Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE704D Lecture 8
Uploaded by
Rishabh Dev Shukla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views21 pagesThis document provides an introduction to solar thermal systems. It discusses how solar energy is received on Earth in an intermittent and dilute form. The key components of solar thermal systems are solar collectors or concentrators to capture solar rays, an energy transport medium to move the thermal energy, energy storage to provide power when the sun is not available, an energy conversion plant to generate electricity or thermal energy, and power conditioning equipment. Common types of solar collectors include parabolic troughs, linear Fresnel reflectors, dish collectors, and central tower systems using distributed reflectors.
Original Description:
PPT on solar Thermal
Original Title
EE704D_Lecture_8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction to solar thermal systems. It discusses how solar energy is received on Earth in an intermittent and dilute form. The key components of solar thermal systems are solar collectors or concentrators to capture solar rays, an energy transport medium to move the thermal energy, energy storage to provide power when the sun is not available, an energy conversion plant to generate electricity or thermal energy, and power conditioning equipment. Common types of solar collectors include parabolic troughs, linear Fresnel reflectors, dish collectors, and central tower systems using distributed reflectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views21 pagesEE704D Lecture 8
Uploaded by
Rishabh Dev ShuklaThis document provides an introduction to solar thermal systems. It discusses how solar energy is received on Earth in an intermittent and dilute form. The key components of solar thermal systems are solar collectors or concentrators to capture solar rays, an energy transport medium to move the thermal energy, energy storage to provide power when the sun is not available, an energy conversion plant to generate electricity or thermal energy, and power conditioning equipment. Common types of solar collectors include parabolic troughs, linear Fresnel reflectors, dish collectors, and central tower systems using distributed reflectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
Lecture-8
Introduction to Solar Thermal
System
Dr. Rishabh Dev Shukla
Electrical Engineering Department, Budge
Budge Institute of Technology Kolkata
Introduction
• Solar Energy or radiation is received on Earth in cyclic,
intermittent and dilute form with very low power density 0 to 1
kW/m2.
• Solar energy received on the ground level is affected by
atmospheric clarity, degree of latitude, etc.
• For design purpose, the variation of available solar power, the
optimum tilt angle of solar flat plate collectors, the location
and orientation of the heliostats should be calculated.
Introduction
• The sun radiates about 3.8 x 1026 W of power in all the
directions.
– Out of this about 1.7 x 1017 W is received by earth.
• The average solar radiation outside the earth’s atmosphere is
1.35 kW/m2 varying from 1.43 kW/m2 (in January) to 1.33
kW/m2(in July).
• Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a
technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal
energy or electrical energy for use in industry, and in the
residential and commercial sectors.
• The first installation of solar thermal energy equipment
occurred in the Sahara Desert approximately in 1910
Solar Energy/Power
• In SI units, energy is expressed in Joule.
• Other units are angley and Calorie.
– 1 angley = 1 Cal/cm2.day
– 1 Cal = 4.186 J
• For solar energy calculations, the energy is measured as an
hourly or monthly or yearly average and is
• Expressed in terms of kJ/m2/day or kJ/m2/hour.
• Solar power is expressed in terms of W/m2 or kW/m2.
Essential subsystems in Solar Energy
• Solar collector or concentrator
• Energy transport medium
• Energy storage
• Energy conversion plant
• Power conditioning, control and protection system
• Alternative or standby power supply
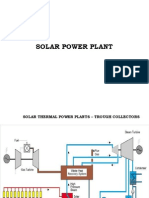
Solar thermal power plant with thermal
storage
Solar collector or concentrator
• Receives solar rays and collects the energy. Solar energy is
absorbed, transformed, and concentrated in a solar thermal collector
over a time or spatial gradient to produce usable energy.
– Flat plate type without focusing
– Parabolic trough type with line focusing
– Paraboloid dish with central focusing
– Fresnel lens with centre focusing
– Heliostats with centre receiver focusing
Classification of Solar collector
• Low (<150oC), Medium (150-300oC) or high-temperature
collectors.
• Low-temperature collectors are flat plates generally used to
heat swimming pools.
• Medium-temperature collectors are also usually flat plates but
are used for heating water or air for residential and commercial
use.
Classification of Solar collector
• High-temperature collectors concentrate sunlight using mirrors
or lenses and are generally used for fulfilling heat
requirements up to 300 degC/20 bar pressure in industries, and
for electric power production.
• Concentrated Solar Thermal (CST) for fulfilling heat
requirements in industries.
• Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) when the heat collected is
used for power generation.
• CST and CSP are not replaceable in terms of application.
Classification of Solar collector
• This heat is extracted by flowing fluid (air or water or mixture
with antifreeze) in the tube of the collector for further
utilization in different applications.
• Non concentrating collectors
• Concentrating (focusing) collectors
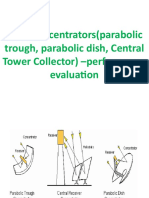
Solar Collector-1
• Solar radiation collection/concentration by parabolic trough
collector.
Parabolic Trough Collector
Solar Collector-2
• Solar radiation collection/concentration by linear Fresnel
collector.
Solar Collector-3
• Solar radiation collection/concentration by central receiver
system with dish collector.
Dish-Stirling prototype systems in Spain
Solar Collector-4
• Solar radiation collection/concentration by central receiver
system with distributed reflectors.
Central Receiver System
Energy Transport Medium
• Substances such as water/ steam, liquid metal or gas are used
to transport the thermal energy from the collector to the heat
exchanger or thermal storage.
• In solar PV systems energy transport occurs in electrical form..
Energy storage
• Solar energy is not available continuously. So we need an
energy storage medium for maintaining power supply during
nights or cloudy periods.
• There are three major types of energy storage
• Thermal energy storage
• Battery storage
• Pumped storage hydro-electric plant.
Energy conversion plant
• Thermal energy collected by solar collectors is used for
producing steam, hot water, etc.
• Solar energy converted to thermal energy is fed to steam-
thermal or gas-thermal power plant.
Thanks
You might also like
- Solar Power PlantDocument37 pagesSolar Power PlantARPIT RASTOGINo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument74 pagesSolar EnergySandeep BabuNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal TechnologiesDocument48 pagesSolar Thermal TechnologiesVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument33 pagesSolaranon_983696239100% (1)
- How to Install & Design Solar Panels Like a ProfessionalFrom EverandHow to Install & Design Solar Panels Like a ProfessionalNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy StorageDocument18 pagesSolar Energy StorageAkash Bhanse100% (1)
- Crocheted Fish PDFDocument10 pagesCrocheted Fish PDFAleyda Bonfil LeónNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal EnergyDocument35 pagesSolar Thermal EnergyMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy StorageDocument13 pagesSolar Energy StorageNandakumarNo ratings yet
- Coastal Suite For Tuba SoloDocument7 pagesCoastal Suite For Tuba SoloSusanna Payne-Passmore100% (1)
- Solar Thermal PowerDocument27 pagesSolar Thermal PowerRittick Ghosh100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Use of Digital Detector Arrays and Computed Radiology For Aerospace Casting Inspections PDFDocument32 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Digital Detector Arrays and Computed Radiology For Aerospace Casting Inspections PDFDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal PowerDocument30 pagesSolar Thermal Powerveerakumars0% (1)
- Synopsis On NIDDocument9 pagesSynopsis On NIDradhika bansal50% (8)
- Solar Energy HarvestingDocument45 pagesSolar Energy Harvestingramji_kkpNo ratings yet
- Solar Power PlantDocument16 pagesSolar Power PlantRajendran Srn100% (2)
- LymphomaDocument20 pagesLymphomaChairul Adilla Ardy100% (1)
- Olar Energy The Renewable Source of Energy: Prepared ByDocument28 pagesOlar Energy The Renewable Source of Energy: Prepared ByNilaya SinghNo ratings yet
- Virgin Galactic Profile & Performance Business ReportDocument10 pagesVirgin Galactic Profile & Performance Business ReportLoic PitoisNo ratings yet
- Solar Concentrators (Parabolic Trough, Parabolic Dish, CentralDocument34 pagesSolar Concentrators (Parabolic Trough, Parabolic Dish, Centralabhilashkrishnantk100% (2)
- Nursing Case Study - 1 - (Acs)Document32 pagesNursing Case Study - 1 - (Acs)nidhiNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy: Deepak B & Arunkumar Harshan C S S Mtech, ICTMDocument16 pagesSolar Energy: Deepak B & Arunkumar Harshan C S S Mtech, ICTMmanojNo ratings yet
- Bombardier Zefiro Technical Description enDocument15 pagesBombardier Zefiro Technical Description ennickerlesstezla100% (1)
- Energy Conversion DevicesDocument20 pagesEnergy Conversion Devicessanjay sajeevNo ratings yet
- Centralloy G4852 Micro R (Cast Austenitic Stainless Steel)Document2 pagesCentralloy G4852 Micro R (Cast Austenitic Stainless Steel)Anonymous w6TIxI0G8lNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal SystemDocument27 pagesSolar Thermal SystemMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesSolar Energy and ApplicationsSanath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Solar EnergyDocument176 pagesUnit 1 Solar EnergyAkhil Dayalu100% (1)
- Solar EnergyDocument39 pagesSolar Energysailaja kontiliNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal Energy Part 1Document19 pagesSolar Thermal Energy Part 1Tushar SanwareyNo ratings yet
- Solar IntroDocument26 pagesSolar IntroPavan Karthik MallelaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Solar Thermal EnergyDocument35 pagesUnit 2 Solar Thermal EnergyAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy SourcesDocument11 pagesRenewable Energy Sources18TUIT016 BALAKRISHNAN .PNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal EnergyDocument9 pagesSolar Thermal EnergyEeshaNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument9 pagesSolar EnergyM ZarakNo ratings yet
- Et PPTDocument31 pagesEt PPTHenrukh larrsonNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal Power PlantDocument18 pagesSolar Thermal Power PlantBARATH BALAJINo ratings yet
- Rer NotesDocument40 pagesRer NotesaakashNo ratings yet
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) : By: Hamza Badran and Ghaith Al-FarajDocument28 pagesConcentrated Solar Power (CSP) : By: Hamza Badran and Ghaith Al-FarajLayla SandyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Solar Energy and Wind EnergyDocument56 pagesUnit 3 - Solar Energy and Wind Energy2GI18AE001AKASH VERNEKARNo ratings yet
- 22661-Ret Notes-Unit 01 RetDocument16 pages22661-Ret Notes-Unit 01 Retjayeshdeore398No ratings yet
- Solar Energy:: Department of Electrical Engineering, Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology BurlaDocument3 pagesSolar Energy:: Department of Electrical Engineering, Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology Burlalhr1No ratings yet
- Unit 2: Solar Energy CollectionDocument40 pagesUnit 2: Solar Energy CollectionJaya RajNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document26 pagesWeek 6Ninja hatoriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.1 - Solar Electric Conversion - r1Document42 pagesLecture 5.1 - Solar Electric Conversion - r1Dum AccountNo ratings yet
- 15EAIME084 Ssolar Power TowersDocument16 pages15EAIME084 Ssolar Power TowersVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Solar Cells: G. Ram Kumar MVGR College of EngineeringDocument14 pagesSolar Cells: G. Ram Kumar MVGR College of Engineeringrk_gummaluri5334No ratings yet
- 2) Solar ThermalDocument49 pages2) Solar Thermalvishal9119No ratings yet
- Alternative Sources of Energy Unit 1Document5 pagesAlternative Sources of Energy Unit 1Avinash Kumar (RA1911001030001)No ratings yet
- UNIT-II Renewable Energy Sources - VIII SEM EEEDocument111 pagesUNIT-II Renewable Energy Sources - VIII SEM EEEPraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- RES-Solar CollectorsDocument55 pagesRES-Solar Collectorsasfvkjsv asgbaegbNo ratings yet
- Solar - Thermal - Energy Mohammad AlrashdanDocument26 pagesSolar - Thermal - Energy Mohammad Alrashdanمحمد الرشدانNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Types and UsesDocument12 pagesSolar Energy Types and UsesNancy TessNo ratings yet
- Solar Water HeaterDocument27 pagesSolar Water HeaterSantosh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal Power PlantDocument34 pagesSolar Thermal Power PlantKripa DevanNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal SystemDocument16 pagesSolar Thermal SystemPratik WakchaureNo ratings yet
- Teku Akhila 18331A01A8 3 Year Civil B' Section Ncse AssignmentDocument15 pagesTeku Akhila 18331A01A8 3 Year Civil B' Section Ncse AssignmentakhilaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy & Its UtilizationDocument32 pagesSolar Energy & Its UtilizationVamsidhar Reddy RNo ratings yet
- Eceg - 4242-SOLARDocument97 pagesEceg - 4242-SOLARaloitagu12No ratings yet
- Solar PowerDocument15 pagesSolar PowerSagar Gupta100% (1)
- Group No 2 PresentationDocument37 pagesGroup No 2 PresentationTabi RajputNo ratings yet
- Slide 6 Solar Ponds PlantsDocument25 pagesSlide 6 Solar Ponds PlantsPriyanshu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Solar Heating: Solar Energy Can Be Used For - Solar Water Heating - Solar Space Heating - Solar Pool HeatingDocument31 pagesSolar Heating: Solar Energy Can Be Used For - Solar Water Heating - Solar Space Heating - Solar Pool HeatingThiaga RajanNo ratings yet
- Solar Thermal - 2Document16 pagesSolar Thermal - 2Fiza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.2 - Solar Energy (Applications)Document67 pagesLecture 1.2 - Solar Energy (Applications)Dum AccountNo ratings yet
- Solar Power TecnologyDocument35 pagesSolar Power TecnologyNyityo PeterNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy and Solar PanelDocument19 pagesSolar Energy and Solar Panelkum1242No ratings yet
- Solarcollector 150223120848 Conversion Gate01Document12 pagesSolarcollector 150223120848 Conversion Gate01Jaya RajNo ratings yet
- SOLARDocument55 pagesSOLARP.KANAGA JOHN CHRISTNo ratings yet
- Review of The Householder's Guide To Community Defence Against Bureaucratic Aggression (1973)Document2 pagesReview of The Householder's Guide To Community Defence Against Bureaucratic Aggression (1973)Regular BookshelfNo ratings yet
- Easa Ad F-1998-537-124R1 1Document1 pageEasa Ad F-1998-537-124R1 1lakshmimurugesanNo ratings yet
- Particulate Ow at The Mouth of The Soummam Watershed (Algeria)Document9 pagesParticulate Ow at The Mouth of The Soummam Watershed (Algeria)bougheraraNo ratings yet
- History of Operating SystemDocument16 pagesHistory of Operating SystemBryan John BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Washback Effect in Teaching English As An International LanguageDocument13 pagesWashback Effect in Teaching English As An International LanguageUyenuyen DangNo ratings yet
- Pride&PrejudiceDocument88 pagesPride&PrejudiceMà Ř YãmNo ratings yet
- Traffic Monitoring SystemDocument16 pagesTraffic Monitoring Systemankit kumarNo ratings yet
- 02 - Thank You Maam Square Task CardsDocument8 pages02 - Thank You Maam Square Task CardsMaria Evelyn Won100% (1)
- Management of Developing DentitionDocument51 pagesManagement of Developing Dentitionahmed alshaariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)Document32 pagesChemistry: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)YinMyat MonNo ratings yet
- Peter Wink Resume Aug 2019Document1 pagePeter Wink Resume Aug 2019api-471317467No ratings yet
- 805-Article Text-3656-1-10-20220310Document16 pages805-Article Text-3656-1-10-20220310abolfazlshamsNo ratings yet
- BDU-BIT-Electromechanical Engineering Curriculum (Regular Program)Document187 pagesBDU-BIT-Electromechanical Engineering Curriculum (Regular Program)beselamu75% (4)
- Avamar - ADS Data Erasure-YES - I Understand All Data Will Be Lost by Performing This Procedure!Document30 pagesAvamar - ADS Data Erasure-YES - I Understand All Data Will Be Lost by Performing This Procedure!dansegui.mir4No ratings yet
- Penjelasan IMRAD StructureDocument2 pagesPenjelasan IMRAD Structureaji bondesNo ratings yet
- HECKMAN, J. James - Schools, Skills and SynapsesDocument36 pagesHECKMAN, J. James - Schools, Skills and SynapsesAndré Gonçalves OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 1620 Ultra High Speed: Continuous Ink Jet PrinterDocument8 pages1620 Ultra High Speed: Continuous Ink Jet PrinterRudiNo ratings yet
- Riddlesdown Collegiate HomeworkDocument7 pagesRiddlesdown Collegiate Homeworkgepuz0gohew2100% (1)
- HW 2Document12 pagesHW 2Munish RanaNo ratings yet
- "L8" Drive End: Operation - Assembly Instructions and Parts List ForDocument7 pages"L8" Drive End: Operation - Assembly Instructions and Parts List ForACCA PumpsNo ratings yet
- Snigdha Chaturvedi PDFDocument5 pagesSnigdha Chaturvedi PDFHitesh KohliNo ratings yet