Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamental Concept of Computer System
Uploaded by
Tanwir Gagrana SialCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamental Concept of Computer System
Uploaded by
Tanwir Gagrana SialCopyright:
Available Formats
Data: Data is a plural form of the Latin Word Datum, Which means “something
given”. Data is a collection of raw, unorganized but related facts and figures. An
example is a collection of names of students on admission forms, their addresses and
subject marks.
Information: Information is the raw data that has been manipulated and
organized in the form of results/outputs, upon which people can take necessary
decisions. In other words, information is the meaningful, processed data which is
relevant and accurate thereby can be used in decision making, Examples are vouchers,
bills, fee registration cards or library cards.
Instruction: It directs the computer to perform a particular task.
Program: An ordered set of computer instructions, which tells the computer to
perform a particular process.
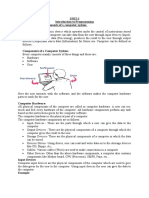
Hardware: The physical components of a computer is called hardware.
Software: Software is a set of computer programs required to utilize and control the
operation of the computer. Such as Disk Operating System (DOS), Windows, MS-Word,
MS-Excel.
Types of Software: There are two types of software.
(a) Application Software: Computer programs which direct a computer system
to perform specific information processing activities required for the solution of
business, scientific and other problems of computer users. For example, MS Word, MS
PowerPoint etc
(b) System Software: It controls & supports the operation of a computer
system such as operating system. In other words System software are programs, which
hold instructions related with the working of the hardware and software of the computer
system. System software behaves like an incharge and performs the responsibility of
overall supervision of input, processing and output of data.
Operating System: It is a type of the system software, which supervises all the
activities, or operations of the computer. It consists of program(s) which provides
communication b/w the user & the computer hardware.
Computer: A computer is an electronic device capable of performing many tasks
like accepting data, process that information to produce output for users & also can
store that output. It can take logical decisions or perform any task faster than human
beings.
Units of a Computer:
Input Unit: The initial unit, which provides communication between the user
and the computer, is the input unit. This unit is used to given information to a computer.
For example: keyboard.
Process: This unit of a computer is responsible to process the data, which is given
by the user. e.g. CPU (Central Processing Unit).
Output: The final part of a computer is the output unit, which provides results to
the user either on the screen or printed on the paper. e.g. Monitor. It is a
communicating link between a computer and people. It is used to transfer information
out of computing system.
Memory: It is like a storeroom of the computer in which we store our data or
programs. It is of two types.
(a) Primary Memory
(b) Secondary Memory
(a) Primary Memory: It is also called internal memory and present
inside the system unit. This device holds input data (before being processed),
results for output purpose (after processing). It has two main types.
(i) RAM
(ii) ROM
(i) Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM stands for Random
Access Memory. The data stored in this part of the memory can be read,
changed or erased completely and thus referred to as read/write memory.
RAM is also known as temporary memory because the information stored
in it is lost when the computer is switched off or the light goes off.
(ii) Read Only Memory (ROM): ROM stands for Read
Only Memory. The information stored in ROM is permanent and is not lost
due to light failure or switching off, of the computer. The data can be
accessed or read any time but cannot be changed or removed or written
on it. ROM is generally used to store manufactured-supplied programs,
routines for immediate access by the user of the system.
(b) Secondary Memory: A computer has the ability to store its
programs, the input data, and the immediate and final results of its calculations.
The term secondary storage is also known as auxiliary storage, external
storage, backup storage or long-term storage. A storage is a device into which
information can be introduced, held, and subsequently obtained. The information
can be erased. E.g. hard disk
Hard Disk: It is secondary storage which is used for more storage i.e. it can
store a huge amount of data and faster access speeds than floppy diskettes. It is also
called fixed disk.
Floppy Diskettes: It is a storage device, which has two types: one is 5.25-inch
disk and other is 3.5 inch. The data stored on diskette can be accessed directly.
Bit: It stands for “Binary digit”. The smallest unit of information in the computer is bit.
The value of the bit is either 0 or 1.
Bus: A set of conducting paths (for movement of data and instructions) which
interconnects the various components of a CPU.
You might also like
- Introduction To ComputerDocument74 pagesIntroduction To ComputerJade TobiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Operating SystemDocument79 pagesChapter 1 Operating SystemMekuanint Aschalew100% (1)
- MS DynamicsDocument3,956 pagesMS DynamicsVD BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- SAP FMS - PlanningDocument38 pagesSAP FMS - PlanningPallavi RastogiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Module 3 - When Humanity and Technology CrossDocument6 pagesMidterm Module 3 - When Humanity and Technology CrossJosa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Computer SkillsDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 Computer SkillsMmonie MotseleNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems & ProgrammingDocument21 pagesComputer Systems & Programmingapi-19505286No ratings yet
- Programming In C Module-1 BasicsDocument77 pagesProgramming In C Module-1 BasicsMityaprangya DasNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganisationDocument25 pagesComputer OrganisationJessy RajasundarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: 1.1 Introduction To ProgrammingDocument79 pagesUnit - 1: 1.1 Introduction To ProgrammingraviNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 PPSDocument80 pagesUnit-1 PPSHarini KolliNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer?: 1. With A Neat Schematic Block Diagram of A Digital Computer Describe Its Functional UnitsDocument38 pagesWhat Is A Computer?: 1. With A Neat Schematic Block Diagram of A Digital Computer Describe Its Functional Unitsranga231980No ratings yet
- Lecture 1-1Document3 pagesLecture 1-1Umair KhalidNo ratings yet
- AICTDocument4 pagesAICTamnamalik5155No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer Programming LectureDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Computer Programming LectureAlpha RomeoNo ratings yet
- Tle Notes-ComputerDocument11 pagesTle Notes-ComputerDENNIS AFABLENo ratings yet
- IT and Computer Applications (Lecture 1)Document29 pagesIT and Computer Applications (Lecture 1)Amelia BrownNo ratings yet
- Primary MemoryDocument3 pagesPrimary Memoryamnamalik5155No ratings yet
- Computer SciencesDocument29 pagesComputer SciencesX x A7md x XNo ratings yet
- Nutshell IctDocument7 pagesNutshell IctberringtonhardyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Computer SystemAmbareesh RNo ratings yet
- C Digital Notes All 5 UnitsDocument193 pagesC Digital Notes All 5 Unitsfahad aliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes AutonomousDocument108 pagesUnit 1 Notes AutonomoussirishaNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalsDocument26 pagesComputer Fundamentalsprashantsingh1331No ratings yet
- Git Unit 1-2Document6 pagesGit Unit 1-2Vivien LancinNo ratings yet
- CIM-LESSON 1- KNOWING COMPUTERDocument23 pagesCIM-LESSON 1- KNOWING COMPUTERJulian Joseph Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Computer and Communication SystemDocument3 pagesElements of A Computer and Communication SystemArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer?Document20 pagesWhat Is A Computer?Arpita SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: An Introduction to Concepts and ComponentsDocument32 pagesComputer Basics: An Introduction to Concepts and ComponentsCristin Porcadilla AranteNo ratings yet
- PPS Unit-1 NotesDocument55 pagesPPS Unit-1 NotesLaxmi VenkiNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument16 pages1 Introductionharikrishna17179No ratings yet
- Intorduction To Computer SystemDocument7 pagesIntorduction To Computer SystemMohsin Ali AwanNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document9 pagesModule 3bscomputersciencelsstiNo ratings yet
- Computer: ProponentsDocument11 pagesComputer: ProponentsLiezyl Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignmnet 42110020Document4 pagesAssignmnet 42110020Mena SemaryNo ratings yet
- The 4 Parts of a ComputerDocument3 pagesThe 4 Parts of a ComputerRobert DoeNo ratings yet
- Computer System: Chapter-1Document23 pagesComputer System: Chapter-1vivek periwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study Notes 1Document4 pagesUnit 3 Study Notes 1Renalyn G. PaderNo ratings yet
- By:-Sir SamanDocument11 pagesBy:-Sir SamanLaxman ThapaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Computer ApplicationDocument7 pagesClass 9 Computer ApplicationKushagra kundanNo ratings yet
- IT HARDWARE TRAINING LAB COURSEDocument11 pagesIT HARDWARE TRAINING LAB COURSENishitha PriyankaNo ratings yet
- IT HARDWARE TRAINING LAB COURSEDocument11 pagesIT HARDWARE TRAINING LAB COURSENishitha PriyankaNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer?Document17 pagesWhat Is Computer?Narender SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2MUHAMMAD RAHEEL BSSE-FA20-100No ratings yet
- Presentation 2 - Hardware and Software-1Document42 pagesPresentation 2 - Hardware and Software-1Ryan NguyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computers in 40 CharactersDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Computers in 40 CharactersJontex 254No ratings yet
- PSCP Unit-1Document9 pagesPSCP Unit-1sachin jainNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 1 Computer SystemDocument34 pagesClass 11 Chapter 1 Computer Systemprasadnehra77No ratings yet
- Understanding Computer Hardware ComponentsDocument23 pagesUnderstanding Computer Hardware Componentsmariam raafatNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: Computer Fundamentals (CSE 105)Document14 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: Computer Fundamentals (CSE 105)Tashfeen AhmedNo ratings yet
- BSC Computer FundamentalsDocument9 pagesBSC Computer FundamentalsbalaNo ratings yet
- Computer Assignment 3Document8 pagesComputer Assignment 3Mussawer HasnainNo ratings yet
- Reading - Material - On ITDocument37 pagesReading - Material - On ITKISHORETNo ratings yet
- GE19141Document125 pagesGE19141AdharshNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTUREDocument9 pagesChapter1-COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTUREbhuvanalakshmi kNo ratings yet
- Eswi Unit-1Document43 pagesEswi Unit-1Balakrishna Reddy100% (1)
- 01 Notes Hardware ConceptsDocument11 pages01 Notes Hardware ConceptsAbhinav AnandNo ratings yet
- CPDSDocument319 pagesCPDSrupakothurNo ratings yet
- Parts of Computers Topic PresentationDocument8 pagesParts of Computers Topic PresentationMuhammad Hadi shakirNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 2 - Information TechnologyDocument48 pagesLecture Note 2 - Information TechnologyMichael EhondorNo ratings yet
- Computer Male or FemaleDocument1 pageComputer Male or FemaleTanwir Gagrana SialNo ratings yet
- Computer Male or FemaleDocument1 pageComputer Male or FemaleTanwir Gagrana SialNo ratings yet
- Hardware DevicesDocument10 pagesHardware DevicesTanwir Gagrana SialNo ratings yet
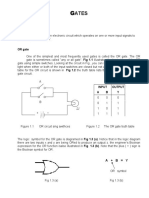
- Logic GatesDocument6 pagesLogic GatesTanwir Gagrana SialNo ratings yet
- CSS Basics PDFDocument35 pagesCSS Basics PDFchagi222No ratings yet
- Buildersbid - Online Construction Bidding Company: Software Requirements SpecificationDocument5 pagesBuildersbid - Online Construction Bidding Company: Software Requirements SpecificationTanwir Gagrana SialNo ratings yet
- 2019 Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad (Grade 12) ExamDocument2 pages2019 Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad (Grade 12) ExamJohnvic AdiqueNo ratings yet
- 2arduino IntroDocument23 pages2arduino IntroMert ÜnverNo ratings yet
- Model Exam Version 7Document20 pagesModel Exam Version 7alexsabebe28No ratings yet
- Etulink Product MapDocument30 pagesEtulink Product MapAlexander PischulinNo ratings yet
- Database Design Using The REA Data ModelDocument15 pagesDatabase Design Using The REA Data Modelمحمود احمدNo ratings yet
- Poster AnalysisDocument20 pagesPoster AnalysisEric AntonioNo ratings yet
- Login Credential ReportbrCollege Name City Academy Law College, Course Name L.L.B 3 (Year) Semester 3Document12 pagesLogin Credential ReportbrCollege Name City Academy Law College, Course Name L.L.B 3 (Year) Semester 3Venkatesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- React. JS Was First Used in 2011 For Facebook's Newsfeed Feature. Facebook Software React-App Version 2.0 Package Was Released inDocument20 pagesReact. JS Was First Used in 2011 For Facebook's Newsfeed Feature. Facebook Software React-App Version 2.0 Package Was Released inhktiwari88No ratings yet
- Robotics Chapter 1Document11 pagesRobotics Chapter 1origafelixNo ratings yet
- Algorithms Data StructureDocument9 pagesAlgorithms Data StructureUzmanNo ratings yet
- VMware AirWatch Android Platform Guide v8 - 4Document101 pagesVMware AirWatch Android Platform Guide v8 - 4RaftNo ratings yet
- Bubt Eee-304 Lab Manual - Edited 25-12-21 v2Document73 pagesBubt Eee-304 Lab Manual - Edited 25-12-21 v2Md. Arif Hasan MasumNo ratings yet
- Here are the translations of the mathematical sentences to symbols:1) x > 52) x < 23) 4x ≥ 30 4) 3x ≥ 95) x + y < 126) x - y > 77) x - y ≤ 58) x + y ≤ 4Document28 pagesHere are the translations of the mathematical sentences to symbols:1) x > 52) x < 23) 4x ≥ 30 4) 3x ≥ 95) x + y < 126) x - y > 77) x - y ≤ 58) x + y ≤ 4jhonafeNo ratings yet
- Wycena Gniazdka LegrandDocument2 pagesWycena Gniazdka LegrandHardy AncymonNo ratings yet
- High-Resolution Chest CT Imaging of The Lungs - Impact of 1024 Matrix Reconstruction and Photon-Counting-Detector CT - PMCDocument19 pagesHigh-Resolution Chest CT Imaging of The Lungs - Impact of 1024 Matrix Reconstruction and Photon-Counting-Detector CT - PMCKelum BuddhikaNo ratings yet
- Maze Ransomware Attack Prevention GuideDocument7 pagesMaze Ransomware Attack Prevention GuideprakashrjsekarNo ratings yet
- Asg 11 - WTL Mini-Project Report FormatDocument14 pagesAsg 11 - WTL Mini-Project Report FormatShreyash DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- A High-Throughput and Power-Efficient FPGA Implementation of Yolo CNN For Object DetectionDocument13 pagesA High-Throughput and Power-Efficient FPGA Implementation of Yolo CNN For Object DetectionVinh Lê HữuNo ratings yet
- An Interactive Wearable Assistive Device For Individuals Who AreDocument10 pagesAn Interactive Wearable Assistive Device For Individuals Who AreSagor SahaNo ratings yet
- ChatcryptoDocument16 pagesChatcryptoKashif JameelNo ratings yet
- Eoy - CS (Vi) 23-24Document3 pagesEoy - CS (Vi) 23-24www.shahbazhaider165No ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science and EngineeringDocument2 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and EngineeringTuhin SisirNo ratings yet
- 02ds Celestis - Nms EkinopsDocument4 pages02ds Celestis - Nms EkinopsDuong Ly HoangNo ratings yet
- TVL - Ict (Computer System Servicing) Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - LO 1.2 Set Up User AccessDocument11 pagesTVL - Ict (Computer System Servicing) Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - LO 1.2 Set Up User AccessRica Jean BlasurcaNo ratings yet
- 190A1E0336 - ProjectDocument67 pages190A1E0336 - ProjectSrisasthagnaneswarsaikumar KonduruNo ratings yet
- Aubay - Sap On AzureDocument3 pagesAubay - Sap On AzureAnkush AdlakhaNo ratings yet
- 2M H.265 Network 32x Zoom Camera: Key FeaturesDocument2 pages2M H.265 Network 32x Zoom Camera: Key Featuresnot jappeningNo ratings yet