Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JCDR 8 ZD06
Uploaded by
niken wibawaningtyasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JCDR 8 ZD06
Uploaded by
niken wibawaningtyasCopyright:
Available Formats
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/9308.
5248
Case Report
Management of Grade III Mobile
Dentistry Section
Anterior Tooth in Function Using
Endostabilizer – A Case Report
Vandana B.Kokane1, Swapnil N.Patil2
ABSTRACT
Impact of implant dentistry is such that today very few dentists think about saving grade III mobile anterior teeth. A patient with grade III
mobility of central incisor due to apical root resorption was treated by using 80 no.stainless steel ‘H’ file as endostabiliser and one year
follow up was done. Endostabiliser reduced the mobility of grade III mobile teeth drastically, immediately after its placement. Tooth was
absolutely asymptomatic throughout one year follow up.
Keywords: Endostabilizer, ‘H’-file,Root resorption, Mobility
Case repot with tooth, but patient was very happy as it saved her tooth from
A 35-year-old female patient reported to the Department of extraction. As mobility was reduced drastically, patient was not
Endodontics with grade III mobility of upper left central incisor (# - ready for flap surgery. Patient was recalled after every three months
21). Patient had complaint of pain while mastication only, otherwise to check the condition of the tooth and radiographs were taken.
she was all right in rest position. There was no relevant medical [Table/Fig-5-8].
history. Past dental history reveals history of trauma two years back.
She was on self-medication and did not report to any dentist. She Discussion
developed pain and discomfort while chewing since last two months With the recent influx of osseointegrated endosseous implant in
and thus came to the hospital for treatment. The Department of Oral dentistry, attention has been drawn away from using endostabiliser
diagnosis advised extraction but as the patient was not ready for as a means of stabilizing and retaining natural tooth [1].
extraction they referred the patient for opinion to the Department of Endostabiliser also called as diodontic implants or endodontic
Endodontics. On clinical examination, there was grade III mobility, endosseous implant is a device intended to be inserted through
fractured incisal edge and severe abrasion involving pulp with the root canal into a periapical affected bone to stabilize a tooth
mild tenderness. Radiographic examination revealed apical root of grade II or III mobility. These are the smooth or tapered rods
resorption with interdental bone resorption. No associated root of chromium cobalt or titanium. Rods matching the corresponding
fracture was seen [Table/Fig-1]. sizes of the root canal instruments cemented into the root canal so
Root canal treatment with endodontic stabilizer and coronal as to extend beyond the root end into periapical bone. It increases
composite restoration followed by flap surgery was planned. Inform the root length artificially and reduces tooth mobility drastically [2].
consent was taken from the patient. Patient was explained about Because of non-availability of these instruments, large number of
possible prognosis and longevity of the tooth. Before starting stainless steel root canal file can be used [3].
endotreatment sub-gingival scaling was done. After that access Use of endostabiliser presents a sound physiologic procedure
opening, working length determination and manual biomechanical for stabilizing mobile teeth that have lost considerable amount of
preparation up to 60 No. instrument was done. Irrigation alveolar support. It increases root length, alter root crown ratio,
protocol followed was sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) as initial and immobilize fractured root and periodontally compromised teeth or
chlorhexidine as final irrigant. While doing all this treatment, tooth supply combination of all these benefits [3,4]. When the resorption is
was stabilized with left hand index finger of the operator 70 and 80 severe enough to endanger the retention of tooth, an endoosseous
No. ‘H’ file were tried in the canal, 80 No. ‘H’ file was snugly fitting stabiliser can be placed through the root and extended into the
in the canal, thus selected as endostabiliser for the tooth. After root bone to stabilize the tooth artificially [5].
canal preparation the root apex is penetrated with 80 No. ‘H’ file Endodontic implant is indicated in (1) periodontally involved teeth
and extended apically 2 mm short of the original root apex and was requiring stabilisation (2) transverse root fracture (3) pathologic
checked radio graphically [Table/Fig-2]. resorption of root apex (4) tooth in which additional root length
Root canal was dried and coated with luting glass ionomer cement.
The 80 No. ‘H’ file is also coated with glass ionomer cement and
immediately fitted up to checked length and further screwed two
mm into resorbed root portion. Instrument was cut at the base of
pulp chamber with inverted cone diamond bur and access cavity
sealed with intermediate restorative material and radiograph was
taken [Table/Fig-3]. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic prescribed and
patient instructed to take it only if required .
Mobility of tooth was drastically reduced to grade I from grade III
immediately after placement of file as endostabilizer. Patient was
recalled after 15 days to check mobility of tooth and comfort of
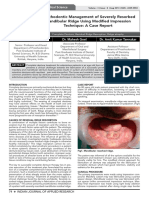
[Table/Fig-1]: Pre-operative radiograph with apical root resorption [Table/Fig-2]:
patient. Radiographic evaluation was done [Table/Fig-4]. Access Diagnostic x-ray trying H-file as endostabilizer [Table/Fig-3]: Post-operative
cavity sealed with composite resin, slight mobility was still present radiograph showing 80 no. H-file as Endo-stabilizer
6 Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2014 Dec, Vol-8(12): ZD06-ZD07
www.jcdr.net Vandana B.Kokane et al., Management of Grade III Mobile Anterior Tooth in Function Using Endostabiliser
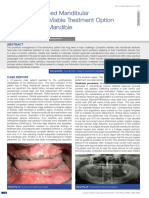
[Table/Fig-4]: Radiograph after 15 days [Table/Fig-5]: Radiograph after 3 months [Table/Fig-6]: Radiograph after 6 months [Table/Fig-7]: Radiograph after 9 months [Table/
Fig-8]: Radiograph after 12 months
is desired for improving alveolar support (5) extensive internal carry mobile tooth until it is lost eventually. Though there is a mixed
resorption affecting the integrity and strength of the root( 6) pulpless response for use of endostabiliser it can be used for their simplicity
tooth with unusually short root (7) previous apical surgeries which in procedure and affordable to poor patients.
leads to undue mobility [3-7].
Contraindicated in(1) active progressive periodontal disease Conclusion
associated with the tooth (2) periodontal communication (probing Although endoimplants have lost a primary role in dentistry, in
defect) near the apex of the tooth (3) anatomical structure in close some limited circumstances they may be good substitute for
proximity of apex of the tooth [7]. tooth extraction. In case of anterior teeth, endostabiliser is like a
As per patient’s expectation endostabiliser is a quick, effective, boon to the patients as it reduces mobility of the tooth drastically,
and economic treatment to save the tooth. The use of larger no. of immediately after its placement. And even if there is poor prognosis
stainless steel ‘H’ file for stabilization of tooth makes the procedure with endostabiliser, patient can think for extraction in future. But
simple and easy. Though studies have contraindicated the use of today he can leave dental office with his own tooth and smile on
stainless steel in close proximity to bone, the use of stainless steel face by opting very simple procedure of endostabiliser.
file was successful in this case [8]. The radiograph clearly showed
adequate bone regeneration in periradicular area. As glass ionomer References
cement is biological acceptable material to periodontal tissue, [1] Feldman H, Feldman G. Endodontic stabiliser. Journal of Endodontic.
1992;18(5):245-48.
use of this cement for coating root canal wall and file to stabilize [2] Nichels E, Torabenjed M. Endostabiliser, endodontic adjutants in Endo, 3rd
in the canal as well as in bone proved successful. It also acts as edition, 1995 : 469 - 77.
supplementary obturating material. [3] Silverbrand H, Rabkin M, Cranin AN. The use of endodontic implant stabilizer in
post traumatic and periodontal diseases. Oral Surgery OM OP. 1978;45(6):920-
With proper case selection, procedure is simple and straightforward 29.
with less chances of damage to vital structure. In one-year follow up [4] Franklin S Weine. Survival of endodontic endosseous implant. J of Endodontis.
mobility of tooth reduced drastically. This type of procedure using 1993;19: 524.
root canal instrument to stabilize root fracture can also be done. [5] Arens DE. An alternative treatment for severely resorbed maxillary lateral incisor.
J of Endodontics. 1995;21(2):95-100.
Because of drastic decrease in mobility of tooth, initial success rate [6] Stephan Cohen, Kenneth Hargreaves. Pathways of the pulp; 9th edition 2006. P.
were reported in literature [8-11]. 637-38.
[7] Endodontic implant/ certified fixed orthodontic courses by Indian dental academy
The reduced crown root ratio can be improved by placement of by Indian dental association on march 19 ,2013.
an inert chrome-cobalt alloy or stainless steel endoimplant. Careful [8] Priyadarshani L, Laxminarayan L. Endodontic miscellanary : Use of endodontic
case selection with proper technique, intraosseous endodontic file as an endodontic implant. Endodontology. 2000;12:37-39.
implant or endodontic stabilizer are safe and effective [12,13]. [9] FARZAD SALEHZ POVR/IRAN – Endodontic stabiliser. Endodontic Journal.
3/2005. 17-18.
‘H’ file was used as endostabiliser because threaded stabilizer [10] Girish Parmar, Pramod kumar AV. Custom fabricated endodontic implant :
gives significantly stronger retention and also has the advantage Report of two cases. J of Endodontic. 2000;26(5):301-03.
[11] James H Simen, Alfred L Frank – Endodontic stabilizer, additional histologic
of transmitting masticatory stresses to bone through the threads
evaluation. J of Endodontics. 1980;6( 2):450-55.
of the rod [14]. The procedure is less time consuming and invasive [12] J Edgar, Valdivia Cardenas, Enrique Hair Salas Beltran, Felipe Hernandez Ananos.
as compared to extraction and then fixed bridge or implant. Long Niti endodontic intraosseous implant. Dental press Endod. 2012;2(1):38-41.
history of trauma without any treatment causes apical root resorption, [13 Sunandan Mittal, Tarun Kumar, Vishal Aggarwal, Ramta Bansal, Dilpreet Kaur.
Endodontic stabilizers for treating mid rootfractures. Journal of Interdisciplinary
which reduces root length and crown ratio causes mobility of that Dentistry. 2011;1(2): 108-11.
tooth, which is also enhances by periodontal problems. Being [14] Maniatopoulos C, Piller RM & Smith DC. Evaluation of the retention of endodontic
anterior tooth, generally patient refuses for extraction and prefer to implant. J of Prosthetic Dent. 1988;59:438-46.
PARTICULARS OF CONTRIBUTORS:
1. Reader, Department of Conservative Dentistry, VSPM’S Dental College & Research Centre, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
2. Lecturer, Department of Conservative Dentistry, VSPM’S Dental College & Research Centre, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
NAME, ADDRESS, E-MAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR:
Dr. Vandana B.Kokane,
2/1, MIG 20, Ridge Road, Near Tukdoji Square, Nagpur-440 027, India. Date of Submission: Mar 17, 2014
Phone : +91-09371404603, E-mail : vandana_kokane@yahoo.com Date of Peer Review: Jul 05, 2014
Date of Acceptance: Jul 19, 2014
Financial OR OTHER COMPETING INTERESTS: None. Date of Publishing: Dec 05, 2014
Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2014 Dec, Vol-8(12): ZD06-ZD07 7
You might also like
- Short ImplantsFrom EverandShort ImplantsBoyd J. TomasettiNo ratings yet
- Treatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsFrom EverandTreatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsNo ratings yet
- Immediate Natural Tooth Pontic - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesImmediate Natural Tooth Pontic - A Case ReportInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Rehabilitation Using Attachment Retained Overdenture - Case ReportsDocument7 pagesProsthodontic Rehabilitation Using Attachment Retained Overdenture - Case ReportsIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Avulsion and Replacement of The Tooth Element Fractured at The Level of The Middle A Case ReportDocument5 pagesAvulsion and Replacement of The Tooth Element Fractured at The Level of The Middle A Case ReportDr.O.R.GANESAMURTHINo ratings yet
- Flexible Thermoplastic Denture Base PDFDocument2 pagesFlexible Thermoplastic Denture Base PDFFitriana WadianurNo ratings yet
- New Treatment Option For An Incomplete Vertical Root Fracture Case StudyDocument4 pagesNew Treatment Option For An Incomplete Vertical Root Fracture Case StudyTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- 35 NiloferDocument5 pages35 NilofereditorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- Esthetic and Endodontic Management of A Deep Crown-Root Fracture of A Maxillary Central IncisorDocument4 pagesEsthetic and Endodontic Management of A Deep Crown-Root Fracture of A Maxillary Central IncisordrgozanNo ratings yet
- Flexible Dentures CaseDocument2 pagesFlexible Dentures CaseLuLu NikhlaturNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Prosdent 2020 03 025Document6 pages10 1016@j Prosdent 2020 03 025prostho booksNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument6 pagesContent ServerNicoll SQNo ratings yet
- Conventional Implant With Orthodontic Treatment For Anterior Missing Tooth ManagementDocument2 pagesConventional Implant With Orthodontic Treatment For Anterior Missing Tooth ManagementErwin SutonoNo ratings yet
- A 5 Year of Evaluation of The MaxillaryDocument4 pagesA 5 Year of Evaluation of The MaxillaryConsultorio dentarioNo ratings yet
- Intentional Re-Plantation of A Vertically Fractured Tooth Repaired With An Adhesive ResinDocument10 pagesIntentional Re-Plantation of A Vertically Fractured Tooth Repaired With An Adhesive Resinveena rNo ratings yet
- The Bio-Col TechniqueDocument9 pagesThe Bio-Col TechniquewnelsenNo ratings yet
- Use of Polyethylene Ribbon To Create A Provisional Fixed Partial DentureDocument4 pagesUse of Polyethylene Ribbon To Create A Provisional Fixed Partial DentureAhmed AbdulazeezNo ratings yet
- 2016 Salvation of Severely Fractured Anterior Tooth An Orthodontic ApproachDocument4 pages2016 Salvation of Severely Fractured Anterior Tooth An Orthodontic ApproachRajesh GyawaliNo ratings yet
- 55 - 2987Document2 pages55 - 2987Huma ZafarNo ratings yet
- RestorationDocument5 pagesRestorationFathira AiniNo ratings yet
- Kaldenbach Carina Articol EPI Engleza PDFDocument9 pagesKaldenbach Carina Articol EPI Engleza PDFFlorin UngureanuNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Topics Volume 31 Issue 1 2014 (Doi 10.1111/etp.12066) Baba, Nadim Z. Goodacre, Charles J. - Restoration of Endodontically Treated Teeth - Contemporary Concepts andDocument16 pagesEndodontic Topics Volume 31 Issue 1 2014 (Doi 10.1111/etp.12066) Baba, Nadim Z. Goodacre, Charles J. - Restoration of Endodontically Treated Teeth - Contemporary Concepts andardeleanoana100% (1)
- Third Molar Autotransplant Planning With A Tooth Replica. A Year of Follow-Up Case ReportDocument6 pagesThird Molar Autotransplant Planning With A Tooth Replica. A Year of Follow-Up Case ReportAlNo ratings yet
- Cu Sil DenturesDocument6 pagesCu Sil Denturessiddu76No ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedDocument2 pagesProsthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedAamir BugtiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Applications of Biodentine: A Case Series: Ase EportDocument5 pagesClinical Applications of Biodentine: A Case Series: Ase EportpoojaNo ratings yet
- JCDR 8 ZD04Document3 pagesJCDR 8 ZD04rajaniNo ratings yet
- AAE Newsletter Covers Endodontic TreatmentDocument6 pagesAAE Newsletter Covers Endodontic TreatmentMehwish MunawarNo ratings yet
- Temporary Flexible Removable Partial DentureDocument4 pagesTemporary Flexible Removable Partial DentureenipurwantiNo ratings yet
- Management of Transverse Root Fracture by Dowel - Inlay: A Case ReportDocument9 pagesManagement of Transverse Root Fracture by Dowel - Inlay: A Case ReportAdzhani SabilaNo ratings yet
- An 2/2 Implant Overdenture: Case ReportDocument3 pagesAn 2/2 Implant Overdenture: Case ReportasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Treatment Using Vital and Non Vital Submerged Roots-Two Case ReportsDocument5 pagesProsthodontic Treatment Using Vital and Non Vital Submerged Roots-Two Case ReportsRoro MoonNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Telescopic Overdenture and Implant Supported Fixed Partial Denture: A Pragmatic Treatment ApproachDocument8 pagesCase Report: Telescopic Overdenture and Implant Supported Fixed Partial Denture: A Pragmatic Treatment ApproachJyoti VermaNo ratings yet
- Conservative Mangement of Tilted AbutmentsDocument3 pagesConservative Mangement of Tilted Abutmentsrayavarapu sunilNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Extrusion of Premolar Teeth - An Improved TechniqueDocument6 pagesOrthodontic Extrusion of Premolar Teeth - An Improved TechniquejorgeNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitating Severely Worn Dentition Using Shortened Dental Arch ConceptDocument5 pagesRehabilitating Severely Worn Dentition Using Shortened Dental Arch Conceptsarah wilderNo ratings yet
- Dentistry: The Use of Indirect Resin Composites in Clinical Practice: A Case SeriesDocument6 pagesDentistry: The Use of Indirect Resin Composites in Clinical Practice: A Case SeriesDebora NatalynaNo ratings yet
- Gigi Tiruan GasketDocument5 pagesGigi Tiruan GasketGus BasyaNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument4 pagesArticleDrRahul Puri GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Protesis Fija Con Ataches. Rep Caso. 2020. Cureus. SivakumarDocument13 pagesProtesis Fija Con Ataches. Rep Caso. 2020. Cureus. SivakumarAngela AcostaNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Ridge Preservation in A Growing Patient With Decoronation. One-Year Follow-UpDocument3 pagesAlveolar Ridge Preservation in A Growing Patient With Decoronation. One-Year Follow-UpAnaMariaCastroNo ratings yet
- 6.clinical Case ReportMultidisciplinary Approach For Rehabilitation of Debilitated Anterior ToothDocument6 pages6.clinical Case ReportMultidisciplinary Approach For Rehabilitation of Debilitated Anterior ToothSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation of The Patient With Severly Worn Out Dentition A Case Report.Document5 pagesFull Mouth Rehabilitation of The Patient With Severly Worn Out Dentition A Case Report.sivak_198100% (1)
- MainDocument11 pagesMainDentist HereNo ratings yet
- Pin-Retained Restoration With Resin Bonded Composite of A Badly Broken ToothDocument3 pagesPin-Retained Restoration With Resin Bonded Composite of A Badly Broken ToothIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Tooth-Support Over Dentures: An Approach To Preventive ProsthodonticsDocument5 pagesTooth-Support Over Dentures: An Approach To Preventive ProsthodonticsAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Repair of Peri-Implant Bone Loss After Occlusal AdjustementDocument6 pagesRepair of Peri-Implant Bone Loss After Occlusal AdjustementAnaïs CATELINNo ratings yet
- Natural Tooth Pontic in Periodontally Compromised ToothDocument5 pagesNatural Tooth Pontic in Periodontally Compromised ToothAmar BhochhibhoyaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Prosthesis for Tooth RetentionDocument4 pagesHybrid Prosthesis for Tooth RetentionGowriKrishnaraoNo ratings yet
- Reattachment of Anterior Teeth Fragments With Two Different Treatment Techniques: Report of Two CasesDocument2 pagesReattachment of Anterior Teeth Fragments With Two Different Treatment Techniques: Report of Two CasesPawan RajNo ratings yet
- Asian Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument7 pagesAsian Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryMichaelAndreasNo ratings yet
- Biologically Oriented Preparation Technique For SurgicallyDocument6 pagesBiologically Oriented Preparation Technique For SurgicallyAbdelrahman Galal100% (1)
- OverdentureDocument47 pagesOverdenturemohid sheikhNo ratings yet
- Article WMC004708 PDFDocument5 pagesArticle WMC004708 PDFAnonymous 2r6nHhNo ratings yet
- Conservative Approach For Management of Complicated Crown Facture Using Tooth Fragment Reattachment TechniqueDocument4 pagesConservative Approach For Management of Complicated Crown Facture Using Tooth Fragment Reattachment TechniqueEseman DentalNo ratings yet
- Reimplantation of Avulsed Teeth After Dry Storage For One WeekDocument5 pagesReimplantation of Avulsed Teeth After Dry Storage For One WeekHesti RahayuNo ratings yet
- RETHINKING FERRULEDocument7 pagesRETHINKING FERRULEpoojaNo ratings yet
- Management of Periodontally Involved Anterior Teeth by Glass Fiber-Reinforced Composite Splinting: A Clinical Report With 5-Year RecallDocument6 pagesManagement of Periodontally Involved Anterior Teeth by Glass Fiber-Reinforced Composite Splinting: A Clinical Report With 5-Year RecallmarethadwiNo ratings yet
- Management of Fractured Lateral Incisor by Surgical Extrusion and Its Prosthetic RehabilitationA Case ReportDocument5 pagesManagement of Fractured Lateral Incisor by Surgical Extrusion and Its Prosthetic RehabilitationA Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Osteoperiosteal Flap: A Simplified Approach to Alveolar Bone ReconstructionFrom EverandThe Osteoperiosteal Flap: A Simplified Approach to Alveolar Bone ReconstructionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: Amir E. Ibrahim, M.DDocument11 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Amir E. Ibrahim, M.DkendoNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 68Document10 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 68sarasjunkNo ratings yet
- FDAR - Salimbagat - HemodialysisDocument2 pagesFDAR - Salimbagat - HemodialysisChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Power Point PresentationDocument6 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome Power Point Presentationapi-237061134No ratings yet
- Jejunostomy Feeding Tube Placement in GastrectomyDocument14 pagesJejunostomy Feeding Tube Placement in GastrectomyHarshit UdaiNo ratings yet
- Day Case Surgery SajeebDocument34 pagesDay Case Surgery SajeebMahbubur Rahman0% (1)
- Pak Orthocon Suppl - GPDocument110 pagesPak Orthocon Suppl - GPhishamkhan002No ratings yet
- Tumors of External and Middle EarDocument42 pagesTumors of External and Middle EarAmiteshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- TOC MillerDocument5 pagesTOC MillerNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- UltrasoundSonographerTechnologist SkillsChecklistDocument3 pagesUltrasoundSonographerTechnologist SkillsChecklistmaureenNo ratings yet
- National College of Nursing: Procedure ONDocument6 pagesNational College of Nursing: Procedure ONSumit Yadav100% (1)
- 2015 ESC Guidelines For The ManagementDocument59 pages2015 ESC Guidelines For The ManagementSri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- PMLS Lesson 4Document3 pagesPMLS Lesson 4Void MelromarcNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Revolution in Bhubaneswar Drives Growth of Medical IndustryDocument9 pagesHealthcare Revolution in Bhubaneswar Drives Growth of Medical IndustryBirupakshya RoutNo ratings yet
- Dr Hira Ali's CV for General SurgeonDocument7 pagesDr Hira Ali's CV for General SurgeonRhea PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Claire La Chapelle Complete PDFDocument244 pagesClaire La Chapelle Complete PDFhuyenthanh1807No ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDocument21 pagesAbdominal Pain in ChildrenDaniel RajNo ratings yet
- Proper Patient Positioning and Draping TechniquesDocument27 pagesProper Patient Positioning and Draping TechniquesJennifer Solano Cruel100% (5)
- Laboratories and Results: Physical PropertiesDocument5 pagesLaboratories and Results: Physical PropertiesBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- MCN Test 2 AnswerDocument3 pagesMCN Test 2 AnswerJhessel CelosoNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery Procedure Charges DraftDocument8 pagesNeurosurgery Procedure Charges DraftRam Kumar ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Procedural Checklist For Tracheostomy CareDocument6 pagesProcedural Checklist For Tracheostomy CareAbegail TabuniagNo ratings yet
- 85-6403 e (C) F (T) PF1 (MH) Pfa (H)Document3 pages85-6403 e (C) F (T) PF1 (MH) Pfa (H)ikeuchi_ogawaNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Point of Care Ultrasound (2023)Document388 pagesCardiopulmonary Point of Care Ultrasound (2023)xf5tsxrgypNo ratings yet
- Onsillectomy and Denoidectomy: Thomas N. ToldDocument9 pagesOnsillectomy and Denoidectomy: Thomas N. Toldmuthia yuniarta sinagaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Surgery Logbook Batch A - EditedDocument11 pagesPlastic Surgery Logbook Batch A - EditedRidham RanaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rubi Li not liable for failure to disclose chemotherapy side effectsDocument2 pagesDr. Rubi Li not liable for failure to disclose chemotherapy side effectsBasil MaguigadNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthetic Drugs 3 Power Point PresentationDocument30 pagesLocal Anaesthetic Drugs 3 Power Point PresentationJosef Cefai100% (1)
- HEMMORRHOIDECTOMYDocument16 pagesHEMMORRHOIDECTOMYLily CentenoNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesMyocardial Infarctionجعفر محمدNo ratings yet