Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Federalism
Uploaded by
Sahil TiwariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Federalism
Uploaded by
Sahil TiwariCopyright:
Available Formats
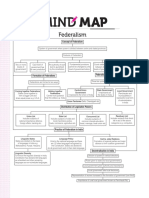
FEDERALISM
Federalism is a system of govt. where power is divided btw Central Authority
( responsible for a few subjects of
Both these levels of governments enjoy their power
independent of the other. common national interest)
Various constituent units of the country
(that look after much of the day-to-day
administering of their state)
FEATURES OF FEDERALISM
2 or more levels of government
each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters
of Legislation, Taxation, & Administration
these jurisdictions are specified in the constitution.
So, existence and authority of each tier is
constitutionally guaranteed.
Fundamental provisions of the constitution
cannot be changed require consent of BOTH LEVELS
unilaterally of govt.
Courts power to interpret CONSTITUTION
act as UMPIRE in disputes between levels
of govt. in exercise of their respective powers
Sources of revenue are clearly specified for each tier of
govt. to ensure FINANCIAL AUTONOMY
COMING TOGETHER FEDERATION HOLDING TOGETHER FEDERATION
Involves independent States coming together on their Large country decides to divide its power between
own to form a bigger unit, so that by pooling National govt. & constituent states.
sovereignty and retaining identity they can increase
their security. Central govt. is more powerful than the States.
Very often different constituent units of the
Const. states usually have equal power & are as strong federation have unequal powers. Some units are
as Central govt. granted special powers.
Ex- India, Belgium, Spain
Ex- U.S.A, Switzerland, Australia
HOW IS FEDERALISM PRACTICED
Linguistic States Language Policy
1st and Major test for Democratic Politics
Many safeguards to protect other languages
Boundaries of old states were changed to create
Besides Hindi, their are 21 other Scheduled
new states
Languages
This made administration easier
States too have their official language. Much
Formation of linguistic states made the country
of the govt. work takes place in the official
more united.
language of concerned state
Some states were created not on the basis of
language but to recognise differences based on
cultural ethnicity or geography. Ex- Nagaland,
Jharkhand
Centre-State Relations
Before 1990 After 1990
Restructuring Centre - State relations has Rise of regional political parties & beginning
strengthened Federalism in practice. of era of COALITION govt. at the CENTRE
For a long time, same party ruled Centre and most No single party got majority at Lok Sabha &
of the states. State govts. didn't exercise their rights majority national party formed alliance with
as AUTONOMOUS FEDERAL UNITS. regional parties to form govt. at the Centre.
Central govts. dismissed state govt. ruled by rival This led to a new culture of Power Sharing &
parties. respect for autonomy of State govt.
A major judgement passed by Supreme
Court made it difficult for Centre Govt. to
dismiss state govt.
What makes India a Federal Country?
3 tiers of govt. --> each enjoys separate jurisdiction
Constitution provided 3 fold distribution of Legislative Powers between Union and State govt.
Union List State List Concurrent List
Defence, Foreign Affairs, Police, Trade, Agriculture, Education, forest, marriage,
Banking, Currency,etc Irrigation, etc adoption, succession, etc.
Union govt. has the power to legislate on Residuary Subjects.
Union and State govt. have the power to raise resources by levying taxes.
Judiciary sees disputes regarding division of powers -
Judiciary oversees implementation of constitutional procedures and provisions.
DECENTRALISATION
A vast country like India can't run be through 2 tiers of government.States in India are as large as countries in
Europe in India are internally very diverse.-->THUS NEED FOR ANOTHER TIER OF GOVT.
What is Decentralisation? --> When powers are taken away from the Central and State Govt. and given to the
Local govt. --> It is called Decentralisation.
Why Decentralisation?
Because a large number of People have better knowledge At Local Level --> There is
problems are best settled at of problems in their localities direct participation of
Local Level. like where to spend money & people in decision making.
manage things efficiently. This also inculcates
democratic participation.
RURAL SELF GOVT.
Each village has a gram Panchayat Few gram panchayat forms
consisting of several ward members panchayat Samiti / Block /
(Panch) and a President (Sarpanch) Mandal. The members of this
.They are directly elected by the adult representative bodies are elected
population of that ward or village . It by all the Panchayat members in
works under the supervision of Gram that area .
Sabha .
In big cities, there are Municipal All panchayat samitis or mandals of
Corporations.Both these local the district together form Zila
government bodies are controlled by Parishad . Members of Loksabha ,
elected bodies consisting of people 's MLAs of that district and some other
representatives. officials of other district level bodies
are also its members .
CONDITION OF LOCAL SELF GOVT.
Before 1992 After 1992
Punchayats (villages) and Municipalities(urban Major Steps were taken. Constitution was
areas) were directly under control of state govt. amended to make 3rd tier of govt. more powerful.
no regular elections. It was constitutionally made mandatory to hold
elections to local govt. bodies
Local govt – no power or resources of its own.
Atleast 1/3rd of all positions reserved for women.
Thus, very little decentralisation in effective terms.
SEC (independent constitution) setup in each
state to conduct panchayat & municipal elections.
State govts. now share power and revenue with
local govt. bodies. However, nature of sharing
varies from state to state.
LOCAL SELF GOVT.
Achievements Challenges
Largest experiment in democracy. Gram Sabhas not held regularly.
36 L elected representatives in punchayats & No significant transfer of powers/resources
municipalities from state govts.
helped deepen democracy (constitutional status for We are still a long very from realising the idea
local govt.) of self govt.
↑sed women’s representation
*SEC - State Election Commission
You might also like
- The Franklin Coverup Child AbuseDocument6 pagesThe Franklin Coverup Child AbuseKenneth Paul100% (2)
- Political Party and Party SystemDocument19 pagesPolitical Party and Party System17Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Henry Kissinger, The American Dream, and The Jewish Immigrant Experience in The Cold WarDocument29 pagesHenry Kissinger, The American Dream, and The Jewish Immigrant Experience in The Cold WarGabriel MaechaouiNo ratings yet
- Evidential Objections - Eastern Engineering V Attorney General of Trinidad and Tobago 2nd MatterDocument15 pagesEvidential Objections - Eastern Engineering V Attorney General of Trinidad and Tobago 2nd MatterJeron JosephNo ratings yet
- Aethiopica 8 (2005) Richard PankhurstDocument25 pagesAethiopica 8 (2005) Richard PankhurstHabtamu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- AttorneyDocument2 pagesAttorneyapi-78514235No ratings yet
- Reagan Doctrine Wars - Final Submision PDFDocument366 pagesReagan Doctrine Wars - Final Submision PDFAristeidis Rigas100% (1)
- ProposalDocument325 pagesProposalendalegge100% (3)
- Neri V SenateDocument4 pagesNeri V SenateAnna Marie DayanghirangNo ratings yet
- (Hart Studies in Constitutional Law) Alexander Horne - Andrew Le Sueur (Editors) - Parliament - Legislation and Accountability-Hart Publishing (2016)Document345 pages(Hart Studies in Constitutional Law) Alexander Horne - Andrew Le Sueur (Editors) - Parliament - Legislation and Accountability-Hart Publishing (2016)Deshdeep DhankharNo ratings yet
- Colin Dictionary of Politics and GovernmDocument289 pagesColin Dictionary of Politics and Governm66171800001No ratings yet
- 3360 Exploring New Political Alternatives For The OromoDocument98 pages3360 Exploring New Political Alternatives For The Oromototoba2648100% (1)
- Zazzaro 2013Document120 pagesZazzaro 2013wedi EritreaNo ratings yet
- Key Ideas in Tort Law (Peter Cane) (Z-Library)Document145 pagesKey Ideas in Tort Law (Peter Cane) (Z-Library)Raja MujahidNo ratings yet
- Federalism Notes PDFDocument4 pagesFederalism Notes PDFramkrishnapasalaNo ratings yet
- DiplomacyDocument26 pagesDiplomacyRiya GargNo ratings yet
- Am Eskinder NegaDocument308 pagesAm Eskinder NegaMelesse Zenebework50% (2)
- Terms of Reference For Research TemplateDocument9 pagesTerms of Reference For Research TemplateOxfamNo ratings yet
- Convergences and Divergences in The Pak US RelationsDocument3 pagesConvergences and Divergences in The Pak US RelationsZulfqar Ahmad100% (1)
- 2007 Understanding Legal Pluralism Past To Present Local To GlobalDocument37 pages2007 Understanding Legal Pluralism Past To Present Local To GlobalAndré Marinho MarianettiNo ratings yet
- Political PartiesDocument28 pagesPolitical PartiesCaesar M. AmigoNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument23 pagesFederalismNeodymiumNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Patent CaseDocument154 pagesAnatomy of A Patent CasePrasanna Bhagwan100% (2)
- Amhara People Mistaken Identity 200Document46 pagesAmhara People Mistaken Identity 200TWWNo ratings yet
- 008 Page 211 Association of Flood Victims vs. ComelecDocument1 page008 Page 211 Association of Flood Victims vs. ComelecNafiesa ImlaniNo ratings yet
- Documenting The Ethiopian Student MovementDocument164 pagesDocumenting The Ethiopian Student MovementMiliyon100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2shwetank choudharyNo ratings yet
- (Rape) Xv-09-Inv-16d-00518 (Dela Paz) - Rape (Rpc266-A)Document5 pages(Rape) Xv-09-Inv-16d-00518 (Dela Paz) - Rape (Rpc266-A)Stephen Celoso EscartinNo ratings yet
- Political Parties in IndiaDocument27 pagesPolitical Parties in IndiaAvesh IXA-20No ratings yet
- History of Sciences2016Document92 pagesHistory of Sciences2016Saurabh MishraNo ratings yet
- Oca v. Judge FloroDocument2 pagesOca v. Judge Florodondz100% (3)
- Doctrine of Proper SubmissionDocument3 pagesDoctrine of Proper SubmissionJani MisterioNo ratings yet
- Beale Vs TaylorDocument11 pagesBeale Vs TaylorAlan Sam100% (4)
- Tapiador Vs OmbudsmanDocument3 pagesTapiador Vs OmbudsmanPatricia BautistaNo ratings yet
- 10 Political Science - Federalism - Notes VLDocument6 pages10 Political Science - Federalism - Notes VLPriyankadevi PrabuNo ratings yet
- 23 1gudinaDocument27 pages23 1gudinaAmbachew A. AnjuloNo ratings yet
- AP Human Chapter 6 LectureDocument44 pagesAP Human Chapter 6 Lecturecatherine8yinNo ratings yet
- Function Strategy PDFDocument5 pagesFunction Strategy PDFTalha HanifNo ratings yet
- 1987 Constitution of EthiopiaDocument3 pages1987 Constitution of EthiopiaMenilek AlemsegedNo ratings yet
- 2004 - MeraraDocument25 pages2004 - MeraraJust BelieveNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Prospects of Democratization Process in EthiopiaDocument11 pagesChallenges and Prospects of Democratization Process in EthiopiaToleraNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Phil. History, Gov't & ConstitionDocument722 pagesLecture of Phil. History, Gov't & ConstitionJulieann Bagunas KimNo ratings yet
- BDS/MBBS Thrombolytics and Antiplatelet DrugsDocument33 pagesBDS/MBBS Thrombolytics and Antiplatelet DrugsDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Part III: Strategic Actions: Strategy Implementation Chapter 12: Strategic LeadershipDocument26 pagesStrategic Management: Part III: Strategic Actions: Strategy Implementation Chapter 12: Strategic LeadershipReema LaserNo ratings yet
- Project SynopsisDocument9 pagesProject SynopsisVipin KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Agreement On Agriculture PDFDocument33 pagesAgreement On Agriculture PDFRamindra SuwalNo ratings yet
- Industrial Tour Report On CSE (Chittagong Stock Exchange)Document42 pagesIndustrial Tour Report On CSE (Chittagong Stock Exchange)Khan Md Fayjul100% (2)
- CMO 05 s2008 NursingDocument121 pagesCMO 05 s2008 NursingRochelle EstebanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 History UNIT FOUR Note.pDocument10 pagesGrade 9 History UNIT FOUR Note.pAkinahom Taye100% (1)
- WHO IMAI Acute - Care PDFDocument138 pagesWHO IMAI Acute - Care PDFJohn Philip TiongcoNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument24 pagesFederalismT3X1CNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument16 pagesFederalismRiya Kumari100% (1)
- CH 2 Federalism Political Science Class 10Document6 pagesCH 2 Federalism Political Science Class 10Hafsah KhanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Civics Chapter 2Document42 pagesClass 10 Civics Chapter 2Manoj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 FederalismDocument20 pagesCH 2 FederalismSujalNo ratings yet
- Federalism Class 10 NotesDocument4 pagesFederalism Class 10 NotesamithsabusNo ratings yet
- FedaralismDocument7 pagesFedaralismMaria JohncyNo ratings yet
- Federalism Full ChapterDocument52 pagesFederalism Full ChapterDarsh AroraNo ratings yet
- XTH Civics CH 02 Federalism NotesDocument8 pagesXTH Civics CH 02 Federalism NotesSandhya SinghNo ratings yet
- AISV6 - X - Political Science - Federalism - RRDocument4 pagesAISV6 - X - Political Science - Federalism - RRHridi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- What Is Federalism?Document4 pagesWhat Is Federalism?K A R M A100% (1)
- ViewpdfDocument4 pagesViewpdfAnant DwivediNo ratings yet
- Fedralism (Prashant Kirad)Document11 pagesFedralism (Prashant Kirad)shrikantmisal17No ratings yet
- FEDERALISM Notes Class 10Document4 pagesFEDERALISM Notes Class 10PARDEEP0% (1)
- FEDERALISMDocument24 pagesFEDERALISMBhavna ShishodiaNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument4 pagesFederalismShweta GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Concept of FederalismDocument1 pageConcept of FederalismPAWANNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument3 pagesFederalismKanishk AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Federalism: 3rd Tier: 1st TierDocument7 pagesFederalism: 3rd Tier: 1st TierSahil Affriya YadavNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Political Science Chapter 2 FederalismDocument5 pagesCBSE Notes Class 10 Political Science Chapter 2 FederalismDghcrNo ratings yet
- Federalisml 2Document29 pagesFederalisml 2Pankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Leibel Answer Brief (Fla. 4th DCA)Document39 pagesLeibel Answer Brief (Fla. 4th DCA)DanielWeingerNo ratings yet
- The Maldivian Legal SystemDocument8 pagesThe Maldivian Legal Systemgunahauna0% (1)
- 1 Bello v. UboDocument5 pages1 Bello v. UboKarla Marie TumulakNo ratings yet
- 6654 Exhibit AB 20190402 1: Contract Between Atiku and Fein & DelValleDocument10 pages6654 Exhibit AB 20190402 1: Contract Between Atiku and Fein & DelValleKúnlé AdébàjòNo ratings yet
- Evidence 18-02-2019Document86 pagesEvidence 18-02-2019เจียนคาร์โล การ์เซียNo ratings yet
- December 2015Document120 pagesDecember 2015ajitkumar jenaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines v. Salem Investment CorporationDocument20 pagesRepublic of The Philippines v. Salem Investment CorporationMaricar Corina CanayaNo ratings yet
- Agripino Pacheco v. The People of Puerto Rico, 300 F.2d 759, 1st Cir. (1962)Document2 pagesAgripino Pacheco v. The People of Puerto Rico, 300 F.2d 759, 1st Cir. (1962)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Dayabhai Chhaganbhai v. State of GujaratDocument2 pagesDayabhai Chhaganbhai v. State of GujaratVrinda Garg100% (1)
- Definition and Scope of Administrative LDocument26 pagesDefinition and Scope of Administrative LAmisha PrakashNo ratings yet
- Coronel V CA GR No 103577 Oct 7 1996Document15 pagesCoronel V CA GR No 103577 Oct 7 1996Bonito BulanNo ratings yet
- Telescope OrderDocument8 pagesTelescope OrderBasseemNo ratings yet
- Underwood To Denerstein Letter 1.13.14Document15 pagesUnderwood To Denerstein Letter 1.13.14Casey SeilerNo ratings yet
- Cases Crimpro LastDocument4 pagesCases Crimpro LastJona MayNo ratings yet
- Phoenix Complaint Federal District Court Without Signature Block and Exhibits (Jose Kerkado)Document34 pagesPhoenix Complaint Federal District Court Without Signature Block and Exhibits (Jose Kerkado)Damas de la Segunda EnmiendaNo ratings yet
- R A - 10951Document5 pagesR A - 10951youngkimNo ratings yet
- Prof. Serfino - Practical Exercises - 2019Document30 pagesProf. Serfino - Practical Exercises - 2019Kichelle MayNo ratings yet
- Resident Marine Mammals of The Protected Seascape of Tañon Strait v. Secretary Angelo ReyesDocument2 pagesResident Marine Mammals of The Protected Seascape of Tañon Strait v. Secretary Angelo ReyesAlicia BanhagNo ratings yet
- In The Matter of Dorothea BaptisteDocument38 pagesIn The Matter of Dorothea BaptisteJoe PatriceNo ratings yet