Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Informasi Produk Iritero 5 ML
Informasi Produk Iritero 5 ML
Uploaded by
Wawan MalawatOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Informasi Produk Iritero 5 ML
Informasi Produk Iritero 5 ML
Uploaded by
Wawan MalawatCopyright:
Available Formats
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
ARTWORK BOX
Batch No.:
Mfg. Date:
Exp. Date:
HET:
Batch coading Expressions will be coded online
along with actual batch details
Details
For Batch coding
Un Varnish Area
2xxxxxx
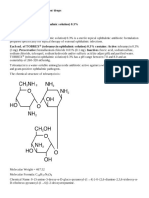
Each mL contains Irinotecan Hydrochloride Mfg. Lic. No.: 28/MN/AP/2011/F/R
trihydrate 20 mg equivalent to
Irinotecan 17.32 mg
Dosage: As directed by the physician.
IRITERO IRITERO Reg. No.:
Irinotecan Hydrochloride Route of administration: Intravenous Irinotecan Hydrochloride
Trihydrate Trihydrate
Store below 30°C and protect from light.
Injection 20 mg/mL Injection 20 mg/mL Manufactured by:
HETERO LABS LIMITED
After Reconstitution: With 0.9% Sodium UNIT-VI, Telangana, INDIA
5 mL single use vial Chloride Injection, the solution is stable 5 mL single use vial
within 24 hours at room temperature.
With 5% Dextrose Injection, the solution
is stable within 6 hours at room
temperature or within 24 hours at Imported and Marketed by :
CYTOTOXIC DRUG temperature 2 - 8°C. CYTOTOXIC DRUG PT. AMAROX PHARMA GLOBAL
Bekasi-Indonesia
Keep out of reach of children.
ON MEDICAL PRESCRIPTION ONLY/
HARUS DENGAN RESEP DOKTER
Refer product insert for more information.
Dimensions: 52 x 35 x 75 mm Font Type:
Colours: 4
01 PANTONE 2766 C
Brand Name: Gotham Bold 13 pt
02 Black
03 PANTONE 485 C
Generic Name: Gotham Bold 10.4 pt
04 PANTONE 1925 C
05 PANTONE 7463 C
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
IRITERO
Irinotecan HCl Trihydrate
Concentrate for solution for infusion
COMPOSITIONS :
IRITERO Concentrate for solution for infusion 40 mg/2 mL and 100 mg/5 mL, each mL contains
: Irinotecan HCl Trihydrate 20 mg euivalent to Irinotecan 17.32 mg.
PHARMACOLOGY :
Pharmacodynamic :
Therapeutic class
Irinotecan Hydrochloride is an antineoplastic agent of the topoisomerase I inhibitor class.
Irinotecan is a semisynthetic derivative of Camptothecin, an alkaloid extract from plants such as
Camptotheca acuminata, or is chemically synthesized.
Mechanism of action
Irinotecan and its active metabolite SN-38 bind to the topoisomerase I – DNA complex and
prevent re-ligation of these single-strand breaks. Current research suggests that the cytotoxicity of
Irinotecan is due to double-strand DNA damage produced during DNA synthesis when replication
enzymes interact with the ternary complex formed by topoisomerase I, DNA, and either
Irinotecan or SN-38.
Irinotecan serves as a water-soluble precursor of the lipophilic metabolite SN-38. SN-38 is
formed from Irinotecan by carboxylesterase-mediated cleavage of the Carbamate bond between
the Camptothecin moiety and the dipiperidino side chain. SN-38 is approximately 1000 times as
potent as Irinotecan as an inhibitor of topoisomerase I. The precise contribution of SN-38 to the
activity of Irinotecan is thus unknown. Both Irinotecan and SN-38 exist in an active lactone form
and an inactive hydroxy acid anion form. A pH-dependent equilibrium exists between the two
forms such that an acid pH promotes the formation of the lactone, while a more basic pH favors
the hydroxy acid anion form.
Pharmacokinetics in special populations :
Geriatric
No differences in the pharmacokinetics of Irinotecan, SN-38, and SN-38 glucuronide in patients <
65 years of age compared with patients ≥ 65 years of age.
Gender
The pharmacokinetics of Irinotecan do not appear to be influenced by gender.
Race
The influence of race on the pharmacokinetics of Irinotecan has not been evaluated.
Hepatic insufficiency
Irinotecan clearance is diminished in patients with hepatic dysfunction while relative exposure to
the active metabolite SN-38 is increased. The magnitude of these effects is proportional to the
degree of liver impairment as measured by elevations in serum total bilirubin and transaminase
concentrations.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Renal insufficiency
The influence of renal insufficiency on the pharmacokinetics of Irinotecan has not been evaluated.
INDICATIONS :
IRITERO is indicated for the treatment of patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
- In combination with 5-fluorouracil and Folinic acid in patients without prior chemotherapy for
advanced disease.
- As a single agent in patients who have failed an established 5-fluorouracil containing treatment
regimen.
Irinotecan combination with Cisplatin is indicated for treatment of patients with small cell lung
cancer.
Strictly follow the recommended dosage unless directed otherwise by the physician.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
IRITERO is contraindicated in patients with :
- A chronic inflammatory bowel disease and/or a bowel obstruction.
- A history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to Irinotencan Hydrochloride Trihydrate or to one
of the excipients of IRITERO.
- In pregnant or breast feeding women.
- In patient with bilirubin > 3 times the ULN.
- In patient with a severe bone marrow failure.
- In patient presenting a risk factor, particularly those with a WHO performance status > 2.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONS :
For adults only. IRITERO solution for infusion should be infused into a peripheral or central
vein.
- In monotherapy (for previously treated patients) :
The recommended dosage of IRITERO is 350 mg/m2 administered as an intravenous infusion
over a 30- to 90 minute period every three weeks.
- In combination therapy (for previously untreated patients) :
Safety and efficacy of IRITERO in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and Folinic acid
(FA) have been assessed with the following schedule. The recommended dosage of IRITERO
is 180 mg/m2 administered once every 2 weeks as an intravenous infusion over a 30- to 90-
minute period, followed by infusion with Folinic acid and 5-fluorouracil.
Irinotecan in combination with Cisplatin
The recommended starting dose is 65 mg/m2 of Irinotecan and 30 mg/m2 of Cisplatin. Cisplatin
infused prior Irinotecan. A lower starting dose of Irinotecan may be considered for patients with
any of the following conditions : Age 65 years and older, prior extensive radiotherapy,
performance status of 2, increased bilirubin levels, or gastric cancer. Treatment should be given in
repeated 6-week cycles, comprising days 1 and 8, every 21 days.
Irinotecan should be administeres as an intravenous infusion over 30 to 90 minutes.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Dosage adjustment :
IRITERO should be administered after appropriate recovery of all adverse events to grade 0 or 1
NCI-CTC grading (National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria) and when treatment-
related diarrhea is fully resolved.
At the start of a subsequent infusion of therapy, the dose of IRITERO, and 5FU when applicable,
should be decreased according to the worst grade of adverse events observed in the prior infusion.
Treatment should be delayed by 1 to 2 weeks to allow recovery from treatment-related adverse
events. With the following adverse events a dose reduction of 15% to 20% should be applied for
IRITERO and/or 5FU when applicable : Haematological toxicity (neutropenia grade 4), febrile
neutropenia (neutropenia grade 3 - 4 and fever grade 2 - 4), thrombocytopenia and leukopenia
(grade 4), non-hematological toxicity (grade 3 - 4).
Duration of treatment :
For both single-agent and combination-agent regimens, treatment with additional cycles of
Irinotecan may be continued indefinitely in patients who attain a tumor response or in patients
whose cancer remains stable. Patients should be carefully monitored for toxicity and should be
removed from therapy if unacceptable toxicity occurs that responsive to dose modifications and
routine supportive care.
Modification recommendations :
Recommended dose modification for Irinotecan and Cisplatin for the start of each cycle of
therapy are described in Table 1, while recommended dose modifications during a cycle of
therapy are described in Table 2.
Table 1. Dose modifications at the start of a new cycle of the Cisplatin and Irinotecan
(mg/m2) combination schedule – based on the worst toxicity observed in the prior cycle
A new cycle of therapy should not begin until the granulocyte count has recovered to ≥
1500/mm3, and the platelet count has recovered to ≥ 100,000/mm3, serum creatinine ≤ 1.7 mg/dL
or ≤ 130 µmol/L, and treatment-related non-hematologic toxicities (excluding alopecia) are
resolved to ≤ grade 1. Treatment should be delayed 1 to 2 weeks to allow for recovery from
treatment-related toxicities. If the patient has not recovered after a 2-week delay, consideration
should be given to discontinuing Irinotecan.
Toxicity Cisplatinb Irinotecanc
NCI gradea
HEMATOLOGIC
Neutropenia/Thrombocytopenia
Grade 0, 1, 2, or 3 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 4 ↓ 1 dose level ↓ 1 dose level
Febrile neutropenia , sepsis, ↓ 2 dose level
d
↓ 2 dose level
thrombocytopenia requiring
transfusion
NON-HEMATOLOGIC
Diarrhea
Grade 0, 1 or 2 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Grade 3 or 4 Maintain dose level ↓ 1 dose level
Vomiting
Grade 0, 1 or 2 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 3 ↓ 1 dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 4 ↓ 1 dose level ↓ 1 dose level
Serum creatinine
≤ 1.7 mg/dL Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
> 1.7 - 2.0 mg/dL ↓ 3 dose level Maintain dose level
> 2.0 mg/dL Discontinue Cisplatin Maintain dose level
Ototoxicity
Grade 0 or 1 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 2 ↓ 2 dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 3 or 4 Discontinue Cisplatin Maintain dose level
Neurotoxicity
Grade 0 or 1 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 2 ↓ 2 dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 3 or 4 Discontinue Cisplatin Maintain dose level
OTHER NON-HEMATOLOGIC TOXICITIES (Except Alopecia)
Grade 0, 1 or 2 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 3 or 4 ↓ 1 dose level ↓ 1 dose level
a
National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria
b
Cisplatin : Dose level reductions = 5 mg/m2 decrements
c
Irinotecan : Dose level reductions = 10 mg/m2 decrements
d
Febrile neutropenia is defined as in CTC version 2 : Temperature ≥ 38.5oC concomitant with an
ANC < 1.0 x 109L.
Table 2. Dose modifications for day 8 of the Cisplatin and Irinotecan (mg/m2) combination
schedule based on the worst toxicity observed in the prior cycle
Toxicity Cisplatinb Irinotecanc
NCI gradea
HEMATOLOGIC
Neutropenia/Thrombocytopenia
Grade 0 or 1 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 2 ↓ 1 dose level ↓ 1 dose level
Grade 3 ↓ 2 dose level ↓ 2 dose level
Grade 4 Omit dose Omit dose
d
Febrile neutropenia , sepsis, Omit dose Omit dose
thrombocytopenia requiring
transfusion
NON-HEMATOLOGIC
Diarrhea
Grade 0 or 1 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 2 Maintain dose level ↓ 1 dose level
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Grade 3 Maintain dose level Omit dose
Grade 4 Omit dose Omit dose
Vomiting
Grade 0, 1 or 2 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 3 ↓ 1 dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 4 ↓ 1 dose level ↓ 1 dose level
Serum creatinine
≤ 1.7 mg/dL Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
> 1.7 – 2.0 mg/dL ↓ 2 dose level Maintain dose level
> 2.0 mg/dL Discontinue Cisplatin Maintain dose level
Ototoxicity
Grade 0 or 1 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 2 ↓ 1 dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 3 or 4 Discontinue Cisplatin Maintain dose level
Neurotoxicity
Grade 0 or 1 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 2 ↓ 1 dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 3 or 4 Discontinue Cisplatin Maintain dose level
OTHER NON-HEMATOLOGIC TOXICITIES (Except Alopecia)
Grade 0 or 1 Maintain dose level Maintain dose level
Grade 2, 3, 4 Omit dose Omit dose
a
National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria
b
Cisplatin : Dose level reductions = 5 mg/m2 decrements
c
Irinotecan : Dose level reductions = 10 mg/m2 decrements
d
Febrile neutropenia is defined as in CTC version 2 : Temperature ≥ 38.5oC concomitant with an
ANC < 1.0 x 109L.
Special population :
Elderly
The dose should be chosen carefully in this population due to their greater frequency of decreased
biological functions. These populations should require more intensive surveillance.
Patients with impaired hepatic function
In monotherapy : In patients with hyperbilirubinemia and prothrombin greater than 50%, the
clearance of Irinotecan is decreased and therefore, the risk of hematotoxicity is increased. Thus,
frequent monitoring of complete blood counts should be conducted in this patient population.
- In patients with bilirubin up to 1.5 times the upper limit of the normal range (ULN), the
recommended dosage of IRITERO is 350 mg/m2.
- In patients with bilirubin ranging from 1.5 to 3 times the ULN, the recommended dosage of
IRITERO is 200 mg/m2.
- Patients with bilirubin beyond to 3 times the ULN should not be treated with IRITERO.
No data are available in patients with hepatic impairment treated by IRITERO in combination.
Patients with impaired renal functions
IRITERO is not recommended for use in patients with impaired renal functions.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Preparation and handling :
As with other antineoplastic agents, IRITERO must be prepared and handled with caution. The
usage of glasses, mask and gloves is required. If IRITERO solution or infusion solution come
into contact with the mucus membranes, wash immediately with water.
Preparation for intravenous infusion administration :
As with any other injectable drugs, the IRITERO solution must be prepared aseptically. If any
precipitate is observed in the vials or after reconstitution, the product should be discarded
according to standard procedurs for cytotoxic agents. Aseptically withdraw the required amount
of IRITERO solution from the vial with a calibrated syringe and inject into a 250 ml infusion bag
or bottle containing either 0.9% Sodium chloride solution or 5% Dextrose solution. The infusion
is then thoroughly mixed by manual rotation.
Administration :
IRITERO solution for infusion should be infused into a peripheral or central vein. IRITERO
should not be delivered as an intravenous bolus or an intravenous infusion shorter than 30 minutes
or longer than 90 minutes.
Disposal :
All material used for dilution and administration should be disposed of according to hospital
standard procedure applicable to cytotoxic agents.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
- Administration : Irinotecan should be administered only under the supervision of a physician,
who is experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Appropriate management of
complications is possible only when adequate diagnostic and treatment facilities are readily
available.
- Irinotecan will only be prescribed in the following cases after the expected benefits have been
weighed against the possible therapeutic risks :
a. In patients presenting a risk factor, particularly those with a WHO performance status = 2.
b. In the few instances where patients are deemed unlikely to observe recommendations
regarding management of adverse events (need for immediate and prolonged antidiarrheal
treatment combined with high fluid intake at onset of delayed diarrhea). Strict hospital
supervision is recommended for such patients.
- Cholinergic symptoms : Patients may have cholinergic symptoms of rhinitis, increased
salivation, miosis, lacrimation, diaphoresis, flushing (vasodilation), bradycardia, and intestinal
hyperperistalsis that can cause abdominal cramping and early diarrhea (i.e., diarrhea generally
occurring during or within 8 hours of administration of Irinotecan). These symptoms may be
observed during or shortly after infusion of Irinotecan, are thought to be related to the
anticholinesterase activity of the Irinotecan parent compound, and are expected to occur more
frequently with higher Irinotecan doses. Therapeutic or prophylactic administration of 0.25 to 1
mg of intravenous or subcutaneous Atropine should be considered (unless contraindicated) in
patients experiencing cholinergic symptoms.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
- Extravasation : While Irinotecan is not a known vesicant, care should be taken to avoid
extravasation, and the infusion site should be monitored for signs of inflammation. Should
extravasation occur, flushing the site, and application of ice is recommended.
- Hepatic : National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Toxicity Criteria grade 3 or 4 liver enzyme
abnormalities have been observed. These events typically occur in patients with known hepatic
metastases and are not clearly related to Irinotecan.
- Hematology : Irinotecan causes neutropenia, leukopenia, and anemia, any of which may be
severe and therefore should not be used in patients with severe bone marrow failure. Serious
thrombocytopenia is uncommon. The frequency of NCI grade 3 and 4 neutropenia has been
significantly higher in patients who received previous pelvic/abdominal irradiation than in those
who had not received such irradiation. Patients with baseline serum total bilirubin levels of 1.0
mg/dL or more also have had a significantly greater likelihood of experiencing first-cycle grade
3 or 4 neutropenia than those with bilirubin levels that were less than 1.0 mg/dL. There were no
significant differences in the frequency of grade 3 and 4 neutropenia by age or gender.
Neutropenic fever (concurrent NCI grade 4 neutropenia and ≥ grade 2 fever) occurred in
patients; however, deaths due to sepsis following severe neutropenia have been reported in
patients treated with Irinotecan. Neutropenic complications should be managed promptly with
antibiotic support. Therapy with Irinotecan should be temporarily discontinued if neutropenic
fever occurs or if the absolute neutrophil count drops below 1000/mm3. The dose of Irinotecan
should be reduced if significant neutropenia occurs.
- Patients with reduced UGT1A1 activity : The metabolic conversion of Irinotecan to the
active metabolite SN-38 is mediated by carboxylesterase enzymes and primarily occurs in the
liver. SN-38 subsequently undergoes conjugation to form the inactive glucuronide metabolite
SN-38G. This glucuronidation reaction is mediated primarily by uridine diphosphate-
glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1), which is encoded by the UGT1A1 gene. The
UGT1A1 gene is highly polymorphic, resulting in variable metabolic capacities among
individuals. One specific variation of the UGT1A1 gene includes a polymorphism in the
promotor region known as the UGT1A1 variant allele. This variant and other congenital
deficiencies in UGT1A1 expression (such as Crigler-Najjar and Gilbert’s syndrome) are
associated with reduced enzyme activity and increased systemic exposure to SN-38. Higher
plasma concentrations of SN-38 are observed in individuals who are homozygous for the
UGT1A1*28 allele (also reffered to as UGT1A1 7/6 genotype) versus patients who have one or
two wild-type alleles.
Patients who are homozygous (UGT1A1*6/*6 of UGT1A1*28*28) or heterozygous
(UGT1A1*6/*28) in allele UGT1A1*6, UGT1A1*28 of UGT may be at increased risk for
serious adverse reactions (especially neutropenia) caused by reduced glucuronidation of SN-38.
Added caution should be exercised when administering in such patients. Patients known to be
homozygous for UGT1A1*28 should be administered the normally indicated Irinotecan starting
dose. However, these patients should be monitored for hematologic toxicities. A reduced
Irinotecan starting dose should be considered for patients who have experienced prior
hematologic toxicity with previous treatment. The exact reduction in starting dose in this
patient population has not been established and any subsequent dose modifications should be
based on individual patient tolerance to treatment.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
- Hypersensitivity reactions : Hypersensitivity reactions, including severe
anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, have been reported.
- Immunosuppressant effects/increased susceptibility to infections : Administration of live or
live attenuated vaccines in patients immunocompromised by chemotherapeutic agents including
Irinotecan, may result in serious or fatal infections. Vaccination with a live vaccine should be
avoided in patients receiving Irinotecan. Killed or inactivated vaccines may be administered;
however, the response to such vaccines may be diminished.
- Late diarrhea : Late diarrhea (generally occurring more than 8 hours after administration of
Irinotecan) can be prolonged, may lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or sepsis and may
be life-threatening.
Patients ≥ 65 years of age should be closely monitored due to a greater risk of early diarrhea
observed. Colonic ulceration, sometimes with bleeding, has been observed in association with
Irinotecan-induced diarrhea.
Late diarrhea should be treated promptly with Loperamide at the first episode of poorly formed
or loose stools or the earliest onset of bowel movements more frequent than normally expected
for the patient.
The recommended dosage regimen for Loperamide is 4 mg at the first onset of late diarrhea and
then 2 mg every 2 hours until the patient is diarrhea-free for at least 12 hours. During the night,
the patient may take 4 mg of Loperamide every 4 hours. Loperamide is not recommended to be
used for more than 48 consecutive hours at these doses, because of the risk of paralytic ileus,
nor for less than 12 hours. Premedication with Loperamide is not recommended. Patients with
diarrhea should be carefully monitored and given fluid and electrolyte replacement if they
become dehydrated and should be given antibiotic support if they develop ileus, fever, or severe
neutropenia. In addition to the antibiotic treatment, hospitalization is recommended for
management of the diarrhea, in the following cases :
a. Diarrhea associated with fever,
b. Severe diarrhea (requiring intravenous hydration),
c. Patients with vomiting associated with delayed (i.e., late) diarrhea,
d. Diarrhea persisting beyond 48 hours following the initiation of high-dose Loperamide
therapy.
After the first treatment, subsequent weekly chemotherapy treatments should be delayed in
patients until return of pre-treatment bowel function for at least 24 hours without need for
antidiarrheal medication. If NCI grade 2, 3, or 4 diarrhea occurs, subsequent doses of Irinotecan
should be reduced within the current cycle.
- Chronic inflammatory bowel disease and/or bowel obstruction : Patients must not be
treated with Irinotecan until resolution of the bowel obstruction.
- Nausea & vomiting : Irinotecan is emetogenic. Nausea and vomiting can be severe and usually
occurs during or shortly after infusion of Irinotecan. It is recommended that patients receive
premedication with antiemetic agents. Antiemetic agents should be given on the day of
treatment, starting at least 30 minutes before administration of Irinotecan. Physicians should
also consider providing patients with an antiemetic regimen for subsequent use as needed.
Patients with vomiting associated with delayed diarrhea should be hospitalized as soon as
possible for treatment.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
- Neurologic : Dizziness has been observed and may sometimes represent symptomatic evidence
of orthostatic hypotension in patients with dehydration.
- Renal : Increases in serum creatinine or blood urea nitrogen have been observed. There have
been cases of acute renal failure. These events have generally been attributed to complications
of infection or to dehydration related to nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Instances of renal
dysfunction due to tumor lysis syndrome have also been reported.
- Respiratory : NCI grade 3 or 4 dyspnea has been observed. The extent to which malignant
pulmonary involvement or other preexisting lung disease may have contributed to dyspnea is
unknown. A potentially life-threatening pulmonary syndrome, consisting of dyspnea, fever, and
a reticulonodular pattern on chest X-ray, was observed in a small percentage of patients in early
Japanese studies. The contribution of Irinotecan to these preliminary events was difficult to
assess because these patients also had lung tumors and some had preexisting nonmalignant
pulmonary disease.
Interstitial pulmonary disease presenting as pulmonary infiltrates is uncommon during
Irinotecan therapy. Interstitial pulmonary disease can be fatal. Risk factors possibly associated
with the development of interstitial pulmonary disease include pre-existing lung disease, use of
pneumotoxic drugs, radiation therapy, and colony stimulating factors. Patients with risk factors
should be closely monitored for respiratory symptoms before and during Irinotecan therapy.
- Others : Since this product contains Sorbitol, it is unsuitable in hereditary fructose intolerance.
- Effects on ability to drive and use machines : Patients should be warned about the potential
for dizziness or visual disturbances which may occur within 24 hours following the
administration of Irinotecan, and advised not to drive or operate machinery if these symptoms
occur.
- Geriatric : Specific dosing recommendations may apply to this population depending upon the
regimen used.
- Hepatic insufficiency : In patients with hyperbilirubinemia, the clearance of Irinotecan is
decreased and therefore the risk of hematotoxicity is increased. The use of Irinotecan in patients
with a serum total bilirubin concentration of > 3.0 x institutional upper limit of normal (IULN)
given as a single-agent on the once-every-3-weeks schedule has not been established. Liver
function should be monitored before initiation of treatment and monthly, or as clinically
indicated.
- Irradiation therapy : Patients who have previously received pelvic/abdominal irradiation are
at increased risk of myelosuppression following the administration of Irinotecan. Physicians
should use caution in treating patients with extensive prior irradiation. Specific dosing
recommendations may apply to this population depending upon the regimen used.
- Performance status : Patients with poor performance status are at increased risk of Irinotecan-
related adverse events. Specific dosing recommendations for patients with an Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 2 may apply depending upon the
regimen used. Patients with performance status of 3 or 4 should not receive Irinotecan. In
patients receiving either Irinotecan/5-FU/LV or 5-FU/LV comparing these agents, higher rates
of hospitalisation, neutropenic fever, thromboembolism, first-cycle treatment discontinuation,
and early deaths were observed in patients with a baseline performance status of 2 than in
patients with a baseline performance status of 0 or 1.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
- Gastric cancer : Patients with gastric cancer appear to experience greater myelosuppression
and other toxicities when given Irinotecan. A lower starting dose should be considered in these
patients.
- Pregnancy and lactation :
a. Pregnancy : Irinotecan may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. If
the drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while receiving this
drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Women of
childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant while receiving
treatment with Irinotecan.
b. Lactation : Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential
for adverse reactions in nursing infants, breast-feeding must be discontinued for the
duration of Irinotecan therapy.
DRUG INTERACTIONS :
- CYP3A4 and/or UGT1A1 inhibitors :
a. Irinotecan and active metabolite SN-38 are metabolized via the human cytochrome P450
3A4 isoenzyme (CYP3A4) and uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1
(UGT1A1). Co-administration of Irinotecan with inhibitors of CYO3A4 and/or UGT1A1
may result in increased systemic exposure to Irinotecan and the active metabolite SN-38.
Physicians should take this into consideration when administering Irinotecan with these
drugs.
b. Ketoconazole : Irinotecan clearance is greatly reduced in patients receiving concomitant
Ketoconazole, leading to increased exposure to SN-38. Ketoconazole should be
discontinued at least 1 week prior to starting Irinotecan therapy and should not be
administered during Irinotecan therapy.
c. Atazanavir sulfate : Co-administration of Atazanavir sulfate, a CYP3A4 and UGT1A1
inhibitor has the potential to increase systemic exposure to SN-38, the active metabolite of
Irinotecan. Physicians should take this into consideration when co-administering these
drugs.
- CYP3A4 inducers :
a. Anticonvulsants : Concomitant administration of CYP3A-inducing anticonvulsant drugs
(e.g., Carbamazepine, Phenobarbital or Phenytoin) leads to reduced exposure to the active
metabolite SN-38. Consideration should be given to starting or substituting non-enzyme-
inducing anticonvulsants at least one week prior to initiation of Irinotecan therapy in
patients requiring anticonvulsant treatment.
b. St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) : Exposure to the active metabolite SN-38 is
reduced in patients taking concomitant St. John’s wort. St. John’s wort should be
discontinued at least 1 week prior to the first cycle of Irinotecan, and should not be
administered during Irinotecan therapy.
- Other interactions :
a. Neuromuscular blocking agents : Interaction between Irinotecan Hydrochloride and
neuromuscular blocking agents cannot be ruled out, since Irinotecan has anticholinesterase
activity. Drugs with anticholinesterase activity may prolong the neuromuscular blocking
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
effects of Suxamethonium and the neuromuscular blockade of non-depolarizing drugs may
be antagonized.
b. Antineoplastic agents : The adverse effects of Irinotecan, such as myelosuppression and
diarrhea, would be expected to be exacerbated by other antineoplastic agents having a
similar adverseeffect profile.
c. Dexamethasone : Lymphocytopenia has been reported in patients receiving Irinotecan, and
it is possible that the administration of Dexamethasone as antiemetic prophylaxis may have
enhanced the likelihood of lymphocytopenia. However, serious opportunistic infections
have not been observed and no complications have specifically been attributed to
lymphocytopenia.
Hyperglycemia has been observed in patients with a history of diabetes mellitus or evidence
of glucose intolerance prior to administration of Irinotecan. It is probable that
Dexamethasone, given as antiemetic prophylaxis, contributed to hyperglycemia in some
patients.
d. Laxatives : Laxative use during therapy with Irinotecan is expected to worsen the incidence
or severity of diarrhea.
e. Diuretics : Dehydration secondary to vomiting and/or diarrhea may be induced by
Irinotecan. The physician may wish to withhold diuretics during dosing with Irinotecan and
during periods of active vomiting or diarrhea.
f. Bevacizumab : Results from a dedicated drug-drug interaction trial demonstrated no
significant effect of Bevacizumab on the pharmacokinetics of Irinotecan and its active
metabolite SN-38.
ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS :
NCI (National Cancer Institute) grade 1 to 4 drug-related adverse events
Gastrointestinal disorders Late diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, early diarrhea,
abdominal cramping/pain, anorexia, stomatitis
Blood and lymphatic system disorders Leukopenia, anemia, neutropenia
General disorders and administration Asthenia, fever
site conditions
Metabolism and nutrition disorders Decreased weight, dehydration
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Alopecia
Vascular disorders Thromboembolic events*
NCI (National Cancer Institute) grade 3 or 4 drug-related adverse events
Gastrointestinal disorders Late diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramping/pain,
vomiting, early diarrhea, constipation, anorexia,
mucositis, rectal disorder, GI monilia
Blood and lymphatic system disorders Leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Alopecia, rash, cutaneous signs
Infections and infestations Infection, sepsis
General disorders and administration Asthenia, fever, pain, chills, malaise
site conditions
Metabolism and nutrition disorders Dehydration, hypovolemia, decreased weight,
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
hypokalemia, hipomagnesemia
Hepatobilliary disorders Bilirubinemia
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal Dyspnea
disorders
Nervous system disorders Abnormal gait, confusion, headache
Cardiac disorders Hypotension, syncope, cardiovascular disorders
Renal and urinary disorders Urinary tract infection
Reproductive system and breast Breast pain
disorders
Investigations Increased creatinine, increased alkaline phosphatase,
increased GGTP
* Includes angina pectoris, arterial thrombosis, cerebral infarct, cerebrovascular accident, deep
thrombophlebitis, embolus lower extremity, heart arrest, myocardial infarct, myocardial ischemia,
peripheral vascular disorder, pulmonary embolus, sudden death, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis,
vascular disorder.
The following additional drug related events have been reported with Irinotecan, but do not meet
the criteria as defined above as either drug-related NCI grades 1 – 4 or as a NCI grade 3 or 4 drug-
related event : Rhinits, increased salivation, miosis, lacrimation, diaphoresis, flushing,
bradycardia, dizziness, extravasation, tumor lysis syndrome, and colonic ulceration.
Cardiac disorders : Myocardial ischemic events have been observed following Irinotecan
therapy predominantly in patients with underlying cardiac disease, other known risk factors for
cardiac disease or previous cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Gastrointestinal disorder : Intestinal obstruction, ileus, megacolon, or gastrointestinal
hemorrhage, and cases of colitis, including typhlitis, ischemic and ulcerative colitis were reported.
In some cases, colitis was complicated by ulceration, bleeding, ileus, or infection. Cases of ileus
without preceding colitis have also been reported. Cases of intestinal perforation were reported.
Cases of symptomatic pancreatitis or asymptomatic elevated pancreatic enzymes have been
observed.
Hypovolemia : There have been cases of renal impairment and acute renal failure, generally in
patients who became infected and/or volume depleted from severe gastrointestinal toxicities.
Renal insufficiency, hypotension or circulatory failure have been observed in patients who
experienced episodes of dehydration associated with diarrhea and/or vomiting, or sepsis.
Immune system disorders : Hypersensitivity reactions including severe anaphylactic or
anaphylactoid reactions have been reported.
Musculoskeletal disorders and connective tissue disorders : Early effects, such as muscular
contraction or cramps and paresthesia, have been reported.
Nervous system disorders : Speech disorders, generally transient in nature, have been reported in
patients treated with Irinotecan; in some cases, the event was attributed to the cholinergic
syndrome observed during or shortly after infusion of Irinotecan.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : Interstitial pneumonia and pneumonitis
presenting as pulmonary infiltrates have been observed. Early effects, such as dyspnea, have been
reported.
Investigations : Cases of hyponatremia mostly related with diarrhea and vomiting have been
reported. Increases in serum levels of transaminases (i.e., AST and ALT) in the absence of
progressive liver metastasis have been reported.
OVERDOSAGE :
Single doses of up to 750 mg/m2 Irinotecan have been given to patients with various cancers. The
adverse events in these patients were similar to those reported with the recommended dosages and
regimens. There have been reports of overdosage at doses up to approximately twice the
recommended therapeutic dose, which may be fatal. The most significant adverse reactions
reported were severe neutropenia and severe diarrhea. There is no knowing antidote for
Irinotecan. Maximum supportive care should be instituted to prevent dehydration due to diarrhea
and to treat any infectious complications.
STORAGE :
Store below 30oC and protect from light. Keep out the reach of children.
SHELF LIFE AFTER RECONSTITUTION :
To reconstitute :
IRITERO must be diluted prior to infusion in 5% Dextrose Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride
Injection to a final concentration range of 0.12 - 2.8 mg/mL.
In 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection : After reconstitution, the solution is stable within 24 hours at
room temperature.
In 5% Dextrose Injection : After reconstitution, the solution is stable within 6 hours at room
temperature or within 24 hours at temperature 2 - 8oC.
PRESENTATIONS :
IRITERO Concentrate for solution for infusion 40 mg/2 mL
Box, Vial @ 2 mL
Reg. No. :
IRITERO Concentrate for solution for infusion 100 mg/5 mL
Box, Vial @ 5 mL
Reg. No. :
ON MEDICAL PRESCRIPTION ONLY
CYTOTOXIC DRUG
Manufactured by :
HETERO LABS LIMITED UNIT VI
Telangana – India
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Imported and marketed by :
PT. AMAROX PHARMA GLOBAL
Bekasi – Indonesia
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
IRITERO
Irinotecan HCl Trihydrate
Larutan konsentrat untuk infus
KOMPOSISI :
IRITERO Larutan konsentrat untuk infus 40 mg/2 mL dan 100 mg/5 mL, tiap mL mengandung :
Irinotecan HCl Trihydrate 20 mg setara dengan Irinotecan 17,32 mg.
FARMAKOLOGI :
Farmakodinamik :
Kelas terapi
Irinotecan Hydrochloride adalah agen antineoplastik dari golongan penghambat topoisomerase I.
Irinotecan adalah turunan semisintetik dari Camptothecin, ekstrak alkaloid dari tanaman seperti
Camptotheca acuminata, atau disintesis secara kimia.
Mekanisme kerja
Irinotecan dan metabolit aktifnya SN-38 berikatan dengan kompleks topoisomerase I - DNA dan
mencegah re-ligasi dari kerusakan untaian tunggal ini. Penelitian saat ini menunjukkan bahwa
sitotoksisitas Irinotecan disebabkan oleh kerusakan untaian DNA ganda yang dihasilkan selama
sintesis DNA ketika enzim replikasi berinteraksi dengan kompleks terner yang dibentuk oleh
topoisomerase I - DNA, dan dengan Irinotecan atau SN-38.
Irinotecan bertindak sebagai prekursor yang larut dalam air dari metabolit lipofilik SN-38. SN-38
dibentuk dari Irinotecan melalui pembelahan ikatan Carbamate yang dimediasi carboxylesterase
antara gugus Camptothecin dan rantai samping dipiperidino. SN-38 kira-kira 1000 kali lebih kuat
dari Irinotecan sebagai penghambat topoisomerase I. Kontribusi yang pasti dari SN-38 terhadap
aktivitas Irinotecan tidak diketahui. Baik Irinotecan dan SN-38 terdapat dalam bentuk lakton aktif
dan dalam bentuk anion asam hidroksi tidak aktif. Suatu kesetimbangan yang tergantung pada pH
terdapat di antara dua bentuk tersebut sehingga pH asam mendorong pembentukan lakton,
sementara pH yang lebih basa lebih cenderung membentuk anion asam hidroksi.
Framakokinetik dalam populasi khusus :
Usia lanjut
Tidak ada perbedaan dalam farmakokinetik Irinotecan, SN-38, dan glukuronida SN-38 pada
pasien usia < 65 tahun dibandingkan dengan pasien usia ≥ 65 tahun.
Jenis kelamin
Farmakokinetik Irinotecan tampaknya tidak dipengaruhi oleh jenis kelamin.
Ras
Pengaruh ras pada farmakokinetik Irinotecan belum dievaluasi.
Insufisiensi hati
Bersihan Irinotecan berkurang pada pasien dengan disfungsi hati sedangkan paparan relatif
terhadap metabolit aktif SN-38 meningkat. Besarnya efek ini sebanding dengan tingkat kerusakan
hati yang diukur dengan peningkatan konsentrasi bilirubin total serum dan transaminase.
Insufisiensi ginjal
Pengaruh insufisiensi ginjal pada farmakokinetik Irinotecan belum dievaluasi.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
INDIKASI :
IRITERO diindikasikan untuk pengobatan pasien dengan kanker kolorektal stadium lanjut.
- Dalam kombinasi dengan 5-fluorouracil dan Folinic acid pada pasien tanpa kemoterapi
sebelumnya untuk penyakit stadium lanjut.
- Sebagai agen tunggal pada pasien yang gagal pada regimen pengobatan 5-fluorouracil.
Kombinasi Irinotecan dengan Cisplatin diindikasikan untuk pengobatan pasien dengan kanker
paru-paru sel kecil.
Ikuti dengan ketat dosis yang direkomendasikan kecuali diarahkan lain oleh dokter.
KONTRAINDIKASI :
IRITERO dikontraindikasikan pada pasien dengan :
- Penyakit radang usus kronis dan/atau obstruksi usus.
- Riwayat reaksi hipersensitivitas parah terhadap Irinotencan Hydrochloride Trihydrate atau salah
satu eksipien IRITERO.
- Pada wanita hamil atau menyusui.
- Pada pasien dengan bilirubin > 3 kali ULN.
- Pada pasien dengan kegagalan sumsum tulang yang berat.
- Pada pasien yang menunjukkan faktor risiko, terutama pasien dengan WHO performance status
> 2.
DOSIS DAN CARA PEMBERIAN :
Hanya untuk dewasa. Larutan IRITERO untuk infus harus diinfuskan kedalam vena perifer
atau sentral.
- Dalam monoterapi (untuk pasien yang sebelumnya diobati) :
Dosis IRITERO yang direkomendasikan adalah 350 mg/m2 diberikan sebagai infus intravena
selama periode 30 hingga 90 menit setiap tiga minggu.
- Dalam kombinasi (untuk pasien yang sebelumnya tidak diobati) :
Keamanan dan efektivitas IRITERO dalam kombinasi dengan 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) dan
Folinic acid (FA) telah dinilai dengan jadwal berikut. Dosis IRITERO yang direkomendasikan
adalah 180 mg/m2 diberikan setiap 2 minggu sekali sebagai infus intravena selama periode 30
sampai 90 menit, diikuti dengan infus dengan Folinic acid dan 5-fluorouracil.
Irinotecan dalam kombinasi dengan Cisplatin
Dosis awal yang direkomendasikan adalah Irinotecan 65 mg/m2 dan Cisplatin 30 mg/m2. Cisplatin
diinfuskan sebelum Irinotecan. Dosis awal yang lebih rendah dari Irinotecan dapat
dipertimbangkan untuk pasien dengan salah satu dari kondisi berikut : Usia 65 tahun dan lebih
tua, sebelum radioterapi ekstensif, performance status 2, peningkatan kadar bilirubin, atau kanker
lambung. Pengobatan harus diberikan dalam siklus 6-minggu berulang, terdiri dari hari 1 dan 8,
setiap 21 hari.
Irinotecan harus diberikan sebagai infus intravena selama 30 hingga 90 menit.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Penyesuaian dosis :
IRITERO harus diberikan setelah pulih total dari semua efek samping untuk NCI-CTC (National
Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria) tingkat 0 atau 1 dan ketika diare terkait pengobatan
diselesaikan sepenuhnya.
Pada awal terapi infus berikutnya, dosis IRITERO, dan 5FU ketika digunakan, harus dikurangi
sesuai dengan tingkat efek samping terburuk yang diamati pada infus sebelumnya. Pengobatan
harus ditunda 1 hingga 2 minggu untuk memungkinkan pemulihan dari efek samping terkait
pengobatan. Pengurangan dosis 15% hingga 20% harus dilakukan untuk penggunaan IRITERO
dan/atau 5FU dengan efek samping seperti : Toksisitas hematologis (neutropenia tingkat 4),
neutropenia demam (neutropenia tingkat 3 - 4 dan demam tingkat 2 - 4), trombositopenia dan
leukopenia (tingkat 4), toksisitas non-hematologis (tingkat 3 - 4).
Lama pengobatan :
Untuk regimen agen tunggal dan kombinasi, pengobatan dengan siklus tambahan Irinotecan dapat
dilanjutkan tanpa batas waktu pada pasien yang mendapat respon tumor atau pada pasien yang
kankernya tetap stabil. Pasien harus dimonitor dengan hati-hati untuk toksisitas dan harus
dikeluarkan dari terapi jika terjadi toksisitas yang tidak dapat diterima yang responsif terhadap
modifikasi dosis dan perawatan suportif yang rutin.
Rekomendasi modifikasi :
Modifikasi dosis yang direkomendasikan untuk Irinotecan dan Cisplatin untuk setiap siklus awal
terapi dijelaskan pada Tabel 1, sedangkan modifikasi dosis yang direkomendasikan selama siklus
terapi dijelaskan pada Tabel 2.
Tabel 1. Modifikasi dosis pada awal siklus baru dari jadwal kombinasi Irinotecan dan
Cisplatin (mg/m2) - berdasarkan toksisitas terburuk yang diamati pada siklus sebelumnya
Siklus baru dari terapi tidak boleh dimulai sampai jumlah granulosit telah pulih hingga ≥
1500/mm3, dan jumlah trombosit telah pulih hingga ≥ 100,000/mm3, kreatinin serum ≤ 1.7 mg/dL
atau ≤ 130 µmol/L, dan toksisitas non-hematologi terkait pengobatan (kecuali alopecia) dapat
teratasi hingga ≤ tingkat 1. Pengobatan sebaiknya ditunda selama 1 hingga 2 minggu untuk
memungkinkan pemulihan dari toksisitas terkait pengobatan. Jika pasien belum pulih setelah
penundaan selama 2 minggu, pertimbangan harus diberikan untuk menghentikan Irinotecan.
Tingkat toksisitas Cisplatinb Irinotecanc
NCIa
HEMATOLOGI
Neutropenia/Trombositopenia
Tingkat 0, 1, 2, atau 3 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 4 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis ↓ 1 tingkat dosis
Febrile neutropenia , sepsis, ↓ 2 tingkat dosis
d
↓ 2 tingkat dosis
trombositopenia yang
membutuhkan transfusi
NON-HEMATOLOGI
Diare
Tingkat 0, 1 atau 2 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Tingkat 3 atau 4 Memelihara tingkat dosis ↓ 1 tingkat dosis
Muntah
Tingkat 0, 1 atau 2 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 4 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis ↓ 1 tingkat dosis
Kreatinin serum
≤ 1.7 mg/dL Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
> 1.7 - 2.0 mg/dL ↓ 3 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
> 2.0 mg/dL Cisplatin dihentikan Memelihara tingkat dosis
Ototoksisitas
Tingkat 0 atau 1 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 2 ↓ 2 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 atau 4 Cisplatin dihentikan Memelihara tingkat dosis
Neurotoksisitas
Tingkat 0 atau 1 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 2 ↓ 2 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 atau 4 Cisplatin dihentikan Memelihara tingkat dosis
TOKSISITAS NON-HEMATOLOGI LAINNYA (Kecuali Alopecia)
Tingkat 0, 1 atau 2 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 atau 4 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis ↓ 1 tingkat dosis
a
National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria
b
Cisplatin : Penurunan tingkat dosis = Penurunan 5 mg/m2
c
Irinotecan : Penurunan tingkat dosis = Penurunan 10 mg/m2
d
Febrile neutropenia didefinisikan dalam CTC versi 2 : Suhu ≥ 38,5oC bersamaan dengan ANC <
1.0 x 109L.
Tabel 2. Dosis modifikasi untuk hari ke 8 dari jadwal kombinasi Cisplatin dan Irinotecan
(mg/m2) berdasarkan toksisitas terburuk yang diamati pada siklus sebelumnya
Tingkat toksisitas Cisplatinb Irinotecanc
NCIa
HEMATOLOGI
Neutropenia/Trombositopenia
Tingkat 0 atau 1 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 2 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis ↓ 1 tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 ↓ 2 tingkat dosis ↓ 2 tingkat dosis
Tingkat 4 Hapus dosis Hapus dosis
d
Febrile neutropenia , sepsis, Hapus dosis Hapus dosis
trombositopenia yang
membutuhkan transfusi
NON-HEMATOLOGI
Diare
Tingkat 0 atau 1 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 2 Memelihara tingkat dosis ↓ 1 tingkat dosis
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Tingkat 3 Memelihara tingkat dosis Hapus dosis
Tingkat 4 Hapus dosis Hapus dosis
Muntah
Tingkat 0, 1 atau 2 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 4 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis ↓ 1 tingkat dosis
Kreatinin serum
≤ 1.7 mg/dL Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
> 1.7 – 2.0 mg/dL ↓ 2 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
> 2.0 mg/dL Cisplatin dihentikan Memelihara tingkat dosis
Ototoksisitas
Tingkat 0 atau 1 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 2 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 atau 4 Cisplatin dihentikan Memelihara tingkat dosis
Neurotoksisitas
Tingkat 0 atau 1 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 2 ↓ 1 tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 3 atau 4 Cisplatin dihentikan Memelihara tingkat dosis
TOKSISITAS NON-HEMATOLOGI LAINNYA (Kecuali Alopecia)
Tingkat 0 atau 1 Memelihara tingkat dosis Memelihara tingkat dosis
Tingkat 2, 3, 4 Hapus dosis Hapus dosis
a
National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria
b
Cisplatin : Penurunan tingkat dosis = Penurunan 5 mg/m2
c
Irinotecan : Penurunan tingkat dosis = Penurunan 10 mg/m2
d
Febrile neutropenia didefinisikan dalam CTC versi 2 : Suhu ≥ 38,5oC bersamaan dengan ANC <
1.0 x 109L.
Populasi khusus :
Usia lanjut
Dosis harus dipilih dengan hati-hati pada populasi ini karena frekuensi penurunan fungsi biologis
yang lebih besar. Populasi ini memerlukan pengawasan yang lebih intensif.
Pasien dengan gangguan fungsi hati
Dalam monoterapi : Pada pasien dengan hiperbilirubinemia dan protrombin lebih besar dari 50%,
pembersihan Irinotecan menurun dan oleh karena itu, risiko hematotoksisitas meningkat. Dengan
demikian, pemantauan rutin terhadap jumlah darah lengkap harus dilakukan pada populasi pasien
ini.
- Pada pasien dengan bilirubin hingga 1,5 kali batas atas kisaran normal (ULN), dosis IRITERO
yang direkomendasikan adalah 350 mg/m2.
- Pada pasien dengan bilirubin berkisar 1,5 hingga 3 kali ULN, dosis IRITERO yang
direkomendasikan adalah 200 mg/m2.
- Pasien dengan bilirubin melebihi 3 kali ULN tidak boleh diobati dengan IRITERO.
Tidak ada data yang tersedia pada pasien dengan gangguan hati yang diobati oleh IRITERO
dalam kombinasi.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Pasien dengan gangguan fungsi ginjal
IRITERO tidak direkomendasikan untuk digunakan pada pasien dengan gangguan fungsi ginjal.
Persiapan dan penanganan :
Seperti agen antineoplastik lainnya, IRITERO harus disiapkan dan ditangani dengan hati-hati.
Diperlukan penggunaan kacamata, masker dan sarung tangan. Jika larutan IRITERO atau larutan
infus bersentuhan dengan selaput lendir, segera cuci dengan air.
Persiapan untuk pemberian infus intravena :
Seperti halnya obat suntik lainnya, larutan IRITERO harus disiapkan secara aseptik. Jika ada
endapan yang diamati dalam botol atau setelah rekonstitusi, produk harus dibuang sesuai dengan
prosedur standar untuk agen sitotoksik. Secara aseptik, ambil jumlah larutan IRITERO yang
diperlukan dari vial dengan jarum suntik yang dikalibrasi dan masukkan ke dalam kantong infus
250 ml atau botol yang mengandung larutan Sodium chloride 0,9% atau larutan Dextrose 5%.
Infus kemudian dicampur dengan rotasi manual.
Cara pemberian :
Larutan IRITERO untuk infus harus dimasukkan ke vena perifer atau sentral. IRITERO tidak
boleh diberikan sebagai bolus intravena atau infus intravena kurang dari 30 menit atau lebih dari
90 menit.
Pembuangan :
Semua bahan yang digunakan untuk pengenceran dan pemberian harus dibuang sesuai dengan
prosedur standar rumah sakit yang berlaku untuk agen sitotoksik.
PERINGATAN DAN PERHATIAN :
- Cara pemberian : Irinotecan harus diberikan hanya di bawah pengawasan dokter, yang
berpengalaman dalam penggunaan agen kemoterapi kanker. Penatalaksanaan komplikasi yang
tepat hanya dimungkinkan bila fasilitas diagnostik dan perawatan yang memadai sudah
tersedia.
- Irinotecan hanya akan diresepkan dalam kasus-kasus berikut setelah manfaat yang diharapkan
telah dipertimbangkan terhadap risiko terapetik yang mungkin :
a. Pada pasien yang menunjukkan faktor risiko, terutama mereka yang memiliki WHO
performance status = 2.
b. Dalam beberapa kasus di mana pasien dianggap tidak mungkin untuk mematuhi
penatalaksanaan efek samping yang direkomendasikan (kebutuhan pengobatan antidiare
langsung dan berkepanjangan yang dikombinasikan dengan asupan cairan yang tinggi pada
onset diare yang tertunda). Pengawasan rumah sakit yang ketat direkomendasikan untuk
pasien tersebut.
- Gejala kolinergik : Pasien mungkin memiliki gejala kolinergik dari rinitis, peningkatan air
liur, miosis, lakrimasi, diaforesis, flushing (vasodilatasi), bradikardia, dan hiperperistalsik usus
yang dapat menyebabkan kram perut dan diare dini (yaitu, diare umumnya terjadi selama atau
dalam 8 jam setelah pemberian Irinotecan). Gejala-gejala ini dapat diamati selama atau segera
setelah infus Irinotecan, dianggap terkait dengan aktivitas antikolinesterase dari senyawa induk
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Irinotecan, dan diharapkan terjadi lebih sering dengan dosis Irinotecan yang lebih tinggi.
Pemberian terapi atau profilaksis 0,25 hingga 1 mg Atropine secara intravena atau subkutan
harus dipertimbangkan (kecuali dikontraindikasikan) pada pasien yang mengalami gejala
kolinergik.
- Ekstravasasi : Walaupun Irinotecan bukan vesicant yang dikenal, pengobatan harus dilakukan
untuk menghindari ekstravasasi, dan tempat pemberian infus harus dimonitor untuk tanda-tanda
peradangan. Jika terjadi ekstravasasi, bilas situs tersebut, dan direkomendasikan untuk
menggunakan es.
- Hati : National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Toxicity Criteria kelainan enzim hati tingkat 3
atau 4 telah diamati. Peristiwa ini biasanya terjadi pada pasien dengan metastasis hati yang
diketahui dan tidak dipastikan terkait dengan Irinotecan.
- Hematologi : Irinotecan menyebabkan neutropenia, leukopenia, dan anemia, yang mungkin
parah dan oleh karena itu sebaiknya tidak digunakan pada pasien dengan kegagalan sumsum
tulang yang berat. Trombositopenia yang serius jarang terjadi. Frekuensi NCI neutropenia
tingkat 3 dan 4 lebih tinggi secara signifikan pada pasien yang menerima iradiasi panggul/perut
sebelumnya daripada pada mereka yang belum menerima iradiasi tersebut. Pasien dengan kadar
bilirubin total serum awal 1,0 mg/dL atau lebih juga memiliki kemungkinan lebih besar untuk
mengalami siklus pertama neutropenia tingkat 3 atau 4 dibandingkan pasien dengan kadar
bilirubin kurang dari 1,0 mg/dL. Tidak ada perbedaan signifikan dalam frekuensi neutropenia
tingkat 3 dan 4 berdasarkan usia atau jenis kelamin.
Demam neutropenik (bersamaan dengan NCI neutropenia tingkat 4 dan ≥ demam tingkat 2)
terjadi pada pasien; namun, kematian akibat sepsis setelah neutropenia parah telah terjadi pada
pasien yang diobati dengan Irinotecan. Komplikasi neutropenia harus segera ditangani dengan
pemberian antibiotik. Terapi dengan Irinotecan harus dihentikan sementara jika demam
neutropenik terjadi atau jika jumlah neutrofil absolut turun di bawah 1000/mm3. Dosis
Irinotecan harus dikurangi jika terjadi neutropenia yang signifikan.
- Pasien dengan penurunan aktivitas UGT1A1 : Konversi metabolik Irinotecan menjadi
metabolit aktif SN-38 dimediasi oleh enzim carboxylesterase dan terutama terjadi di hati. SN-
38 kemudian mengalami konjugasi untuk membentuk metabolit glukuronida SN-38G yang
tidak aktif. Reaksi glukuronidasi ini dimediasi terutama oleh uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyl
transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1), yang dikodekan oleh gen UGT1A1. Gen UGT1A1 sangat
polimorfik, menghasilkan kapasitas metabolik variabel di antara individu. Satu variasi spesifik
gen UGT1A1 termasuk polimorfisme di wilayah promotor yang dikenal sebagai alel varian
UGT1A1. Varian ini dan defisiensi bawaan lainnya dalam ekspresi UGT1A1 (seperti Crigler-
Najjar dan sindrom Gilbert) dikaitkan dengan penurunan aktivitas enzim dan peningkatan
paparan sistemik ke SN-38. Konsentrasi plasma SN-38 lebih tinggi diamati pada individu yang
homozigot untuk alel UGT1A1*28 (juga disebut sebagai genotipe UGT1A1 7/6 UGT1A1)
dibandingkan pasien yang memiliki satu atau dua alel tipe liar.
Pasien yang homozigot (UGT1A1*6/*6 dari UGT1A1*28*28) atau heterozigot
(UGT1A1*6/*28) dalam alel UGT1A1*6, UGT1A1*28 dari UGT mungkin berisiko tinggi
untuk efek samping yang serius (khususnya neutropenia) yang disebabkan oleh berkurangnya
glukuronidasi SN-38. Perhatian tambahan harus dilakukan ketika memberikan pada pasien
tersebut. Pasien yang diketahui homozigot untuk UGT1A1*28 harus diberikan dosis awal
Irinotecan yang diindikasikan secara normal. Namun, pasien ini harus dipantau untuk toksisitas
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
hematologi. Penurunan dosis awal Irinotecan harus dipertimbangkan untuk pasien yang pernah
mengalami toksisitas hematologi sebelumnya dengan pengobatan sebelumnya. Pengurangan
yang tepat dalam dosis awal dalam populasi pasien ini belum ditetapkan dan modifikasi dosis
berikutnya harus didasarkan pada toleransi masing-masing pasien terhadap pengobatan.
- Reaksi hipersensitivitas : Reaksi hipersensitivitas, termasuk reaksi anafilaksis/anafilaktoid
yang parah, telah terjadi.
- Efek imunosupresan/peningkatan kerentanan terhadap infeksi : Pemberian vaksin hidup
atau vaksin yang dilemahkan pada pasien yang immunocompromised oleh agen kemoterapi
termasuk Irinotecan, dapat mengakibatkan infeksi serius atau fatal. Vaksinasi dengan vaksin
hidup harus dihindari pada pasien yang menerima Irinotecan. Vaksin yang terbunuh atau tidak
aktif dapat diberikan; namun, respon terhadap vaksin tersebut dapat dikurangi.
- Diare yang tertunda : Diare yang tertunda (umumnya terjadi lebih dari 8 jam setelah
pemberian Irinotecan) dapat diperpanjang, dapat menyebabkan dehidrasi, ketidakseimbangan
elektrolit, atau sepsis dan dapat mengancam jiwa.
Pasien yang berusia > 65 tahun harus dimonitor secara ketat karena risiko diare dini yang lebih
besar diamati. Ulserasi kolon, kadang dengan perdarahan, telah diamati terkait dengan diare
yang disebabkan Irinotecan.
Diare yang tertunda harus segera diobati dengan Loperamide pada episode pertama dari tinja
yang terbentuk buruk atau mencret atau onset awal dari pergerakan usus yang lebih sering
daripada yang diperkirakan pada pasien.
Regimen dosis yang direkomendasikan untuk Loperamide adalah 4 mg pada awal onset diare
yang tertunda dan kemudian 2 mg setiap 2 jam sampai pasien bebas diare selama setidaknya 12
jam. Pada malam hari, pasien dapat mengonsumsi Loperamide 4 mg setiap 4 jam. Loperamide
tidak direkomendasikan untuk digunakan selama lebih dari 48 jam berturut-turut pada dosis ini,
karena risiko ileus paralitik, juga tidak kurang dari 12 jam. Premedikasi dengan Loperamide
tidak direkomendasikan. Pasien dengan diare harus dimonitor dengan hati-hati dan diberi
penggantian cairan dan elektrolit jika mereka mengalami dehidrasi dan harus diberi tambahan
antibiotik jika mereka mengalami ileus, demam, atau neutropenia yang parah. Selain
pengobatan antibiotik, rawat inap direkomendasikan untuk penatalaksanaan diare, dalam kasus
berikut :
a. Diare yang berhubungan dengan demam,
b. Diare parah (membutuhkan hidrasi intravena),
c. Pasien dengan muntah yang berhubungan dengan diare yang tertunda (yaitu, terlambat)
d. Diare bertahan lebih dari 48 jam setelah dimulainya terapi Loperamide dosis tinggi.
Setelah pengobatan pertama, pengobatan kemoterapi mingguan berikutnya harus ditunda pada
pasien sampai kembalinya fungsi usus sebelum pengobatan kurang lebih 24 jam tanpa perlu
obat antidiare. Jika NCI diare tingkat 2, 3, atau 4 terjadi, dosis Irinotecan berikutnya harus
dikurangi dalam siklus saat ini.
- Penyakit radang usus kronis dan/atau obstruksi usus : Pasien tidak boleh diobati dengan
Irinotecan sampai resolusi obstruksi usus.
- Mual & muntah : Irinotecan bersifat emetogenik. Mual dan muntah bias menjadi parah dan
biasanya terjadi selama atau segera setelah infus Irinotecan. Direkomendasikan untuk pasien
menerima premedikasi dengan agen antiemetik. Agen antiemetik harus diberikan pada hari
pengobatan, yang dimulai setidaknya 30 menit sebelum pemberian Irinotecan. Dokter juga
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
harus mempertimbangkan memberi pasien regimen antiemetik untuk penggunaan berikutnya
yang sesuai kebutuhan. Pasien dengan muntah yang berhubungan dengan diare yang tertunda
harus dirawat di rumah sakit sesegera mungkin untuk pengobatan.
- Neorologik : Pusing telah diamati dan kadang-kadang dapat menjadi tanda gejala hipotensi
ortostatik pada pasien dengan dehidrasi.
- Ginjal : Peningkatan kadar kreatinin serum atau nitrogen urea darah telah diamati. Terdapat
beberapa kasus gagal ginjal akut. Kejadian-kejadian ini umumnya dikaitkan dengan komplikasi
infeksi atau dehidrasi terkait mual, muntah, atau diare. Kasus disfungsi ginjal akibat sindrom
lisis tumor juga dapat terjadi.
- Pernapasan : NCI dispnea tingkat 3 atau 4 telah diamati. Sejauh mana keterlibatan keganasan
paru-paru atau penyakit paru-paru lain yang sudah ada sebelumnya mungkin berkontribusi
terhadap dispnea yang tidak diketahui. Sindrom paru yang berpotensi mengancam jiwa, terdiri
dari dispnea, demam, dan pola retikulonodular pada rontgen dada, yang diamati pada sebagian
kecil pasien. Kontribusi Irinotecan pada kondis awal ini sulit untuk dinilai karena pasien ini
juga memiliki tumor paru dan beberapa telah memiliki penyakit paru yang tidak ganas yang
sudah ada sebelumnya.
Penyakit paru interstisial yang muncul sebagai infiltrat paru jarang terjadi selama terapi
Irinotecan. Penyakit paru interstisial bisa berakibat fatal. Faktor risiko yang mungkin terkait
dengan perkembangan penyakit paru interstitial meliputi penyakit paru yang sudah ada
sebelumnya, penggunaan obat pneumotoxic, terapi radiasi, dan faktor perangsang koloni. Pasien
dengan faktor risiko harus dimonitor secara ketat untuk gejala pernapasan sebelum dan selama
terapi Irinotecan.
- Lainnya : Karena produk ini mengandung Sorbitol, sehingga tidak cocok untuk intoleransi
fruktosa herediter.
- Efek pada kemampuan mengemudi dan menggunakan mesin : Pasien harus diingatkan
tentang potensi pusing atau gangguan penglihatan yang mungkin terjadi dalam 24 jam setelah
pemberian Irinotecan, dan disarankan untuk tidak mengemudi atau mengoperasikan mesin jika
gejala ini terjadi.
- Usia lanjut : Rekomendasi dosis spesifik dapat diterapkan untuk populasi ini tergantung pada
regimen yang digunakan.
- Insufisiensi hati : Pada pasien dengan hiperbilirubinemia, pembersihan Irinotecan menurun
dan karena itu risiko hematotoksisitas meningkat. Penggunaan Irinotecan pada pasien dengan
konsentrasi total bilirubin serum > 3,0 x batas atas institusi normal (IULN) yang diberikan
sebagai agen tunggal pada jadwal 3 minggu sekali belum ditentukan. Fungsi hati harus dipantau
sebelum memulai pengobatan dan setiap bulan, atau seperti yang ditunjukkan secara klinis.
- Terapi iradiasi : Pasien yang sebelumnya pernah menerima iradiasi panggul/perut berisiko
lebih tinggi mengalami mielosupresi setelah pemberian Irinotecan. Dokter harus berhati-hati
dalam mengobati pasien dengan ekstensif sebelum iradiasi. Rekomendasi dosis spesifik dapat
berlaku untuk populasi ini tergantung pada rejimen yang digunakan.
- Performance status : Pasien dengan performance status yang buruk berada pada peningkatan
risiko efek samping yang berhubungan dengan Irinotecan. Rekomendasi dosis spesifik untuk
pasien dengan Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status 2 dapat
diterapkan tergantung pada regimen yang digunakan. Pasien dengan performance status 3 atau
4 tidak boleh menerima Irinotecan. Pada pasien yang menerima Irinotecan/5-FU/LV atau 5-
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
FU/LV dibandingkan agen ini, tingkat kejadian lebih tinggi untuk rawat inap, demam
neutropenia, tromboemboli, penghentian pengobatan siklus pertama, dan kematian dini diamati
pada pasien dengan baseline performance status 2 dibandingkan pada pasien dengan baseline
performance status 0 atau 1.
- Kanker lambung : Pasien dengan kanker lambung tampaknya mengalami mielosupresi yang
lebih besar dan toksisitas lain ketika diberikan Irinotecan. Dosis awal yang lebih rendah harus
dipertimbangkan pada pasien ini.
- Kehamilan dan menyusui :
a. Kehamilan : Irinotecan dapat menyebabkan kerusakan janin saat diberikan kepada wanita
hamil. Jika obat ini digunakan selama kehamilan, atau jika pasien hamil saat menerima obat
ini, pasien harus diberitahu tentang potensi bahaya pada janin. Wanita yang berpotensi
melahirkan disarankan untuk tidak hamil saat menerima pengobatan dengan Irinotecan.
b. Menyusui : Karena banyak obat diekskresikan dalam ASI, dan karena potensi efek
samping pada bayi menyusui, pemberian ASI harus dihentikan selama terapi Irinotecan.
INTERAKSI OBAT :
- Penghambat CYP3A4 dan/atau UGT1A1 :
a. Irinotecan dan metabolit aktif SN-38 dimetabolisme melalui isoenzim sitokrom P450 3A4
(CYP3A4) dan uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1). Pemberian
bersama Irinotecan dengan penghambat CYO3A4 dan/atau UGT1A1 dapat menghasilkan
peningkatan paparan sistemik terhadap Irinotecan dan metabolit aktif SN-38. Dokter harus
mempertimbangkan hal ini ketika memberikan Irinotecan dengan obat-obatan ini.
b. Ketoconazole : Pembersihan Irinotecan sangat berkurang pada pasien yang menerima
Ketoconazole secara bersamaan, yang menyebabkan peningkatan paparan SN-38.
Ketoconazole harus dihentikan setidaknya 1 minggu sebelum memulai terapi Irinotecan dan
tidak boleh diberikan selama terapi Irinotecan.
c. Atazanavir sulfate : Pemberian bersama Atazanavir sulfate, penghambat CYP3A4 dan
UGT1A1 memiliki potensi untuk meningkatkan paparan sistemik terhadap SN-38,
metabolit aktif Irinotecan. Dokter harus mempertimbangkan hal ini ketika pemberian
bersama obat ini.
- Penginduksi CYP3A4 :
a. Antikonvulsi : Pemberian bersamaan dengan obat antikonvulsan yang menginduksi CYP3A
(misalnya Carbamazepine, Phenobarbital atau Phenytoin) menyebabkan berkurangnya
paparan pada metabolit aktif SN-38. Pertimbangan harus diberikan untuk memulai atau
mengganti antikonvulsan yang tidak menginduksi enzim setidaknya satu minggu sebelum
memulai terapi Irinotecan pada pasien yang membutuhkan pengobatan antikonvulsan.
b. St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) : Paparan terhadap metabolit aktif SN-38
berkurang pada pasien yang menggunakan St. John's wort secara bersamaan. St. John's wort
harus dihentikan setidaknya 1 minggu sebelum siklus pertama Irinotecan, dan tidak boleh
diberikan selama terapi Irinotecan.
- Interaksi lain :
a. Agen penghambat neuromuskular : Interaksi antara Irinotecan Hydrochlorida dan agen
penghambat neuromuskular tidak dapat dihindari, karena Irinotecan memiliki aktivitas
antikolinesterase. Obat-obatan dengan aktivitas antikolinesterase dapat memperpanjang
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
efek penghambatan neuromuskular dari Suxamethonium dan penghambatan neuromuskular
dari obat-obatan non-depolarisasi dapat menjadi antagonis.
b. Agen antineoplastik : Efek samping dari Irinotecan, seperti mielosupresi dan diare,
diperkirakan akan diperburuk oleh agen antineoplastik lainnya yang memiliki profil efek
samping yang serupa.
c. Dexamethasone : Limfositopenia telah terjadi pada pasien yang menerima Irinotecan, dan
ada kemungkinan bahwa pemberian Dexamethasone sebagai profilaksis antiemetik dapat
meningkatkan kemungkinan limfositopenia. Namun, infeksi oportunistik yang serius belum
diamati dan tidak memiliki komplikasi spesifik yang dikaitkan dengan limfositopenia.
Hiperglikemia telah diamati pada pasien dengan riwayat diabetes mellitus atau terbukti
intoleransi glukosa sebelum pemberian Irinotecan. Kemungkinan Dexamethasone, yang
diberikan sebagai profilaksis antiemetik, berkontribusi terhadap hiperglikemia pada
beberapa pasien.
d. Pencahar : Penggunaan pencahar selama terapi dengan Irinotecan diperkirakan dapat
memperburuk kejadian atau keparahan diare.
e. Diuretik : Dehidrasi sekunder hingga muntah dan/atau diare dapat disebabkan oleh
Irinotecan. Dokter mungkin ingin menunda diuretik selama pemberian dengan Irinotecan
dan selama periode muntah atau diare aktif.
f. Bevacizumab : Hasil dari uji interaksi obat-obat tertentu menunjukkan tidak ada efek
signifikan Bevacizumab pada farmakokinetik Irinotecan dan metabolit aktifnya SN-38.
EFEK SAMPING OBAT :
NCI (National Cancer Institute) tingkat 1 sampai 4 terkait efek samping obat
Gangguan saluran pencernaan Diare yang tertunda, mual, muntah, diare lebih awal,
kram/nyeri perut, anoreksia, stomatitis
Gangguan sistem limfatik dan darah Leukopenia, anemia, neutropenia
Gangguan umum dan kondisi tempat Asthenia, demam
pemberian
Gangguan metabolisme dan nutrisi Penurunan berat badan, dehidrasi
Gangguan kulit dan jaringan subkutan Alopecia
Gangguan pembuluh darah Kasus tromboembolik*
NCI (National Cancer Institute) tingkat 3 atau 4 terkait efek samping obat
Gangguan saluran pencernaan Diare yang tertunda, mual, kram/nyeri perut, muntah,
diare lebih awal, konstipasi, anoreksia, mukositis,
gangguan rektal, GI monilia
Gangguan sistem limfatik dan darah Leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, trombositopenia
Gangguan kulit dan jaringan subkutan Alopecia, ruam, tanda-tanda kulit
Infeksi dan infestasi Infeksi, sepsis
Gangguan umum dan kondisi tempat Asthenia, demam, nyeri, menggigil, malaise
pemberian
Gangguan metabolisme dan nutrisi Dehidrasi, hypovolemia, penurunan berat badan,
hipokalemia, hipomagnesimia
Gangguan hepatobiliari Bilirubinemia
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Gangguan pernapasan, toraks, dan Dispnea
mediastinum
Gangguan sistem saraf Abnormal gait, kebingungan, sakit kepala
Gangguan jantung Hipotensi, sinkop, gangguan jantung
Gangguan ginjal dan urin Infeksi saluran urin
Gangguan sistem reproduksi dan Nyeri payudara
payudara
Investigasi Peningkatan kreatinin, peningkatan alkaline
phosphatase, peningkatan GGTP
* Termasuk angina pektoris, trombosis arteri, infark serebral, cedera serebrovaskular,
tromboflebitis dalam, ekstremitas bawah embolus, henti jantung, infark miokard, iskemia
miokard, kelainan pembuluh darah perifer, embolus paru, kematian mendadak, tromboflebitis,
gangguan pembuluh darah, kelainan pembuluh darah.
Berikut peristiwa terkait obat tambahan telah terjadi dengan Irinotecan, tetapi tidak memenuhi
kriteria sebagaimana didefinisikan di atas baik sebagai kasus NCI tingkat 1 - 4 yang terkait
dengan obat maupun sebagai NCI tingkat 3 atau 4 yang terkait obat : Rinitis, peningkatan air liur,
miosis, lakrimasi, diaforesis, flushing, bradikardia, pusing, ekstravasasi, sindrom lisis tumor, dan
ulserasi kolon.
Cardiac disorders : Myocardial ischemic events have been observed following Irinotecan
therapy predominantly in patients with underlying cardiac disease, other known risk factors for
cardiac disease or previous cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Gastrointestinal disorder : Intestinal obstruction, ileus, megacolon, or gastrointestinal
hemorrhage, and cases of colitis, including typhlitis, ischemic and ulcerative colitis were reported.
In some cases, colitis was complicated by ulceration, bleeding, ileus, or infection. Cases of ileus
without preceding colitis have also been reported. Cases of intestinal perforation were reported.
Cases of symptomatic pancreatitis or asymptomatic elevated pancreatic enzymes have been
observed.
Hypovolemia : There have been cases of renal impairment and acute renal failure, generally in
patients who became infected and/or volume depleted from severe gastrointestinal toxicities.
Renal insufficiency, hypotension or circulatory failure have been observed in patients who
experienced episodes of dehydration associated with diarrhea and/or vomiting, or sepsis.
Immune system disorders : Hypersensitivity reactions including severe anaphylactic or
anaphylactoid reactions have been reported.
Musculoskeletal disorders and connective tissue disorders : Early effects, such as muscular
contraction or cramps and paresthesia, have been reported.
Nervous system disorders : Speech disorders, generally transient in nature, have been reported in
patients treated with Irinotecan; in some cases, the event was attributed to the cholinergic
syndrome observed during or shortly after infusion of Irinotecan.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : Interstitial pneumonia and pneumonitis
presenting as pulmonary infiltrates have been observed. Early effects, such as dyspnea, have been
reported.
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Investigations : Cases of hyponatremia mostly related with diarrhea and vomiting have been
reported. Increases in serum levels of transaminases (i.e., AST and ALT) in the absence of
progressive liver metastasis have been reported.
OVERDOSIS :
Dosis tunggal Irinotecan sampai 750 mg/m2 telah diberikan kepada pasien dengan berbagai jenis
kanker. Efek samping pada pasien ini serupa dengan yang terjadi dengan dosis dan regimen yang
direkomendasikan. Terdapat laporan mengenai overdosis pada dosis hingga kira-kira dua kali
dosis terapi yang direkomendasikan, yang mungkin berakibat fatal. Efek samping yang paling
signifikan terjadi adalah neutropenia parah dan diare parah. Tidak ada obat penawar untuk
Irinotecan. Perawatan suportif maksimum harus diterapkan untuk mencegah dehidrasi akibat diare
dan untuk mengobati adanya komplikasi infeksi.
PENYIMPANAN :
Simpan di bawah suhu 30oC dan terlindung dari cahaya. Jauhkan dari jangkauan anak-anak.
PENYIMPANAN SETELAH REKONSTITUSI :
Untuk rekonstitusi :
IRITERO lebih dianjurkan diencerkan dalam injeksi Dextrose 5% sebelum infus atau injeksi
Sodium Chloride 0,9% dalam rentang konsentrasi akhir 0,12 - 2,8 mg/mL.
Dalam injeksi Sodium Chloride 0,9% : Setelah rekonstitusi, larutan stabil dalam 24 jam pada suhu
kamar.
Dalam injeksi Dextrose 5% : Setelah rekonstitusi, larutan stabil dalam waktu 6 jam pada suhu
kamar atau dalam 24 jam pada suhu 2 - 8oC.
KEMASAN :
IRITERO Larutan konsentrat untuk infus 40 mg/2 mL
Dus, Vial @ 2 mL
No. Reg. :
IRITERO Larutan konsentrat untuk infus 100 mg/5 mL
Dus, Vial @ 5 mL
No. Reg. :
HARUS DENGAN RESEP DOKTER
OBAT SITOTOKSIK
Diproduksi oleh :
HETERO LABS LIMITED UNIT VI
Telangana – India
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
Diimpor dan dipasarkan oleh :
PT. AMAROX PHARMA GLOBAL
Bekasi – Indonesia
DISETUJUI OLEH BPOM : 27/09/2019 EREG10042511800054
You might also like
- Glanders in HorseDocument43 pagesGlanders in HorseWerner AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Case StudyDocument7 pagesBlood Transfusion Case StudyErin ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Calcipotriol+Betamethasone OintmentDocument50 pagesCalcipotriol+Betamethasone OintmentJai MurugeshNo ratings yet
- 306941Document10 pages306941Guneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- Biolife: Nutrient AgarDocument2 pagesBiolife: Nutrient AgarZoza SalamaNo ratings yet
- Amphotericin B From Streptomyces SP.: Streptomyces Sp. It Has A High Affinity For SterolsDocument2 pagesAmphotericin B From Streptomyces SP.: Streptomyces Sp. It Has A High Affinity For SterolsNapassorn KeeratibunharnNo ratings yet
- Total Protein: Erba Lachema S.r.o., Karásek 2219/1d, 621 00 Brno, CZDocument4 pagesTotal Protein: Erba Lachema S.r.o., Karásek 2219/1d, 621 00 Brno, CZMatibar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Actemra PM E PDFDocument142 pagesActemra PM E PDFMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- BLOSR6X2010Document7 pagesBLOSR6X2010MustafaNo ratings yet
- Protéines Totales Biuret - ENDocument2 pagesProtéines Totales Biuret - ENYousra NanoNo ratings yet
- Actemra PM EDocument143 pagesActemra PM ELala Nur HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Revised: May 2018 AN: 00005/2018Document8 pagesRevised: May 2018 AN: 00005/2018Kishyorr KarthikNo ratings yet
- The Pesticide LabelDocument24 pagesThe Pesticide LabelJevelyn Mendoza FarroNo ratings yet
- Intron A: Escherichia ColiDocument44 pagesIntron A: Escherichia ColiAristoteles Esteban Cine VelazquezNo ratings yet
- LifePearl Loading Instructions Irino 3Document2 pagesLifePearl Loading Instructions Irino 3rasfahanNo ratings yet
- Fluorouracil FolinicAcid IrinotecanDocument6 pagesFluorouracil FolinicAcid Irinotecanromeo.aragon21No ratings yet
- MSDS Rentokil-Klerat-EN-SDS - 01 - CHIPDocument8 pagesMSDS Rentokil-Klerat-EN-SDS - 01 - CHIPpurwadiNo ratings yet
- Biuret-Gornall Protein Assay: Product DescriptionDocument3 pagesBiuret-Gornall Protein Assay: Product Descriptioninsiya insiyaNo ratings yet
- Terrific Broth: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesTerrific Broth: Product DescriptionNabila Putri SabilaNo ratings yet
- Phytosan PP - Specification - 2017-04 - eDocument3 pagesPhytosan PP - Specification - 2017-04 - ejoanamarie cuyungNo ratings yet
- Neupogen Product Monograph Page 1 of 51Document51 pagesNeupogen Product Monograph Page 1 of 51Osi Oseda0% (1)
- Creatinine: Kinetic MethodDocument2 pagesCreatinine: Kinetic MethodCarina AngelNo ratings yet
- TOBREX - Tobramycin S Olution/ Drops Alcon Laboratories, IncDocument5 pagesTOBREX - Tobramycin S Olution/ Drops Alcon Laboratories, IncMOCH FARCHAN N C CNo ratings yet
- Sndoct 21Document24 pagesSndoct 21satishNo ratings yet
- TYGACIL PM E 159612 6dec2012Document67 pagesTYGACIL PM E 159612 6dec2012Asto Ata InteristiNo ratings yet
- Total Protein FS : Order InformationDocument2 pagesTotal Protein FS : Order InformationMikko DecolongonNo ratings yet
- BETA-SSA Agar (Group A Streptococci Selective Agar)Document3 pagesBETA-SSA Agar (Group A Streptococci Selective Agar)uttam.micro404No ratings yet
- At 13450Document2 pagesAt 13450dr_joe23No ratings yet
- Uma Co., Ltd. Hba1C Diluent: 2-19-6 Yokosuka Matsudo, Chiba, JapanDocument1 pageUma Co., Ltd. Hba1C Diluent: 2-19-6 Yokosuka Matsudo, Chiba, JapanTrần Văn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Gentacalm Topical Spray Pack InsertDocument1 pageGentacalm Topical Spray Pack InsertFkhugm 2016No ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Plant Tissue CultureDocument3 pagesAntibiotics in Plant Tissue CultureMohammad Sadegh BagheriNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Alkaline Phosphatase (Calf Intestine)Document2 pagesCertificate of Analysis: Alkaline Phosphatase (Calf Intestine)xprakashNo ratings yet
- ErythromycinDocument21 pagesErythromycinMuhammad Zubair NoorNo ratings yet
- Complement C3c FS : Order InformationDocument3 pagesComplement C3c FS : Order InformationAlejandraNo ratings yet
- United States Environmental Protection Agency Washington, DC 20460Document10 pagesUnited States Environmental Protection Agency Washington, DC 20460kaya kurtNo ratings yet
- AU Instructions For Use Albumin: PrincipleDocument6 pagesAU Instructions For Use Albumin: PrincipleAnas TjNo ratings yet
- MH144 SJSMSNDocument3 pagesMH144 SJSMSNsulistyani sapardiNo ratings yet
- PI e CREA - JAFFE 2Document3 pagesPI e CREA - JAFFE 2fitri fadhilahNo ratings yet
- Us Bactroban OintmentDocument4 pagesUs Bactroban OintmentJayCee AriasNo ratings yet
- The Use of Isotretinoin in AcneDocument8 pagesThe Use of Isotretinoin in AcneMelisa Silvia SembiringNo ratings yet
- AU Instructions For Use Total Protein: PrincipleDocument6 pagesAU Instructions For Use Total Protein: PrincipleAnas TjNo ratings yet
- at Gamma GTDocument2 pagesat Gamma GTNia MarianiNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Indicador Biologico BT20Document4 pagesFicha Tecnica Indicador Biologico BT20CATALINA FAJARDONo ratings yet
- Tribrissen1 PDFDocument5 pagesTribrissen1 PDFmuhammad imranNo ratings yet
- Public Summary: 1 - Amcal Spf50+ Sunscreen LotionDocument2 pagesPublic Summary: 1 - Amcal Spf50+ Sunscreen LotionRadoNo ratings yet
- Public Summary: 1 - Amcal Dry Touch Sunscreen Lotion Spf50Document2 pagesPublic Summary: 1 - Amcal Dry Touch Sunscreen Lotion Spf50RadoNo ratings yet
- Irinotekan QILU-spcDocument24 pagesIrinotekan QILU-spcSrechko MilichNo ratings yet
- Telmisartan 80 MG TabletDocument5 pagesTelmisartan 80 MG TabletMd. Abdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 47 1 Lipids Profile INGDocument6 pages47 1 Lipids Profile INGGuneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- Package Insert - PYROGENT™-5000 (English) - Original - 29682Document17 pagesPackage Insert - PYROGENT™-5000 (English) - Original - 29682Putri DozanNo ratings yet
- M125 Thermoacidurans AgarDocument2 pagesM125 Thermoacidurans AgarsusanikarnoNo ratings yet
- Proteinase K Solution: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesProteinase K Solution: Product DescriptionrakaryawanNo ratings yet
- ArtesunateDocument4 pagesArtesunateSyifa Ari SuciyaniNo ratings yet
- Phenylephrine HCL - 10mg TabletDocument5 pagesPhenylephrine HCL - 10mg TabletMd. Abdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- MSDS Pyridoxine HCL (VB6) - Jiangxin Tianxin-SSNDocument7 pagesMSDS Pyridoxine HCL (VB6) - Jiangxin Tianxin-SSNHari TrisusiloNo ratings yet
- Product Monograph: Nitrofurantoin Capsules, House Standard (Nitrofurantoin Monohydrate/macrocrystals) 100 MGDocument21 pagesProduct Monograph: Nitrofurantoin Capsules, House Standard (Nitrofurantoin Monohydrate/macrocrystals) 100 MGdriftithegreatNo ratings yet
- Gifu Anaerobic Broth (GAM) : Intended UseDocument3 pagesGifu Anaerobic Broth (GAM) : Intended UseVishwanath Unique BiotechNo ratings yet
- Public Summary: 1 - Anko SPF50+ Kids Sunscreen (Spray)Document2 pagesPublic Summary: 1 - Anko SPF50+ Kids Sunscreen (Spray)RadoNo ratings yet
- Review Article Sep 2018Document11 pagesReview Article Sep 2018Vitor JacóNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document4 pagesVitamin B12hairiNo ratings yet
- GGT enDocument2 pagesGGT enKaoueche OmarNo ratings yet
- Insersi PesariumDocument21 pagesInsersi PesariumiFha AM.No ratings yet
- Woman's Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageWoman's Reproductive SystemDiana ObeidNo ratings yet
- P1 Facts About AnencephalyDocument8 pagesP1 Facts About AnencephalyAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Must KnowDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Must Knownathanmrrk pacayNo ratings yet
- Brucellosis: Synonyms in AnimalsDocument5 pagesBrucellosis: Synonyms in AnimalsVenkatapradeepNo ratings yet
- Cancer Plan After 1 YrDocument46 pagesCancer Plan After 1 YrShirley SpenceNo ratings yet
- Corneal Dystrophy and DegenerationsDocument12 pagesCorneal Dystrophy and Degenerationsamritnam satyadasNo ratings yet
- Siddha Therapeutic Index - 18-Article Text-133-1-10-20210308Document7 pagesSiddha Therapeutic Index - 18-Article Text-133-1-10-20210308Dr.kali.vijay kumkarNo ratings yet
- Case Report LaringomalaciaDocument10 pagesCase Report LaringomalaciaagitNo ratings yet
- Radiologi DR Budi - Pediatric Congenital Neurological DiseasesDocument30 pagesRadiologi DR Budi - Pediatric Congenital Neurological DiseasesPusparasmi Mas Ayu SuprabhaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Bladder: Hinese Name Location: ClassificationDocument33 pagesUrinary Bladder: Hinese Name Location: ClassificationHari YukthaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Giorgi Kochiashvili, Rupesh Mohanadas, Mohammed Bilal, AbivarmaDocument29 pagesCase Presentation: Giorgi Kochiashvili, Rupesh Mohanadas, Mohammed Bilal, AbivarmaRupesh MohandasNo ratings yet
- Testicular TorsionDocument12 pagesTesticular TorsionlicutNo ratings yet
- Puerperal Infection of The Genital TractDocument11 pagesPuerperal Infection of The Genital TractNatalia Vasquez MedicoNo ratings yet
- Small Fibre Neuropathy: ReviewDocument10 pagesSmall Fibre Neuropathy: ReviewMaria RenjaanNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Infection PDFDocument12 pagesAcute Respiratory Infection PDFSanti Galang GuadesNo ratings yet
- Social Case StudyDocument5 pagesSocial Case StudyMa. Corazon BandaNo ratings yet
- Iaedp Newsletter Spring-2016Document1 pageIaedp Newsletter Spring-2016api-250253869No ratings yet
- Migraine Headache - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument17 pagesMigraine Headache - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal EndosDocument28 pagesGastrointestinal EndosAqeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Harriet Lane handbook of Pediatrics 22nd Edition export (1)Document1 pageHarriet Lane handbook of Pediatrics 22nd Edition export (1)Kashaf ZuhaNo ratings yet
- Theratalk RatesDocument1 pageTheratalk Rateslouise santosNo ratings yet
- Script For OrientationDocument2 pagesScript For OrientationAngela CudiaNo ratings yet
- DR Ty BLS PALS1Document4 pagesDR Ty BLS PALS1Burt Robinson LayosNo ratings yet
- Vaccine CDCDocument40 pagesVaccine CDCnasibdinNo ratings yet
- Anemia in ChildrenDocument67 pagesAnemia in ChildrenAgung Maulana ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Health Daily News Healthmedicinet 2024-03-25Document5 pagesHealth Daily News Healthmedicinet 2024-03-25tuni santeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Jaundice Group 2 FinalDocument44 pagesBiochemistry of Jaundice Group 2 FinalShanna SolideoNo ratings yet