Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MW Lecture10
Uploaded by
mark mark0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesOriginal Title
MW lecture10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesMW Lecture10
Uploaded by
mark markCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Magic T and Isolators
• A magic tee is a combination of the £-plane tee and H -plane tee
Magic tee characteristics:
1. If two waves of equal magnitude and the same phase are fed into
port 1 and port 2, the output will be zero at port 3 and additive at
port 4.
2. If a wave is fed into port 4 (the Harm), it will be divided equally
between port 1 and port 2 of the collinear arms and will not appear
at port 3 (the E arm).
3. If a wave is fed into port 3 (the E arm), it will produce an output of
equal magnitude and opposite phase at port 1 and port 2. The
output at port 4 is zero.
• If a wave is fed into one of the collinear arms at port 1 or port 2, it will
not appear in the other collinear arm at port 2 or port 1 because the
E arm causes a phase delay while the Harm causes a phase advance.
That is, S12 = S21 = 0.
• Therefore the S matrix of a magic tee can be expressed as
Magic Tee applications
• The magic tee is commonly used for mixing, duplexing, and
impedance measurements.
• Suppose, for example, there are two identical radar transmitters in
equipment stock. A particular application requires twice more input
power to an antenna than either transmitter can deliver. A magic tee
may be used to couple the two transmitters to the antenna in such a
way that the transmitters do not load each other.
• The two transmitters should be connected to ports 3 and 4,
respectively, as shown in Fig. 4-4-8. Transmitter 1, connected
to port 3, causes a wave to emanate from port 1 and another
to emanate from port 2; these waves are equal in magnitude
but opposite in phase. Similarly, transmitter 2, connected to
port 4, gives rise to a wave at port 1 and another at port 2,
both equal in magnitude and in phase. At port 1 the two
opposite waves cancel each other. At port 2 the two in-phase
waves add together; so double output power at port 2 is
obtained for the antenna as shown in Fig. 4-4-8.
Ex:
If a signal of 2𝑽𝒑𝒑 is applied to port 1 of magic Tee determine the power at each other port
assuming all ports are matched
Sol:
The power will split between 3&4
And nothing will reach port 2.
(Vrms) 2
P= , lets R=1;
𝑅
Vrms=2/2 2 =0.707
P=0.5 watt
Power at port 1 =0.5 watt
Power at port 2=0 watt
Power at port 3=0.25 watt
Power at port 4=0.25 watt
Isolators
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Maxwell's Equations: 1'st Equation (From Faraday Law)Document4 pagesMaxwell's Equations: 1'st Equation (From Faraday Law)mark markNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Force and Boundary ConditionDocument6 pagesMagnetic Force and Boundary Conditionmark markNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Flux and Magnetic Flux DensityDocument6 pagesMagnetic Flux and Magnetic Flux Densitymark markNo ratings yet
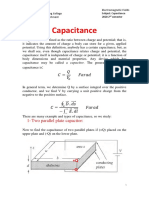
- Capacitance: 1-Two Parallel Plate CapacitorDocument7 pagesCapacitance: 1-Two Parallel Plate Capacitormark markNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field: 1-Biot-Savart LawDocument8 pagesMagnetic Field: 1-Biot-Savart Lawmark markNo ratings yet
- Assad SDDocument36 pagesAssad SDmark markNo ratings yet
- Circular WaveguidesDocument27 pagesCircular Waveguidesmark markNo ratings yet
- AsdasdDocument27 pagesAsdasdmark markNo ratings yet
- Microwave Cavities and Waveguide TEEDocument36 pagesMicrowave Cavities and Waveguide TEEmark markNo ratings yet
- TM Mode in Circular WaveguideDocument17 pagesTM Mode in Circular Waveguidemark markNo ratings yet
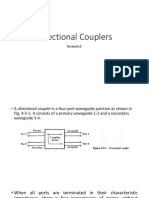
- Directional CouplersDocument12 pagesDirectional Couplersmark markNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)