Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anemia Part II
Anemia Part II
Uploaded by
J Pao Bayro - LacanilaoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anemia Part II
Anemia Part II
Uploaded by
J Pao Bayro - LacanilaoCopyright:
Available Formats
SAN FERNANDO, PAMPANGA
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
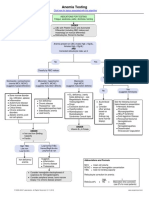
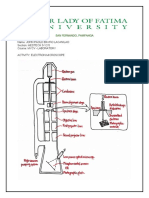
MACROCYTIC ANEMIA
THE ORDER PERIPHERAL SMEAR TO EVALUATE FOR
HYPERSEGMENTED NEUTROPHILS THAT INDICATES
THE MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA
NON-MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA
MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA
OBTAIN RETICULOCYTE COUNT
TEST FOLATE AND VITAMIN B12 LEVELS
LOW HIGH
VITAMIN B12 LEVEL LOW FOLATE LEVEL LOW BOTH LEVELS LOW and NORMAL
EVALUATE FOR ALCOHOLISM, EVALUATE FOR
HYPOTHYROIDISM, OR HEMOLYSIS OR
Treat and retest, consider Treat and retest, HEPATIC DISEASE HEMORRHAGE
treating for pernicious provide dietary
anemia or ileal disease counseling
REFER TO PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGIST
FOR CONSIDERATION OF BONE CAUSE UNKNOWN
NO IMPROVEMENT MARROW DISORDERS
DEFICIENCY DIAGNOSIS EVALUATION
Pernecious anaemia, Nutritional, Schilling’s test, Anti-IF and Anti Parietal
Vitamin B12
Malabsorption cell antibodies
Folate Nutritional, Malabsorption History and examination
Both Malabsorption History and examination
Inherited DNA synthesis defects,
None History
cytotoxic drugs
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
NORMOCYTIC ANEMIAS
(MCV 80-100 um3)
Corrected reticulocyte count
<3% >3 %
Blood loss <1 week INTRINSIC RBC DEFECT
EXTRINSIC RBC DEFECT
Early-stage iron deficiency Membrane defects:
Early-stage anemia Hereditary spherocytosis Blood loss >1 week
chronic disease Hereditary elliptocytosis Immune hemolytic anemias
Aplastic anemia Paroxysmal nocturnal Micro/macroangiopathic
Renal disease hemoglobinuria hemolytic anemia
Malignancy Abnormal hemoglobins: Malaria
Sickle cell disease
Deficient enzymes:
G6PD deficiency
Pyruvate kinase deficiency
NORMOCYTIC ANEMIA:
TYPE OF NORMOCYTIC PERIPHERAL BLOOD BONE MARROW
ANEMIA
APLASTIC ANEMIA AA is defined by peripheral a hypoplastic bone marrow
blood pancytopenia with a that has fatty replacement
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
hypocellular bone marrow in and that may have relatively
which normal hemopoiesis is increased nonhematopoietic
replaced to a greater or elements, such as mast cells
lesser extent by fat cells in
the absence of genetic,
malignant or predictable
myelosuppressive causes.
ACQUIRED APLASTIC ANEMIA AA is defined by peripheral Acquired aplastic anemia
blood pancytopenia with a (AA) is characterized by a
hypocellular bone marrow in hypoplastic, fatty bone
which normal hemopoiesis is marrow (BM) with profound
replaced to a greater or reductions in hematopoietic
lesser extent by fat cells in stem/progenitor cells
the absence of genetic, (HSCs/HPCs) that lead to
malignant or predictable defective mature blood cell
myelosuppressive causes. production and peripheral
pancytopenia
INHERITED APLASTIC ANEMIA Aplastic anemia occurs when
your bone marrow doesn't
make enough red and white
blood cells, and platelets.
Having fewer red blood cells
causes hemoglobin to drop.
FANCONI’S ANEMIA May look for dark spots on FA is a rare, inherited blood
the skin called café au lait disorder that prevents the
spots. The most common test bone marrow from producing
for Fanconi anemia is a blood enough new blood cells for
test called a chromosomal the body to function properly,
breakage test. or that causes the bone
marrow to make faulty blood
cells.
PURE RED CELL APLASIA Defined by a normocytic a bone marrow disorder
normochromic anemia with characterized by a reduction
severe reticulocytopenia and of red blood cells
marked reduction or absence (erythrocytes) produced by
of erythroid precursors from the bone marrow. Signs and
the bone marrow. Diamond- symptoms may include
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
Blackfan anemia is a fatigue, lethargy, and/or
congenital form of PRCA abnormal paleness of the
skin (pallor) due to the
anemia the caused by the
disorder.
DIAMOND BLACKFAN-ANEMIA A bone marrow aspiration DBA the bone marrow cannot
and biopsy (removing a small make enough red blood cells
amount of the liquid portion of to meet the body's needs.
bone marrow through a DBA is characterized by a
needle) along with genetic shortage of red blood cells
testing can confirm the which usually becomes
diagnosis evident during the first year of
life when the patient develops
anemia
MYELOPTHISIC ANEMIA The peripheral blood smear Bone marrow fibrosis often
will show characteristic occurs as a secondary
leukoerythroblastic reactions process as well.
with the presence of Splenomegaly may develop.
immature myeloid and Characteristic changes in
nucleated erythrocytes, peripheral blood include
including abnormal anisocytosis, poikilocytosis,
erythrocytes such as and excessive numbers of
schistocytes, and dacrocytes red blood cell and white
(teardrop) and blood cell precursors.
anisopoikilocytosis cells
MACROCYTIC ANEMIA:
TYPE OF MACROCYTIC
PERIPHERAL BLOOD BONE MARROW MISCELLANEOUS
ANEMIA
MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA Megaloblasts are large bone marrow produces Form of anemia
nucleated red blood cell unusually large, structurally characterized by very large
precursors with no condensed abnormal, immature red blood red blood cells and a
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
decrease in the number of
those cells. Anemias are
blood disorders that occur
when the body has fewer
chromatin. cells (megaloblasts) red blood cells than
normal. Red blood cells
carry oxygen throughout
the body using a protein
called hemoglobin.
the lack of folic acid in the
blood. Folic acid is a B
causes the body to produce the red blood cells are
vitamin that helps your
abnormally large red blood cells abnormally large. Such cells
body make red blood cells.
that cannot function properly. are called macrocytes. They
FOLATE DEFICIENCY If you don't have enough
Red blood cells carry oxygen are also called megaloblasts,
red blood cells, you have
around the body using a when they are seen in the
anemia. Red blood cells
substance called hemoglobin. bone marrow
carry oxygen to all parts of
your body.
Well recognized and reversible
Round macrocytes are Weakness and fatigue are
cause of bone marrow failure.
commonly seen in a variety of common symptoms of
Macrocytic anemias secondary
chronic illnesses, and round vitamin B12 deficiency.
to folate and/or vitamin B12
target-appearing macrocytes They occur because your
deficiency are characterized by
VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY are characteristic of liver body doesn't have enough
typical morphological
disease such as hepatitis, vitamin B12 to make red
abnormalities in the bone
obstructive jaundice, and acute blood cells, which transport
marrow, attributable to flaws in
and chronic alcoholism with liver oxygen throughout your
both the synthesis and repair
disease body.
of DNA
Disease conditions can also Malabsorption is a clinical
limit iron absorption; this can term that refers to the
happen as a result of insufficient impaired absorption of
bone marrow produces
stomach acid, lack of intrinsic nutrients. It encompasses
unusually large, structurally
IMPAIRED ABSORPTION factor (IF), celiac disease, defects that occur during
abnormal, immature red blood
inflammatory conditions such as the digestion and
cells (megaloblasts)
Crohn's disease, and in absorption of food nutrients
autoimmune diseases and by, and infections of, the
hormone imbalances. gastrointestinal tract
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
COLLEGE OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE
You might also like
- Approach To Diagnosis of Haemolytic AnaemiasDocument2 pagesApproach To Diagnosis of Haemolytic AnaemiasGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test InterpretationDocument8 pagesLaboratory Test InterpretationSukhrian MuhdaNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2011 Student Dental FDocument64 pagesAnemia 2011 Student Dental Fkays30002403No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument8 pagesAnemiasibanah menor100% (1)
- Patho HematologyDocument39 pagesPatho HematologyCastleKGNo ratings yet
- His127 Slide Haemolytic Anaemia PDFDocument69 pagesHis127 Slide Haemolytic Anaemia PDFclaudya zaraNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Hemopoietic SystemDocument29 pagesDiseases of Hemopoietic SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- CH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument6 pagesCH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaGshshNo ratings yet
- Anemia HemolitikDocument37 pagesAnemia HemolitikBintang Ruth Cecilia FebrinaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Aniemia in ChildrenDocument33 pagesApproach To Aniemia in Childrenvidya RamisettiNo ratings yet
- MED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaDocument5 pagesMED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaFlora XuNo ratings yet
- Anemia OutlineDocument21 pagesAnemia OutlineQuazi Akif TahmidNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Anemia: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Prima IndonesiaDocument24 pagesClinical Approach To Anemia: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Prima IndonesiaDzil FikriNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument7 pagesAnemiaoktavianprNo ratings yet
- Degenevie - HematologyDocument71 pagesDegenevie - Hematologykkq7fhkwvkNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Diagnostic ApproachDocument36 pagesAnemia: Diagnostic ApproachRizky LumalessilNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow FailureDocument2 pagesBone Marrow FailureGerardLum100% (1)
- M.03 Hemolytic AnemiaDocument5 pagesM.03 Hemolytic AnemiaRaymund AldabaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument40 pagesAnemiaGreenNo ratings yet
- Hematology 4Document21 pagesHematology 4saad samyNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology:: in The Absence of Abnormal Infiltrate and With No Increase in ReticulinDocument6 pagesEpidemiology:: in The Absence of Abnormal Infiltrate and With No Increase in ReticulinSandeep m rNo ratings yet
- Hematology Part 1 NotesDocument23 pagesHematology Part 1 NotesDr. Benson BenjaminNo ratings yet
- ANAEMIADocument4 pagesANAEMIAPrashin RocharamNo ratings yet
- ANEMIADocument34 pagesANEMIAAkashNo ratings yet
- Anemia - SFFTDocument5 pagesAnemia - SFFTShikha UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument11 pagesAnemiaNada AmjadNo ratings yet
- ANEMIADocument3 pagesANEMIAjessa tabanginNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pancytopenia (3) - 1Document37 pagesApproach To Pancytopenia (3) - 1RahulNo ratings yet
- Erythrocyte Disorders: (Anemias: Red Blood Cell Morphology and Approach To Diagnosis)Document15 pagesErythrocyte Disorders: (Anemias: Red Blood Cell Morphology and Approach To Diagnosis)ALMIRAH PEDRAZANo ratings yet
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument110 pagesAnemia in PregnancyMonika shankarNo ratings yet
- Blood: Nikita Sebastian 1 Year Post Graduate Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics JSSDCHDocument94 pagesBlood: Nikita Sebastian 1 Year Post Graduate Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics JSSDCHNikita SebastianNo ratings yet
- Anemia, Ida 1Document131 pagesAnemia, Ida 1zaha shamseerNo ratings yet
- Approach To Hemolytic AnemiaDocument63 pagesApproach To Hemolytic AnemiaSarath Menon R100% (2)
- Anemia Pada Anak - DR AuliaDocument61 pagesAnemia Pada Anak - DR AuliaSamuel ManurungNo ratings yet
- HaematologyDocument62 pagesHaematologyManmeet SNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pancytopenia: Moderator - DR Vishal Gupta MD Medicine Presented By-Dr Narendra Singh Resident Doctor 2Document35 pagesApproach To Pancytopenia: Moderator - DR Vishal Gupta MD Medicine Presented By-Dr Narendra Singh Resident Doctor 2ntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Aplastic Anemia and Approach To Diagnosis in A Case of AnemiaDocument19 pagesAplastic Anemia and Approach To Diagnosis in A Case of Anemia2006suzainNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lab V2Document14 pagesPhysiology Lab V2Mohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- ANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)Document31 pagesANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)mabec pagaduan70% (10)
- Aplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias Including Mylodysplastic SyndromeDocument47 pagesAplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias Including Mylodysplastic SyndromeRahul Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach To A Patient With Suspected AnaemiaDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Approach To A Patient With Suspected AnaemiaJustkillme AlifNo ratings yet
- JSparacello Lesson 8 ApplicationDocument10 pagesJSparacello Lesson 8 Applicationred.eyn21No ratings yet
- Anaemia IntroductionDocument61 pagesAnaemia Introductionzarairahad486No ratings yet
- Anemia 230224184146 9c7f6852Document76 pagesAnemia 230224184146 9c7f6852Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- Anemia Testing Algorithm PDFDocument1 pageAnemia Testing Algorithm PDFBilly AuNo ratings yet
- Anemia Testing Algorithm PDFDocument1 pageAnemia Testing Algorithm PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Rhabdomyolysis: DR - Marwa Elwasif NephrologistDocument28 pagesRhabdomyolysis: DR - Marwa Elwasif NephrologistAbualauon AlbeblawyNo ratings yet
- Hematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisaDocument31 pagesHematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisatzuquinoNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Darah 1 FKG 2020Document74 pagesKelainan Darah 1 FKG 2020Jeremy Kartika SoeryonoNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2 and Malaria 1Document30 pagesAnemia 2 and Malaria 1Aishwarya JeeNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic AnemiaDocument49 pagesMacrocytic AnemiaANo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Anemia Classification1Document17 pagesLec 2 Anemia Classification1Omar MaanNo ratings yet
- Approachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02Document63 pagesApproachtohemolyticanemia 131001003025 Phpapp02adnansirajNo ratings yet
- BMLT Class Note On Anemia ClassificationDocument2 pagesBMLT Class Note On Anemia ClassificationSubhasish BarikNo ratings yet
- Approach To AnemiaDocument3 pagesApproach To Anemianoor AliNo ratings yet
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaNo ratings yet
- Medical Technologist Q&A'sDocument6 pagesMedical Technologist Q&A'sjilliangarcia0406No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument93 pagesAnemiaShalini ChanduNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Déficit en pyruvate kinase: Sensibilisation à cette maladie génétique rareFrom EverandFast Facts: Déficit en pyruvate kinase: Sensibilisation à cette maladie génétique rareRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Laboratory Activity Dna SequencingDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity Dna SequencingJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Sequence AlignmentDocument2 pagesSequence AlignmentJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- PCR & Cell Culture WorksheetDocument2 pagesPCR & Cell Culture WorksheetJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Lacanilao Dash3 Wk13 Lab WorksheetDocument4 pagesLacanilao Dash3 Wk13 Lab WorksheetJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Electron MicroscopeDocument2 pagesElectron MicroscopeJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Cellophane Tape Mount & Slide Culture Worksheet-1Document2 pagesCellophane Tape Mount & Slide Culture Worksheet-1J Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Cam Assay-1Document1 pageCam Assay-1J Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Lacanilao John Paolo ActivityDocument4 pagesLacanilao John Paolo ActivityJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Medtech Week: Widespread Virus (Squid Game Inspired)Document4 pagesMedtech Week: Widespread Virus (Squid Game Inspired)J Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- SPOROZOADocument1 pageSPOROZOAJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- TASK 8 - Stanbio Glucose Oxidase MethodDocument2 pagesTASK 8 - Stanbio Glucose Oxidase MethodJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Bact211 Lect Assignment.01Document2 pagesBact211 Lect Assignment.01J Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination: Moses Gerizim P. Casas, RMTDocument77 pagesMicroscopic Examination: Moses Gerizim P. Casas, RMTJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- TABLE 1: Protozoan Species "Cyst" Protozoan Species Size Number of Nuclei Karyosome Peripheral Chromatin Cystoplasm / and InclusionsDocument3 pagesTABLE 1: Protozoan Species "Cyst" Protozoan Species Size Number of Nuclei Karyosome Peripheral Chromatin Cystoplasm / and InclusionsJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Summary TrematodesDocument3 pagesSummary TrematodesJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- "Hemoflagellates Species": Trypanos Oma CruziDocument3 pages"Hemoflagellates Species": Trypanos Oma CruziJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Student Loan Repayment Manual: As of May 2021Document6 pagesStudent Loan Repayment Manual: As of May 2021J Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Para Lect Prelims (Reviewer) : Lumbricoides Is An Example of A/anDocument17 pagesPara Lect Prelims (Reviewer) : Lumbricoides Is An Example of A/anJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Prayer GuideDocument36 pagesPrayer GuideJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Module Educ. 211 Special Topics Mental Hygiene Personality Adevt. Social EtiquetteDocument66 pagesModule Educ. 211 Special Topics Mental Hygiene Personality Adevt. Social EtiquetteJona Esmilla0% (1)
- CH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaDocument29 pagesCH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaChristian LeepoNo ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease Diagnosis and Management PDF 66141784856005Document37 pagesDiverticular Disease Diagnosis and Management PDF 66141784856005Javiera Paz Guerrero CassanelloNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease in Pregnancy FinalDocument24 pagesHeart Disease in Pregnancy FinalBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infectios in ICU Burnham2016Document13 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infectios in ICU Burnham2016Rafael SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Vaidyam 2007 Jul - SepDocument32 pagesVaidyam 2007 Jul - SepPaulNo ratings yet
- Colibacillinum in Recurrent Cystitis: Case TwoDocument1 pageColibacillinum in Recurrent Cystitis: Case Twommalam1969No ratings yet
- 신경생리검사 간단정리Document2 pages신경생리검사 간단정리이승재No ratings yet
- Abnormal Behavior and Psychopathology: Clinical PsychologyDocument5 pagesAbnormal Behavior and Psychopathology: Clinical PsychologyJerine Bonus ApostolNo ratings yet
- 9) Medical Complications of Drug TakingDocument44 pages9) Medical Complications of Drug TakingDr. Zirwa AsimNo ratings yet
- Q. P. Code: 544178: Answer ALL QuestionsDocument10 pagesQ. P. Code: 544178: Answer ALL QuestionsJude Aldo PaulNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Goulds Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 5th Edition by VanmeterDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Goulds Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 5th Edition by Vanmeterjosephestradakmbaizgpyj100% (29)
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument27 pagesAspiration PneumoniaReya Awali SuasoNo ratings yet
- Appendiceal Abscess Ef FixDocument24 pagesAppendiceal Abscess Ef FixrezaNo ratings yet
- Dementia Prof Oliver and DR Solomons Branded Merged PresentationDocument58 pagesDementia Prof Oliver and DR Solomons Branded Merged PresentationAjjugal SushmajaNo ratings yet
- Prognosis of Permanent Teeth With Internal Resorption - A Clinical ReviewDocument8 pagesPrognosis of Permanent Teeth With Internal Resorption - A Clinical ReviewFlorin IonescuNo ratings yet
- ISSN 0189-6016©2007: Research PaperDocument9 pagesISSN 0189-6016©2007: Research PaperMichaelNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Report Vol I 10 06 2016 PDFDocument190 pagesMental Health Report Vol I 10 06 2016 PDFVaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument8 pagesThalassemiaIsabel HigginsNo ratings yet
- Application For EmploymentDocument5 pagesApplication For EmploymentFennia Bintari PutriNo ratings yet
- General Comparison of Health Claims With Regards To Food and Supplement Legislation in Europe, US, and CanadaDocument4 pagesGeneral Comparison of Health Claims With Regards To Food and Supplement Legislation in Europe, US, and CanadaBudi Utami WibawaniNo ratings yet
- The Theatre Experience 14Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesThe Theatre Experience 14Th Edition Full Chapterwendy.schmidt892100% (27)
- Icha 1Document5 pagesIcha 1kadek ayu ichaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept MapRAYAMAE LUMOGDANGNo ratings yet
- Meal Replacement PresentationDocument14 pagesMeal Replacement Presentationapi-276849892No ratings yet
- Psychiatric MedicationsDocument6 pagesPsychiatric MedicationsMr. Psycho SamNo ratings yet
- Hospitalization PolicyDocument33 pagesHospitalization PolicySudheer ChNo ratings yet
- Company Profile - Dr. Sarup's Pest Control PVT - LTDDocument4 pagesCompany Profile - Dr. Sarup's Pest Control PVT - LTDbuddy05071No ratings yet
- Japan and Mali Comparison OutlineDocument2 pagesJapan and Mali Comparison OutlineEmily GillisNo ratings yet
- MEDIATRIXDocument67 pagesMEDIATRIXMaria Consuelo LingcasoNo ratings yet