Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 Excercise 2
Uploaded by
Qama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageoop chapter 8 question 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentoop chapter 8 question 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageChapter 8 Excercise 2
Uploaded by
Qamaoop chapter 8 question 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> //for strcpy(), strlen()
#include <process.h> //for exit()
using namespace std;
class String //user-defined string type
{
private:
enum { SZ = 80 }; //size of String objects
char str[SZ]; //holds a C-string
public:
String() //no-arg constructor
{ strcpy(str, ""); }
String( char s[] ) //1-arg constructor
{ strcpy(str, s); }
void display() //display the String
{ cout << str; }
String operator += (String ss) //add a String to this one
{ //result stays in this one
if( strlen(str) + strlen(ss.str) >= SZ )
{ cout << "\nString overflow"; exit(1); }
strcat(str, ss.str); //add the argument string
return String(str); //return temp String
}
};
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main()
{
String s1 = "Merry Christmas! "; //uses 1-arg ctor
String s2 = "Happy new year!"; //uses 1-arg ctor
String s3; //uses no-arg ctor
s3 = s1 += s2; //add s2 to s1, assign to s3
cout << "\ns1="; s1.display(); //display s1
cout << "\ns2="; s2.display(); //display s2
cout << "\ns3="; s3.display(); //display s3
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Chapter 9 Excercise 6Document1 pageChapter 9 Excercise 6QamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Excercise 5Document2 pagesChapter 8 Excercise 5QamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Excercise 4Document1 pageChapter 8 Excercise 4QamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Excercise 3Document1 pageChapter 8 Excercise 3QamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Excercise 1Document2 pagesChapter 8 Excercise 1QamaNo ratings yet
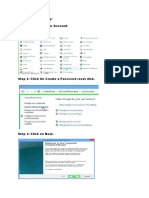
- Password Reset KeyDocument3 pagesPassword Reset KeyQamaNo ratings yet
- Password Reset KeyDocument3 pagesPassword Reset KeyQamaNo ratings yet
- Active DirectoryDocument1 pageActive DirectoryQamaNo ratings yet
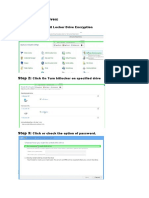
- Bit LockerDocument3 pagesBit LockerQamaNo ratings yet
- System ImageDocument2 pagesSystem ImageQamaNo ratings yet
- RecoveryDocument3 pagesRecoveryQamaNo ratings yet
- BackupDocument4 pagesBackupQamaNo ratings yet
- 102 - Introduction To Mass Communication 1Document72 pages102 - Introduction To Mass Communication 1farhad ahmed100% (2)
- MMC1009 Intro To Mass Communications Section119F Cleland Spring 2018Document5 pagesMMC1009 Intro To Mass Communications Section119F Cleland Spring 2018QamaNo ratings yet
- What Is Saas?Document3 pagesWhat Is Saas?QamaNo ratings yet
- 06 NaiveBayes ExampleDocument2 pages06 NaiveBayes Examplekakalott77No ratings yet
- Decision Trees / NLPDocument27 pagesDecision Trees / NLPQamaNo ratings yet
- 06 NaiveBayes ExampleDocument2 pages06 NaiveBayes Examplekakalott77No ratings yet
- DHCP in LinuxDocument2 pagesDHCP in LinuxQamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Classification & Prediction: 4.1 Basic Concepts of Classification and Prediction 4.2 Decision Tree InductionDocument19 pagesChapter 4: Classification & Prediction: 4.1 Basic Concepts of Classification and Prediction 4.2 Decision Tree InductionQamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Classification & Prediction: 4.1 Basic Concepts of Classification and Prediction 4.2 Decision Tree InductionDocument19 pagesChapter 4: Classification & Prediction: 4.1 Basic Concepts of Classification and Prediction 4.2 Decision Tree InductionQamaNo ratings yet
- IT-318: Scalable and Cloud Computing: Programming at Scale Concurrency and ConsistencyDocument37 pagesIT-318: Scalable and Cloud Computing: Programming at Scale Concurrency and ConsistencyQamaNo ratings yet
- Intel IT Architecting SaaSDocument10 pagesIntel IT Architecting SaaSQamaNo ratings yet
- Intel IT Architecting SaaSDocument40 pagesIntel IT Architecting SaaSQamaNo ratings yet
- Intel IT Architecting SaaSDocument10 pagesIntel IT Architecting SaaSQamaNo ratings yet
- IT-318: Cloud Computing: What Is The Cloud?Document68 pagesIT-318: Cloud Computing: What Is The Cloud?QamaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)