof technology enables various use cases
DoIP in Combination with other Standards DoIP at the OSI Reference Model The DoIP Standard: ISO 13400 DoIP at D-PDU API Standard
Do IP S t andard Ove r view
Comparison to ISO
OTX (Open Test sequence eXchange) OSI Layer ISO UDS on DoIP
UDS on CAN Part 1 – General information and use case definition Two Use Cases:
Tester Application
• ISO 13209 • With physical module: Real MVCI which supports DoIP protocol
• DoIP extensions in preparation ISO 14229-5 ISO 14229-3 • With virtual modules: Direct access of tester to vehicle (=MVCI)
7: Application Part 2 – Transport protocol and network layer services
UDS on IP UDS on CAN
© 2016 Softing Automotive Electronics GmbH. Despite all due care and attention, Softing accepts no liability and extends no guarantee for the correctness, completeness or currentness of the information.
• Assignment of IP address
MCD-3D API OTX Runtime • Vehicle search
6: Presentation
• ISO 22900-3 MCD-3D API • Link connection
Different combination modes / network topologies:
• ASAM MCD-3D 3.0 required • Status information
MVCI D-Server ISO 14229-2 ISO 14229-2
5: Session • Single tester and single ECU (DoIP Entity)
UDS UDS • Data routing to sub buses
D-PDU API D-PDU API • Message types • Single tester and single vehicle (DoIP Vehicle and DoIP Group)
• ISO 22900-2 KWP UDS proprietary 4: Transport TCP / UDP • Error handling • Single tester and multiple vehicles (DoIP Collection and DoIP Group)
• DoIP specified as amendment ISO 13400-2 ISO 15765-2
DoIP Diag on CAN
• Multiple tester and single / multiple vehicles
DoIP (LAN / WLAN) 3: Network IPv4 / IPv6 Part 3 – Wired vehicle interface based on IEEE 802.3
UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services)
• ISO 14229-5 for DoIP FlexRay BroadR-Reach
Gateway 2: Data Link Part 4 – Ethernet-based high-speed data link connector Specification of vehicle identification (discovery)
CAN IEEE 802.3 ISO 13400-3 ISO 11898
WWH-OBD ECU ECU ECU Ethernet DoIP CAN
Definition of DoIP specific Communication Parameter (ComParams)
• ISO 27145 for DoIP and CAN ECU ECU ECU 1: Physical Part 5 – Conformance test specification Description of DoIP socket and protocol handling
ECU
Vehicle
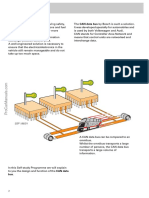
DoIP Communication Principles DoIP Communication Sequence Message Structure DoIP Vehicle Access
DoIP Co mmun icati on
Diagnostic tester communicates with vehicle via Gateway ECU Tester DoIP Gateway ECU DoIP Message Ethernet pin assignment at OBD connector
• Ethernet Activation Line enables Ethernet port of the Gateway DoIP Payload Data (up to 4 GByte) Option #1
Routing Activation Request
• Gateway is routing the message to sub buses CAN / FlexRay / MOST 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
DoIP
Routing Activation Response Header Diagnostic Services (UDS) Option #2
Link connection
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
• Configuration of the Gateway with valid IP address (DHCP) 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Diagnostic Request Diagnostic Request Cable
• Tester sends Vehicle Identification Request (UDP) ISO 15031 signals DoIP signals
(for DoIP via Ethernet)
• Gateway responses with Vehicle Announcement Message (UDP), OEM specific CAN signals
Diagnostic Response Diagnostic Response
contains VIN, Gateway address etc.
Ethernet Frame
Ethernet Payload Data (42 – 1500 Byte)
Diagnostic Request Diagnostic Request
Diagnostic commands
• Routing Activation Request: Command for routing of subsequent diagnostic
Ethernet TCP / UDP DoIP Message /
messages to ECUs behind the Gateway (TCP) Header Header Segment of DoIP Message WLAN-Ethernet Bridge VCI
(for DoIP via WLAN) (for DoIP and CAN)
• Diagnostic communication based on UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services)
Simplified illustration
O r d e r a d d i t i o n a l c o p i e s : i n f o . a u t o m o t i v e @ s o f t i n g . c o m / w w w. a u t o m o t i v e . s o f t i n g . c o m
You might also like
- UDS in CAN Flash ProgrammingDocument8 pagesUDS in CAN Flash ProgrammingAshutoshNo ratings yet
- CANLabDocument6 pagesCANLabSonny SoodNo ratings yet
- 000004100Document34 pages000004100v53No ratings yet
- Rimac Automobili Cybersecurity EngDocument1 pageRimac Automobili Cybersecurity EngudbarryNo ratings yet
- An IND 1 016 Using LXI Devices in CANoeDocument6 pagesAn IND 1 016 Using LXI Devices in CANoeWolfgang StarkmannNo ratings yet
- VeCo12 3 Diagnostics 1 Geffers Lecture PDFDocument24 pagesVeCo12 3 Diagnostics 1 Geffers Lecture PDFGraciella Valeria Viana100% (1)
- MVB Ug d000656-003145 PDFDocument109 pagesMVB Ug d000656-003145 PDFBala Raju ReddyboyaNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Road Vehicles - Unified Diagnostic Services (Uds) - Uds On Local Interconnect Network (Udsonlin)Document24 pagesInternational Standard: Road Vehicles - Unified Diagnostic Services (Uds) - Uds On Local Interconnect Network (Udsonlin)Korkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- IEC Certification Kit: Model-Based Design For ISO 26262Document31 pagesIEC Certification Kit: Model-Based Design For ISO 26262Ícaro VianaNo ratings yet
- Brochure of Luxoft Automotive Software by Luxoft Software DevelopmentDocument4 pagesBrochure of Luxoft Automotive Software by Luxoft Software DevelopmentluxoftNo ratings yet
- Simplified Electronic Design of The Function AEE2010 and AEE2010ECODocument4 pagesSimplified Electronic Design of The Function AEE2010 and AEE2010ECObadrNo ratings yet
- UDS Protocol - PiEmbSysTechDocument30 pagesUDS Protocol - PiEmbSysTechgreen_way26No ratings yet
- H Da Barth Functional Safety On MulticoreDocument23 pagesH Da Barth Functional Safety On Multicores.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- SDV EbookDocument59 pagesSDV EbookYogan SriNo ratings yet
- Vector Safety SolutionDocument53 pagesVector Safety SolutionGirish KasturiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Ensure Freedom From Interference FFI For ASIL Applications - TASKINGDocument19 pages4 - Ensure Freedom From Interference FFI For ASIL Applications - TASKINGDumitru IngeauaNo ratings yet
- Full Text 02Document124 pagesFull Text 02AnoopNo ratings yet
- Uds ImpDocument6 pagesUds ImppriyaNo ratings yet
- Analog Devices, Inc. Protocol 6 Flash/Ee Programming Via Lin Downloading Software With Canoe - LinDocument16 pagesAnalog Devices, Inc. Protocol 6 Flash/Ee Programming Via Lin Downloading Software With Canoe - LinUpendra VaddeNo ratings yet
- Autosar Practical ApplicationDocument135 pagesAutosar Practical ApplicationohmprakashNo ratings yet
- AUTOSAR SWS DiagnosticCommunicationManager PDFDocument553 pagesAUTOSAR SWS DiagnosticCommunicationManager PDFyuvarajnarayanasamyNo ratings yet
- Autosar IntroDocument54 pagesAutosar IntroaravindNo ratings yet
- Iso 22900-3Document460 pagesIso 22900-3EricNo ratings yet
- 07.TAI Seminar WHAT Is FUNCTIONAL SAFETY BKK 25june2015 HandsoutDocument33 pages07.TAI Seminar WHAT Is FUNCTIONAL SAFETY BKK 25june2015 HandsoutsunithaNo ratings yet
- Davinci Configures Vlinkgen - Programmer Sought PDFDocument4 pagesDavinci Configures Vlinkgen - Programmer Sought PDFChittaranjan BaralNo ratings yet
- MICROSAR ProductInformation enDocument92 pagesMICROSAR ProductInformation ensrikanthboddunaNo ratings yet
- ISO14229-5 2013 11-EnDocument24 pagesISO14229-5 2013 11-EnKorkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- An and 1 118 Canoe Tfs TutorialDocument47 pagesAn and 1 118 Canoe Tfs TutorialAndra Groza-Radu100% (1)
- CANalyzer Workshops Overview FactSheet enDocument2 pagesCANalyzer Workshops Overview FactSheet enPrasad GNo ratings yet
- Automotive SPICE Process Reference Model: TitleDocument47 pagesAutomotive SPICE Process Reference Model: TitleHoa LuuNo ratings yet
- Emaus Vector Canoe SlidesDocument12 pagesEmaus Vector Canoe SlidesvlsishekarNo ratings yet
- Invehicular Communication Using Vector CANoeDocument16 pagesInvehicular Communication Using Vector CANoesravan BattulaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 SystemDesk 4Document10 pagesUnit 4 SystemDesk 4Farwa ZahidNo ratings yet
- An-Ind-1-001 Canoe Canalyzer As Diagnostic Tools PDFDocument31 pagesAn-Ind-1-001 Canoe Canalyzer As Diagnostic Tools PDFratnamsNo ratings yet
- An-InD-1-001 CANoe CANalyzer As Diagnostic ToolsDocument31 pagesAn-InD-1-001 CANoe CANalyzer As Diagnostic ToolsAnoopNo ratings yet
- SN IND 1 011 - InteractionLayerDocument10 pagesSN IND 1 011 - InteractionLayerVishnu R Nair100% (1)
- Iso Sae Fdis 21434Document15 pagesIso Sae Fdis 21434MOHAMED BOUCHNAKNo ratings yet
- Simulink-Targetlink Datatypes Defnt ProblemDocument16 pagesSimulink-Targetlink Datatypes Defnt ProblemmonisivaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Driver Assistance (ADAS) Solutions GuideDocument29 pagesAdvanced Driver Assistance (ADAS) Solutions GuideDharmody0% (1)
- Red Bend Update Car Ecu PDFDocument14 pagesRed Bend Update Car Ecu PDFtomsiriNo ratings yet
- CANoe ProductInformation ENDocument57 pagesCANoe ProductInformation ENpawan waghNo ratings yet
- Vector Controller Accessories Manual EN PDFDocument61 pagesVector Controller Accessories Manual EN PDFJacob CherianNo ratings yet
- Traction Control For BikeDocument10 pagesTraction Control For BikeSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Ecall Standards Update v2Document24 pagesEcall Standards Update v2alex alex100% (1)
- Autosar Exp NvdatahandlingDocument51 pagesAutosar Exp NvdatahandlingSugadevNo ratings yet
- CANoe Manual enDocument209 pagesCANoe Manual envtechvishnuNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 Serial CommunicationDocument51 pagesUnit - 5 Serial CommunicationM.venkateshNo ratings yet
- ANSYS LAB Manual PDFDocument98 pagesANSYS LAB Manual PDFVem Baiyan CNo ratings yet
- VTESTstudio ConceptManual enDocument48 pagesVTESTstudio ConceptManual enAntonio li causi50% (2)
- XCP ReferenceBookDocument116 pagesXCP ReferenceBookSathish SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Safety-Oriented System Hardware Architecture Exploration in Compliance With ISO 26262Document29 pagesApplied Sciences: Safety-Oriented System Hardware Architecture Exploration in Compliance With ISO 26262Girish KasturiNo ratings yet
- Vector Webinar CANoeDiVa 20200612 PDFDocument29 pagesVector Webinar CANoeDiVa 20200612 PDFAnup KumarNo ratings yet
- Sowmya TK Senior Software Engineer: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSowmya TK Senior Software Engineer: Objectivesowmya tkNo ratings yet
- Dspace-Paper Hil Overview Waeltermann e 160405 PDFDocument14 pagesDspace-Paper Hil Overview Waeltermann e 160405 PDFPranay VermaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Communication Manager Module in AUTOSARDocument7 pagesDiagnostic Communication Manager Module in AUTOSARShyam Bhat100% (1)
- CarMaker WhitepaperDocument9 pagesCarMaker WhitepapersegiropiNo ratings yet
- CRC Generating and Checking: Example 1: Modulo-2 CalculationDocument24 pagesCRC Generating and Checking: Example 1: Modulo-2 Calculationmirbaz_pathan2001No ratings yet
- Automotive Services Solution enDocument12 pagesAutomotive Services Solution ensaika_1982100% (1)
- DoIP - UDS Guide - AutoPiDocument11 pagesDoIP - UDS Guide - AutoPiKorkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- SSP 269 d1 PDFDocument60 pagesSSP 269 d1 PDFAdrian BuzasNo ratings yet
- LH Kwp2000 Flashen v1.1 enDocument36 pagesLH Kwp2000 Flashen v1.1 enArda AkberkNo ratings yet
- SSP 186 CanDocument29 pagesSSP 186 CanKorkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- J2819 - Base For TP20Document22 pagesJ2819 - Base For TP20Korkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- Can 20Document72 pagesCan 20hemanthbbcNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Road Vehicles - Unified Diagnostic Services (Uds) - Uds On Local Interconnect Network (Udsonlin)Document24 pagesInternational Standard: Road Vehicles - Unified Diagnostic Services (Uds) - Uds On Local Interconnect Network (Udsonlin)Korkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- ISO14229-4 2012 12-EnDocument24 pagesISO14229-4 2012 12-EnKorkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- ISO14229-5 2013 11-EnDocument24 pagesISO14229-5 2013 11-EnKorkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Road Vehicles - Unified Diagnostic Services (Uds) - Uds On Local Interconnect Network (Udsonlin)Document24 pagesInternational Standard: Road Vehicles - Unified Diagnostic Services (Uds) - Uds On Local Interconnect Network (Udsonlin)Korkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- ISO14229-6 2013 03-EnDocument20 pagesISO14229-6 2013 03-EnKorkut ErdenNo ratings yet
- List of TCP and UDP Port Numbers - WikipediaDocument28 pagesList of TCP and UDP Port Numbers - WikipediaGancearuc DumitruNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Networking OverviewDocument12 pagesUnit 10 Networking OverviewRichie BallyearsNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Gold Bible PDFDocument0 pagesCCNA 2 Gold Bible PDFrichbartonNo ratings yet
- NFN PC GatewayDocument30 pagesNFN PC GatewaypujFierrosNo ratings yet
- 05-IP and MPLS Tunnel IntroductionDocument52 pages05-IP and MPLS Tunnel IntroductionPaulo DembiNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Internetworking Terms and Acronyms 1-58720-045-7Document18 pagesDictionary of Internetworking Terms and Acronyms 1-58720-045-7Jessica a MillerNo ratings yet
- Pre-Requisite: CS307 Data Communication Course ObjectivesDocument2 pagesPre-Requisite: CS307 Data Communication Course Objectivesfaseen mohammedNo ratings yet
- Tenix Data Diode EAL7 - Servicii Suportate PDFDocument4 pagesTenix Data Diode EAL7 - Servicii Suportate PDFGheorghe GeorgelNo ratings yet
- Sathyabama: Packet Sniffing Using Python in Kali LinuxDocument19 pagesSathyabama: Packet Sniffing Using Python in Kali LinuxDivya BharathyNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide 3 in 1 - Beginner - Stuart NicholasDocument378 pagesCisco CCNA Command Guide 3 in 1 - Beginner - Stuart NicholaskkkkNo ratings yet
- SEI ModbusSlave EDocument72 pagesSEI ModbusSlave EcontrolmaestroNo ratings yet
- HSS9860 V900R008C20 Data Configuration and O&M (LTE)Document51 pagesHSS9860 V900R008C20 Data Configuration and O&M (LTE)sirjimyNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Basic - Config - Ind - Ether - RS20 - RS30Document198 pagesUser Manual - Basic - Config - Ind - Ether - RS20 - RS30Marcos RosenbergNo ratings yet
- Mbusmaster Delphi PDFDocument230 pagesMbusmaster Delphi PDFadesa2013No ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking Itpc 17Document108 pagesData Communication and Networking Itpc 17Colleen VenderNo ratings yet
- The Hows and Whys of Ethernet Networks in Substations: ThernetDocument27 pagesThe Hows and Whys of Ethernet Networks in Substations: ThernetbansalrNo ratings yet
- Sage Intergy EHR EMR New Jersey York Medical BillingDocument284 pagesSage Intergy EHR EMR New Jersey York Medical BillingdtriviNo ratings yet
- Full System FlashDocument81 pagesFull System FlashNicolasNärgrath100% (1)
- Smart CampusDocument8 pagesSmart Campusravi196100% (1)
- Winter 2018 Computing and InformaticsDocument47 pagesWinter 2018 Computing and Informaticsishu kaliaNo ratings yet
- Modicon M340 Annex RTU - W@DeDocument6 pagesModicon M340 Annex RTU - W@Desachin BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9.2.1Document11 pagesLesson 9.2.1Rye Rye LasorNo ratings yet
- Doc.9896-En Manual On The Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Using Internet Protocol Suite (IPS) Standards and ProtocolsDocument112 pagesDoc.9896-En Manual On The Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Using Internet Protocol Suite (IPS) Standards and ProtocolsMaher Ben JemiaNo ratings yet
- TDi Installation Instructions 080219Document20 pagesTDi Installation Instructions 080219jose mondacaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Direct To Home TechnologyDocument25 pagesWelcome: Direct To Home Technologyversatility100% (1)
- Implementation of A Distributed Rtu Monitoring System Using The Iec60870-5-104 Protocol Over Gprs Networks Arzuaga, A., Ojinaga, Z., Llano, A. Usyscom, Iberdrola SpainDocument8 pagesImplementation of A Distributed Rtu Monitoring System Using The Iec60870-5-104 Protocol Over Gprs Networks Arzuaga, A., Ojinaga, Z., Llano, A. Usyscom, Iberdrola SpainSGQNo ratings yet
- 02.Point-To-Point Links, HDLC, PPP, and Frame RelayDocument37 pages02.Point-To-Point Links, HDLC, PPP, and Frame Relayasegunlolu100% (1)
- Mobile Application Penetration Testing - Sample ChapterDocument26 pagesMobile Application Penetration Testing - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Asa2ftd Migration Guide 620Document56 pagesAsa2ftd Migration Guide 620Mohamed FoutaNo ratings yet