Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alf Forppt 1
Uploaded by
1S VILLEGAS Gabriel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesAlf Forppt 1
Uploaded by
1S VILLEGAS GabrielCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
For PPT
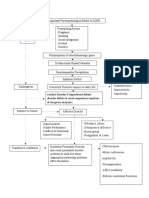
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a devastating syndrome that triggers a cascade of events, leading to
multiple organ failure and often death.
ALF is a syndrome defined by the occurrence of encephalopathy, coagulopathy and jaundice in
an individual with a previously normal liver.
Patients with high grades of encephalopathy, the chances of survival are less than 20% with
medical management alone. Early deaths in ALF are often caused by cerebral oedema or
cardiovascular collapse, whereas late deaths tend to result from sepsis and multiple organ failure.
O’Grady System
Hyperacute (0 - 1 week
Acute (From 1 week - 4 weeks)
Subacute (From 4th week - 12 weeks)
Causes of Acute Liver Failure
1. Viral Hepatitis
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E
- CMV, EBV, VZV
2. Drugs/Toxins
-Acetaminophen
-Herbal supplements
-Antibiotics
-Mushroom poisoning
3. Shock/ ischemic liver
4. Alcoholic hepatitis
5. Autoimmune disease
6. Cryptogenic
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of acute liver failure may include:
Yellowing of your skin and eyeballs (jaundice)
Pain in your upper right abdomen
Abdominal swelling (ascites)
Nausea
Vomiting
A general sense of feeling unwell (malaise)
Disorientation or confusion
Sleepiness
Breath may have a musty or sweet odor
Tremors
Complications
Acute liver failure often causes complications, including:
Excessive fluid in the brain (cerebral edema).
Bleeding and bleeding disorders.
Infections.
Kidney failure.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Acute Liver Failure Group 3Document16 pagesAcute Liver Failure Group 31S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- PDF Nutrition CM 2 CU 6 LAB WEEK 7Document4 pagesPDF Nutrition CM 2 CU 6 LAB WEEK 71S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure: Group IIIDocument16 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure: Group III1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Mary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPTDocument34 pagesMary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPT1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- 418rle-M2-Ru9 Case Scenario Dka Vs HhsDocument4 pages418rle-M2-Ru9 Case Scenario Dka Vs Hhs1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Mary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPTDocument45 pagesMary Ann E. Lopez Man RN LPT1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Philippine Health Care Delivery System: Mary Ann E. Lopez MAN RN LPTDocument40 pagesPhilippine Health Care Delivery System: Mary Ann E. Lopez MAN RN LPT1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Name: Villegas, Gabriel G. Section: BSN 4Y1-1Document2 pagesName: Villegas, Gabriel G. Section: BSN 4Y1-11S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Volvulus GROUP 4Document7 pagesVolvulus GROUP 41S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- AlcoholismDocument30 pagesAlcoholism1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Meniere FinalDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Meniere Final1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Subjective: No Subjective Cues. ObjectiveDocument2 pagesSubjective: No Subjective Cues. Objective1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- ADHD PsychopathologyDocument1 pageADHD Psychopathology1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet