Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture - 01
Uploaded by
Mominul HaqueCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture - 01
Uploaded by
Mominul HaqueCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture - 01
Acid: Acid is a class of chemical compound which dissolves in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+).
Classification of acids: Acids can be classified in different ways – Depending on their -
a. Sources b. Strength c. Concentration
a. Types of acids on the basis of sources: Inorganic and organic acids
1. Inorganic acid or mineral acid: The acid that is obtained from minerals (e.g. water, soil, air etc) is
called an inorganic acid or mineral acid.
Properties of mineral acids:
generally much stronger
most do not occur naturally
usually have simpler molecules
Name of acid Formula Strength
Sulfuric acid H2SO4
Hydrochloric acid HCl Strong
Nitric acid HNO3
Sulfurous acid H2SO3
Phosphoric acid H3PO4 Moderate strong
Phosphorous acid H3PO3
Carbonic acid H2CO3 Weak acid
2. Organic acid: The acid that is derived from living sources (e.g. plants and animals) is called an
organic acid. Organic acids belongs to the homologous series fatty acids and general formula of this
homologous series is CnH2n+1COOH or R-COOH.
Properties of organic acids:
naturally occurring
found in vegetables, fruit and other foodstuffs
usually weaker and less corrosive
Organic acid Formula Where it is found
Lactic acid CH3-CH(OH)-COOH or C3H6O3 Sour milk
Oxalic acid (COOH)2 or HOOC-COOH or C2H2O4 Rhubarb plant, tomatoes etc
Citric acid HOOC-CH2-C(COOH)(OH)- CH2-COOH or Limes, lemons and
C6H8O7 oranges(citrus food) etc
Formic acid HCOOH or CH2O2 Insect bites (e.g. ant, bee etc),
stinging nettles etc
Tartaric acid HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COOH or C4H6O6 Grape juice, tamarind etc
Tannic acid C76H52O46 Tea
Acetic / CH3COOH or C2O2H4 Vinegar
ethanoic acid
Apples, pears and pineapples
Malic acid HOOC-CH2-CH(OH)-COOH or C4H6O5 etc
Amloki
Ascorbic acid C6H8O6
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Common Names of ChemicalsDocument6 pagesCommon Names of ChemicalstpplantNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Science 10 Chemistry Unit PlanDocument24 pagesScience 10 Chemistry Unit Planapi-477617112No ratings yet
- Ws-Word Equations and BalancingDocument4 pagesWs-Word Equations and Balancingapi-351363594No ratings yet
- Chem Exam 2000Document9 pagesChem Exam 2000Alex JinNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02 States of Matter (MCQ'S)Document4 pagesChapter - 02 States of Matter (MCQ'S)Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry & General Chemistry Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnalytical Chemistry & General Chemistry Review QuestionsMicahmae MorbsNo ratings yet
- Halogen DerivativesDocument11 pagesHalogen DerivativesJayjayjay 5100% (1)
- Gamsat Chemistry Sample Questions PDFDocument6 pagesGamsat Chemistry Sample Questions PDFBandita DattaNo ratings yet
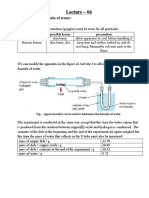
- Lecture - 06Document3 pagesLecture - 06Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 09: The Iris ReflexDocument2 pagesLecture - 09: The Iris ReflexMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 06Document3 pagesLecture - 06Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument3 pagesPollinationMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- What Is Good Design? Answer: What Makes A Design Good? AnswerDocument4 pagesWhat Is Good Design? Answer: What Makes A Design Good? AnswerMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 01 (Physical Quantities and Their Measurements)Document10 pagesChapter - 01 (Physical Quantities and Their Measurements)Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02 (Motion)Document2 pagesChapter - 02 (Motion)Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Activity 3: Practical: Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesActivity 3: Practical: Risk AssessmentMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- 556995-2022-Syllabus Cie Igcse Biology-8-52Document45 pages556995-2022-Syllabus Cie Igcse Biology-8-52Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- 556995-2022-Syllabus Cie Igcse Biology-53Document1 page556995-2022-Syllabus Cie Igcse Biology-53Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 06: Determine The Formula of Water: Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesLecture - 06: Determine The Formula of Water: Risk AssessmentMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 02: Transition Elements / MetalsDocument3 pagesLecture - 02: Transition Elements / MetalsMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology Student Book-41Document1 pageEdexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology Student Book-41Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Chemistry Student Book-30Document1 pageEdexcel International GCSE (9-1) Chemistry Student Book-30Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology Student Book-58Document1 pageEdexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology Student Book-58Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- PDF CropDocument1 pagePDF CropMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 1 Chm624Document11 pagesLab Report Experiment 1 Chm624Hazwan HamimNo ratings yet
- Binder 2Document33 pagesBinder 2aNo ratings yet
- Advanced Chemistry 1Document8 pagesAdvanced Chemistry 1ogbugodwinc0No ratings yet
- 016) Main GroupDocument31 pages016) Main GroupHarish RamachandraNo ratings yet
- Module 01 Study On The Effect of Pressure Mixing and Temperature Between Baking Soda and Acetic AcidDocument9 pagesModule 01 Study On The Effect of Pressure Mixing and Temperature Between Baking Soda and Acetic AcidFarah -H100% (1)
- Sample Paper 24Document13 pagesSample Paper 24DeekshanNo ratings yet
- Wa0007Document13 pagesWa0007Amogh R.GowdaNo ratings yet
- 1.B.2 Typical Reactions of AcidsDocument22 pages1.B.2 Typical Reactions of Acidsal katerjiNo ratings yet
- D2942-02 (2013) Standard Test Method For Total AciDocument3 pagesD2942-02 (2013) Standard Test Method For Total Acijose floresNo ratings yet
- Liquid FertilizerDocument5 pagesLiquid Fertilizerpakde jongkoNo ratings yet
- Shibuya Chiba2010Document7 pagesShibuya Chiba2010Anderson KaianNo ratings yet
- Rust Removal: With Various Metals and AlloysDocument4 pagesRust Removal: With Various Metals and AlloysHans TorresNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY Lab Manual - Sept - 2023Document28 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY Lab Manual - Sept - 2023Rồi QuênNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Unit 1Document33 pagesDBMS - Unit 1AayushNo ratings yet
- 9701 w22 QP 23oct-NovDocument16 pages9701 w22 QP 23oct-NovnellyistantiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Test Bankwendelngosseuk100% (25)
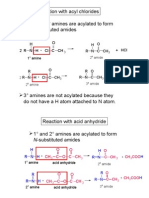
- Matriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 2Document13 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 2ridwanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins With Minerals Oral PowderDocument8 pagesVitamins With Minerals Oral PowderWH PANDWNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Past Year Question (Combination)Document6 pagesChapter 10 Past Year Question (Combination)angelNo ratings yet
- Star TestDocument26 pagesStar TestEamon BarkhordarianNo ratings yet
- CHEM 02 C05 Determining PH Level Using Universal IndicatorsDocument4 pagesCHEM 02 C05 Determining PH Level Using Universal IndicatorsblablaNo ratings yet
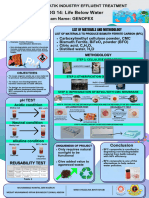
- Batik Industry Effluent TreatmentDocument1 pageBatik Industry Effluent Treatmentfaridahfadzil73No ratings yet
- Organic Chem Lab Final ExamDocument7 pagesOrganic Chem Lab Final ExammvmbappleNo ratings yet