Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 Carbonyl 2019
9 Carbonyl 2019
Uploaded by
Keth LaurelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 Carbonyl 2019
9 Carbonyl 2019
Uploaded by
Keth LaurelCopyright:
Available Formats
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
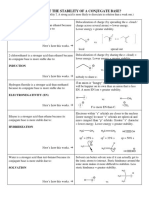
Copyright 2019 O O
O M O M NR 2 M
R–OH/ H 2O/ NaBH 4 LiAlH 4
James Ashenhurst R–MgX RO R R–NH 2 M–CN
masterorganicchemistry.com OR R R R–OM M–OH
β−keto ester amine alcohol/ water/ Sodium Lithium aluminum
james@masterorganicchemistry.com
Grignard Ester enolate Ketone enolate Enamine Cyanide
enolate (primary amine) alkoxide hydroxide borohydride hydride
O OH OH O OH O OH NR 2 O O R OH RO OR HO OH OH OH
N
A R H R R R OR R R R R RO R R CN R H R H R H R H
R H H H H
Aldehyde 2° alcohol Aldol Reaction Aldol Reaction R Imine Cyanohydrin Acetal Hydrate 1° alcohol 1° alcohol
Knoevenagel (aldimine) Requires acid (usu. thermodynaically
heating under basic conditions will lead to Condensation catalysis to form disfavored, except for
elimination of OH - Aldol condensation electron poor aldehydes)
also note that reaction can be reversible If aldehyde is enolizable,
under basic conditions : Retro-aldol reaction hydroxide can form enolate.
O OH O O O O O NR 2 O OH O O O O OH OH
B R Cl R R R OR R R R R RO R R NHR R CN R OR R OH R H R H
R H H
Acyl chloride 3° alcohol β−keto ester O R Amide Acid nitrile Ester Carboxylic acid 1° alcohol 1° alcohol
(Schotten-Bauman
reaction)
O O O O O NR 2 O O O O O O OH
O O OH
R OR R R R R RO R R NHR R CN R OR R OH Borderline R H
C R O R' R
R
R H
Anhydride 3° alcohol O R Amide Acid nitrile Ester Carboxylic Acid 1° alcohol
O OH OH O OH O OH NR 2 O O R OH RO OR HO OH OH OH
N
D R R' R R R OR R R R R RO OR R CN R R' R R R H R H
R' R' R' R R R' R' R' R'
Ketone 3° alcohol Aldol Reaction Aldol Reaction R R Imine Cyanohydrin Acetal Hydrate 2° alcohol 2° alcohol
(ketimine) Requires acid see above: even less
Note: best when ketones are favored than with aldehydes
catalysis
identical or when only one can due to sterics
enolize (to avoid scrambling)
O O O O O O NR 2 O OH O O O O
Varies with Varies with conditions: 1,2
E R conditions: 1,2 R OR R R R R RO R R R R R adduct is kinetic product, 1,4
adduct is adduct is thermodynamic.
kinetic pdt. RHN NC RO RO
α, β unsaturated Michael Reaction Michael Reaction
ketone (enone)
O R Note: in both cases, very prone to Note: Easily
the reverse reaction (elimination) reversible
O OH O O O O O O O OH
F Borderline Borderline NR NR H
R OR R R R OR R R R NHR R OR' R OH R
R H
Ester 3° alcohol β−keto ester: 1,3 diketone: Amide Transesterification Saponification 1° alcohol
Claisen Condensation Claisen Condensation Can be done under basic (basic conditions)
or acidic conditions. Can also hydrolyze
O with aqueous acid OH
O O
G R OH NR R H
Deprotonation Deprotonation Deprotonation NR Deprotonation R NHR H
R OR' ––– NR
Carboxylic acid 1° alcohol
Usually requires Fischer esterification
dehydration (requires acid, heat)
agent (e.g. DCC)
O O
1° and 2° amides: 1° and 2° amides: Borderline reaction: H H
H R NH 2 Deprotonation deprotonation deprotonation NR NR NR NR requires strong acid, R OH NR NH 2
3°amides: NR 3°amides: NR alcohol as solvent, heat R
Amide Amide Hydrolysis Amine
Requires strong
conc. acid, heat
O O NR 2 O O
Mix of addition R
I R X /deprotonation R OR R R R RO R R NHR R CN R OR R OH NR R H
R
Alkyl halide Enolate Enolate Stork enamine Amine Williamson requires Alkane
Alkylation Alkylation reaction Ether Synthesis basic
note: capable of caution! product conditions
alkylating is a good nucleophile; requires basic
a second time multiple alkylations conditions
usually result
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A90 (Installation Guideline)Document18 pagesA90 (Installation Guideline)shakibur rahman60% (5)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lecture 1: Natural Coordinates: X X N and N L LDocument74 pagesLecture 1: Natural Coordinates: X X N and N L LGhanshyam SahNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Theories Test Bank 2019 PDFDocument43 pagesCost Accounting Theories Test Bank 2019 PDFKristian Paolo De LunaNo ratings yet
- Solucionario de Ingenieria Economica TarquinDocument10 pagesSolucionario de Ingenieria Economica TarquinHugo Bohorquez AliagaNo ratings yet
- Medical Device Materials - Stainless SteelDocument5 pagesMedical Device Materials - Stainless Steelmaran.suguNo ratings yet
- D5 PDFDocument392 pagesD5 PDFramanNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation LessonDocument30 pagesNatural Vegetation LessonAn SaNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning: Seungsang OhDocument39 pagesDeep Learning: Seungsang OhKaAI KookminNo ratings yet
- Universal Adhesives: The Next Evolution in Adhesive Dentistry?Document13 pagesUniversal Adhesives: The Next Evolution in Adhesive Dentistry?kartika tiaraNo ratings yet
- Project On CAA & NRC CompleteDocument22 pagesProject On CAA & NRC CompleteSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Embedded Journalism: Global Media Scenario Tejaswini Semester 3, Section CDocument8 pagesEmbedded Journalism: Global Media Scenario Tejaswini Semester 3, Section CTejaswini Mishra0% (1)
- Unit 1 Introduction To Hotel: SpeakingDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Hotel: SpeakingSvensen AngelNo ratings yet
- Go Getter 2 (Unit 1-2)Document5 pagesGo Getter 2 (Unit 1-2)Julia BaghdasaryanNo ratings yet
- A. & B. Beginning WIPDocument31 pagesA. & B. Beginning WIPChampy MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linguistics SALUD, APRIL M.Document4 pagesIntroduction To Linguistics SALUD, APRIL M.Jasper OlosNo ratings yet
- Accountability of Public OfficersDocument10 pagesAccountability of Public OfficersJazel GalauraNo ratings yet
- An Unfinished CinemaDocument1 pageAn Unfinished CinemaDian WeysNo ratings yet
- Computational Design PortfolioDocument11 pagesComputational Design PortfolioMUditaLauNo ratings yet
- Low Platelet CountDocument9 pagesLow Platelet Countfatimah_zkhanNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Management: Islam Awni Abu SamraDocument41 pagesIV Fluid Management: Islam Awni Abu SamraIslam AwniNo ratings yet
- Active Teaching For Active Learning: DR M.S.V.K.V.Prasad Associate Professor Department of Civil EngineeringDocument25 pagesActive Teaching For Active Learning: DR M.S.V.K.V.Prasad Associate Professor Department of Civil EngineeringswathiprasadNo ratings yet
- A Unified Approach To The Construction of Categories of GamesDocument160 pagesA Unified Approach To The Construction of Categories of Gamessfwc100% (1)
- Corrosion Resistance of Welded Joints Made by Wet Underwater WeldingDocument8 pagesCorrosion Resistance of Welded Joints Made by Wet Underwater WeldingMaksimovNo ratings yet
- Readingpractietest4 v9 18865116Document17 pagesReadingpractietest4 v9 18865116Hssan RiahiNo ratings yet
- Brochure l150h l180h l220h t3 en 30 20047153 DDocument28 pagesBrochure l150h l180h l220h t3 en 30 20047153 Dgosiamail100% (1)
- Comparing and Merging Files Patch Diff Diff3 Sdiff CMPDocument24 pagesComparing and Merging Files Patch Diff Diff3 Sdiff CMPdupipiNo ratings yet
- Factor Affecting SolubilityDocument1 pageFactor Affecting SolubilityBeatrice ShokryNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Economics - NotesDocument10 pagesClass 9 Economics - NotesSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase StudyVarl SomiNo ratings yet