Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Ijso PDF
Uploaded by
SidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Ijso PDF
Uploaded by
SidCopyright:
Available Formats
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
CAREER POINT
PRE-FOUNDATION COURSE
IJSO
SUMMER WORKSHOP
Daily Practice Problem Sheet
Subject : Biology DPPS. NO. – 01 .
Topic : Photosynthesis
Q.1 The enzyme phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase catalyses the combination of CO2 and phosphoenol pyruvate to
form oxaloacetic acid in –
(A) Pea (B) Sugarcane (C) Pinus (D) Apple
Q.2 The energy in photosynthesis for attaching a phosphate group to ADP comes from –
(A) Breaking down glucose (B) Protons moving from the thylakoid compartment
(C) Taking a phosphate off of a sugar (D) All of the above
Q.3 When Rubisco acts as an oxygenase –
(A) Phsophoglycerate and phosphoglycolate are produced
(B) Phosphoenol pyruvate is oxidized
(C) Net carbon fixation is enhanced
(D) It must mean that the plant is deprived of CO2
Q.4 Calvin Cycle represents which of the following phenomenon –
(A) Oxidative Carboxylation (B) Substrate level phosphorylation
(C) Dark respiration (D) Reductive carboxylation
Q.5 The mechanisms of ATP formation both in chloroplast and mitochondria is explained by –
(A) Relay pump theory of Godlewski (B) Cholodny Went's model
(C) Chemiosmotic theory (D) Munch's pressure/mass flow model
Q.6 In which of the following cells of a C 3 leaf would you find the highest concentration of enzyme rubisco –
(A) Epidermal cell (B) Mesophyll cell (C) Bundle sheat cell (D) (B) and (C)
Q.7 In C4 plant, during photosynthesis C4 acid undergoes decarboxylation in _________ to produce C3 acid
(pyruvic acid) and __________.
(A) Mesophyhll, O2 (B) Bundle sheath, CO2 (C) Grana, CO2 (D) Bundle sheat, CO2
Q.8 During photosynthesis C3 acid is transported from cells of bundle sheath where it is converted to –
(A) Pyruvic acid (B) PEP (C) OAA (D) Malic acid
Q.9 Which one is correct for C 4-plants?
Mesophyll Bundle Sheath
(A) PEPCase C4-Cycle RUBisCO C3-Cycle
(B) PEPCase Calvin cycle RUBisCO C4-Cycle
(C) RUBisCO C4-Cycle PEPCase C3-Cycle
(D) RUBisCO C2-Cycle PEPCase C3-Cycle
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 1
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.10 Which one of the following correctly identifies X and Y and shows their functions?
X Y
Structure Function Structure Function
(A) Grana Photolysis of water Stroma CO2fixation
(B) Grana CO2 fixation Stroma Photolysis of water
(C) Stomata Photolysis Grana CO2 fixation
(D) Grana CO2 fixation Lamellae Photolysis of water
Q.11 The diagram shows the ultrastructure of a chloroplast as seen in section.What are the fucntions of P, Q and R?
P Q R
(A) Carbohydrate storage Carbohydrate synthesis Light reaction
(B) Light reaction Carbohydrate synthesis Carbohydrate storage
(C) Light reaction Carbohydrate storage Carbohydrate synthesis
(D) Light absorption Carbohydrate synthesis Carbohydrate storage
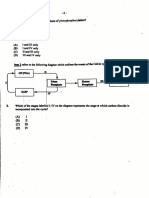
Q.12 The diagram shows the movement of substances into in and out of a chloroplast –
2 4
Light Light
dependent Independent
reaction reaction
1 3
The diagram shows the
movement into in and out
of a chloroplast
What do labels 1 to 4 represent?
1 2 3 4
(A) CO2 ATP H2O Starch
(B) CO2 H2O Sugars O2
(C) H2O O2 CO2 Sugar
(D) Sugar H2O ATP O2
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 2
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.13 All C4 plants show Kranz anatomy and it is –
(A) Environmentally determined (B) Non-gentically determined
(C) Edaphically determined (D) Genetically determined
Q.14 The term Kranz (wreath) of Kranz-anatomy of leaf C4 plant refers to arrangement of cells. These cells are cells
of –
(A) Mesophyll (B) Spongyparenchyma
(C) Bundle sheath (D) Both mesophyll and bundle sheath
Q.15 I. Photorespiration is favoured by high O2 low CO2, rise in temperature, high light intensity.
II. Chloroplasts of cells of bundle sheath of C4 plants are granaless and have RUBisCO but noPEPCo.
III. Chloroplasts of mesophyll cells of C4 plant are granale, have PEPCo PEPcase but no RUBisCo.
IV. Maize and Sorghum are C4 plants
Which of the above statement are true?
(A) All are correct (B) I and IV are correct
(C) II and III are correct (D) Only IV is correct
Q.16 Rate of photosynthesis is independent of –
(A) Quality of light (B) Intensity of light
(C) duration of exposure to light (D) All
Q.17 At higher light insensities gradually photosynthesis rate does not show further increase - why?
(A) Higher light intensity activate more chlorophylls
(B) Higher light intensity causes more transpiration
(C) No need of more sugar formation
(D) Other factors become limiting
Q.18 Photosynthesis occurs maximum at –
(A) Red light (B) Blue light (C) Orange light (D) White light
Q.19 Light is rarely a limiting factor in nature except in –
(A) Maize (B) Sugarcane
(C)Sorghum (D) Plants - plants growing in shade or in dense forests
Q.20 lncrease in light intensity beyond saturation point causes –
(A) More photosynthesis
(B) Less photosynthesis
(C) Breakdown of the chlorophyll and a decrease in photosynthesis
(D) Heliotropism
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 3
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
CAREER POINT
PRE-FOUNDATION COURSE
IJSO
Daily Practice Problem Sheet
Subject : Biology DPPS. NO. – 02 .
Topic : Control and Coordination in Plants
Q.1 Arithmetic growth includes all except –
(A) constant growth rate (B) It is found in root and shoot cells
(C) It is expressed as Lt = Lo + rt (D) Its characteristic graph is sigmoid
Q.2 Which one is the correct graph of arithmetic growth?
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Q.3 Why a linear curve is obtained in arithmetic growth?
(A) Because it has lag, log and stationary phase
(B) Because on daughter cell remains meristematic while the other daughter cell differentiates and matures
(C) Because of the effect of environment on mitosis
(D) None
Q.4 Go through the following points –
I. Slow growth, thereafter exponential group and then stationary phase
II. Geometric and arithmetic phases
III. Characteristic of all living organisms growing in natural environment
IV. W1 = W0ert
Sigmoid curve Exponential growth Embryo development
(A) II I III, IV
(B) I, III IV III, IV
(C) I II, III IV
(D) III, IV I II
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 1
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.5
A-Leaf B-Leaf
AGR RGR AGR RGR
(A) 1% 1 2% 2
(B) 100% 5 10% 5
(C) 5 100% 5 10%
(D) 0.5 100% 1.5 100%
Q.6 For growth which one(s) is essential –
(A) Nutrients (B) H2O (C) O2 (D) All
Q.7 Water is needed for –
(A) Cell-enlargement (B) Providing aqueous medium for enzymatic reactions
(C) Both (D) Oxidizing glucose to provide energy
Q.8 I. O2 helps in releasing metabolic energy essential for growth activities.
II. Nutrients (Micro and Macromolecules) are required by plants for the synthesis of protoplasm as well as act
as source energy.
III. Optimum temperature for plant growth is needed
IV. Environmental signal like light and gravity affect certain phases of growth.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(A) All are correct (B) All are incorrect
(C) I, II and IV are correct (D) I and IV are corrct
Q.9 Under certain conditions regaining the lost capacity of division by living cells is called –
(A) Dedifferentiation (B) Redifferentiation (C) Differentiation (D) Efficiency index
Q.10 Which one is the example of dedifferentiated cells?
(A) Procambium + Vascular cambium (B) Vascular cambium + Interfascicular cambium
(C) Phellogen + Procambium (D) Cork cambium + Interfascicular cambium
Q.11 Which one(s) is/are redifferentiated cell(s)?
(A) Cork (B) Secondary cortex (C) Both (D) None
Q.12 Growth in plants is –
(A) Only determinate (B) Only indeterminate
(C) Mostly determinate (D) Open (both determinate and indeterminate)
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 2
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.13 Differentiation in plant is open because cells/tissues arising out of the same meristem –
(A) have same structure at maturity (B) Have different structures at maturity
(C) Have capacity to disappear their cell walls (D) Have same fate
Q.14 Column I Column II
I. IAA A. Terpenes
II. GA B. Indole compounds
III. ABA C. Adenine derivatives
IV. C2H4 D. Gases
V. Kinetin, (N6-furfuryl amino purin) E. Cerotenoid derivatives
The correct match is –
(A) I-B, II-A, III-E, IV-D, V-C (B) I-A, II-B, III-C, IV-D, V-E
(C) I-E, II-D, III-A, IV-B, V-C (D) None
Q.15 Which one includes growth promoters?
(A) Auxin, Cytokinin, ABA (B) GA, Cytokinin, C2H4
(C) C2H4, ABA (D) Auxin, Cytokinin, GA
Q.16 Which one include growth inhibitors ?
(A) ABA, Cytokinin (B) GA, IAA (C) ABA, C2H4 (D) None
Q.17 PGRs include –
(A) Only growth promoters
(B) Only growth inhibitors
(C) Both growth promoters and growth inhibitors
(D) Only solid hormones, not gaseous hormones
Q.18 Which of the following growth regulators can fit either of the groups (promoter and inhibitor) –
(A) C2H4 (B) ABA (C) GA (D) IAA
Q.19 I. Cell division
II. Cell enlargement
III. Pattern formation
IV. Tropic growth
V. Flowering
VI. Fruiting
VII. Seed germination
VIII. Response to wound
IX. Response to stresses of biotic and abiotic origin
Which one is correct?
Functions of growth promoters Functions of growth inhibitor
(A) I, II, VII, IX III, IV, V, VI, VIII
(B) VIII, IX I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII
(C) I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII VIII, IX
(D) I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, IX VIII
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 3
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.20 Column I Column II
I. C. Darwin and F. Darwin A. Cytokinin
II. Miller and Skoog B. ABA
III. F. W Went C. C2H4
IV. Kurosawa D. Auxin
E. GA
Correct Match is –
I II III IV
(A) D A D E
(B) D A C B
(C) C A B D
(D) E D B A
Q.21 Statement I - Confirmation of the release of volatile substances from ripened oranges that hastened the
ripening of stored unripe bananas.
Statement II - Callus formation from the internodal segments of tobacco stem with the Auxin and extracts of
vascular tissues/yeast/coconut milk/DNA. Later, Cytokinesis promoting substance was identified, crystallized
and named as KINETIN.
Statement III - Reporting of appearance of symptoms of bakane/foolish seedling disease caused by fungus.
Gibberella fujikuroi, in uninfected seedling when they were treated with sterile filtrates of the fungus. The
active substances were later identified as GA.
Choose the correct option –
I II III
(A) Miller + Skoog Cousins Kurosawa
(B) Kurosawa Cousins Miller + Skoog
(C) Cousins Kurosawa Miller + Skoog
(D) Cousins Miller + Skoog Kurosawa
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 4
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
CAREER POINT
PRE-FOUNDATION COURSE
IJSO
SUMMER WORKSHOP
Daily Practice Problem Sheet
Subject : Biology DPPS. NO. – 03 .
Topic : Transportation in Plants
Q.1
After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed?
(A) The water level is higher in side A than in side B
(B) The water level is higher in side B than in side A
(C) No' Change is Observed
(D) First the level of water is high in tube A and then water level is decreased
Q.2 Water potential of plasmolysed cell will be –
(A) w = –s + p (B) s = p (C) w = 0 (D) w= –s – p
Q.3 When does a concentration gradient exist?
(A) When solute concentrations are low
(B) When membrane rupture
(C) When solute concentration is high
(D) When solute concentration differ on either side of a membrane
Q.4 What would be p of a fully flaccid cell?
(A) +3 (B) +2 (C) –3 (D) 0
Q.5 During plasmolysis what occurs?
(A) Movement of water occurs across the membrane from an area of higher water potential to lower water
potential
(B) Movement of water occurs across the membrane from an area of low water potential to high water
potential
(C) Water moves inside the cell until equilibrium is reached
(D) O.P. of cell remains the same
Q.6 When a plasmolysed cell is placed in water or hypotonic solution, what happens?
(A) T.P. of cell decreases (B) T.P. of cell becomes zero
(C) T.P. increases (D) Water potential of cell decreases
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 1
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.7 As various ions from the soil are actively transported into vascular tissues of root, water follows and increases
the pressure inside the xylem. This positive pressure is called –
(A) Mass pressure (B) Root pressure (C) osmotic potential (D) None
Q.8 Attraction of water molecules to polar surface is known as :
(A) Cohesion (B) Adhesion (C) Capillarity (D) Tensile strength
Q.9 Go through the four statements given below –
I. Root pressure provides a light push in the overall process of water transport
II. Most plants meet their water need by transpiration pull
III. The greatest of root pressure my be to re-establish the continuous chains of water molecules in the xylem
vessel which often break under enormous tension created by transpiration
IV. Guttation is the cause of transpiration pull
The correct statement are –
(A) I, II, III, IV (B) I, II, III (C) II, III, IV (D) II, III
Q.10 According to transpiration-cohesion theory water is pulled upward through the xylem. The cause of the pull
is –
(A) Guttation (B) Root pressure (C) transpiration (D) condensation
Q.11 The lowest water potentials in the xylem are in the –
(A) root hairs (B) vascular cylinders of root
(C) tracheids of the stem (D) leaves
Q.12 The energy source that drives the upward flow of water is –
(A) light (B) sucrose (C) solar heat (D) ATP
Q.13 Which of the following is not a major factor in the movement of xylem sap up in a tall tree?
(A) Plasmodesmata (B) Cohesion and adhesion
(C) Tension (D) Transpiration
Q.14 Adhesion is the result of –
(A) hydrogen bonding between the water molecules
(B) Transpiration pull
(C) High surface tension
(D) Attraction of water molecules to polar surface/hydrophilic wall of the xylem tube.
Q.15 Which of the following statement is correct concerning the flow of sap in xylem of trees?
(A) In the morning sap begins to flow first in the twigs and later in the trunk
(B) Flow is driven by high cone. of sugar in the vessel elements
(C) Flow from the roots to the twigs would be accelerated if the leaves are removed
(D) Rapid flow of water puts the xylem under a pressure much greater than atmospheric pressure.
Q.16 Which of the following is a difference between transport by xylem and transport by phloem?
(A) Active transport moves xylem but not phloem sap
(B) Transpiration moves phloem sap but not xylem sap
(C) xylem sap moves up; phloem sap moves up and down
(D) xylem moves from sugar source-to sink but phloem does not
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 2
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.17 What keeps the force of gravity from pulling water molecules out of the leaves ?
(A) Upward pressure from root (B) High water pressure in leaves
(C) Movement of water towards a sugar sink (D) Cohesion and adhesion of water molecules
Q.18 Which one is correct –
(A) Unlike water all minerals cannot be passively absorbed by roots
(B) Most of the minerals enter the root by active transport
(C) Ions are absorbed from soil by both passive and active transport
(D) All
Q.19 In root there is one way active transport of ions because of presence of –
(A) Pericycle (B) Diffusion (C) ATP (D) Endodermis
Q.20 Ions from soil reach to xylem of root through –
(A) Active uptake only (B) Passive uptake only
(C) Only diffusion (D) Active or passive uptake or a combination of both
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 3
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
CAREER POINT
PRE-FOUNDATION COURSE
IJSO
SUMMER WORKSHOP
Daily Practice Problem Sheet
Subject : Biology DPPS. NO. – 04 .
Topic : Genetics
Q.1 Column A Column B
I. Sickel-cell anaemia A. 7th chromosomes
II. Phenylketonuria B. 4th chromosome
III. Cystic fibrosis C. 11th chromosome
IV. Huntington's disease D. X-chromosome
V. Colour blindness E. 12 th chromosome
The correct match is –
(A) I-B, II-A, III-D, IV-C, V-D (B) I-D, II-A, III-B, IV-C, V-D
(C) I-D, II-B, III-A, IV-C, V-D (D) I-C, II-E, III-A, IV-B, V-D
Q.2 Column A Column B
I. Autosomal linked recessive trait A. Down's syndrome
II. Sex linked recessive disease B. Phenylketonuria
III. Metabolic error linked to autosomal recessive trait C. Haemophilia
st
IV. Additioal 21 chromosome D. Sickle cell Anaemia
The correct match is –
(A) I-B, II-A, III-D, IV-C (B) I-D, II-A, III-B, IV-C
(C) I-D, II-C, III-B, IV-A (D) I-C, II-D, III-A, IV-B
Q.3 The experiment shown in the figure has been carried out by Morgan to show the phenomenon of linkage and
recombination. If in Cross I, genes are tightly linked and in Cross II, genes are loosely linked then what will be
the percentage of recombinants produced in Cross I and Cross II respectively ?
(A) 98.7% and 62.8% (B) 1.3% and 37.2% (C) 37.2 and 1.3% (D) 62.8% and 98.7%
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 1
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.4 Observe the sex determination in the following
I. Human males = XY II. Female hen = ZW
III. Male Drosophila = XY IV. Male grasshopper = XO
V. Male birds = ZZ
Male heterogamety = A
Female heterogamety = B
Male homogamety = C
Which of the following combination is correct-
A B C
(A) I, III, IV II V
(B) II, IV I III
(C) III, IV, II I
(D) II, IV I II
Q.5 Identify the steps in cross in pea.
A. Removal of anthers B. Transfer of Pollen C. Raising the next generation
(A) A - Pollination, B - Fertilisation, C - Fruit formation
(B) A- Emasculation, B - Fertilisation, C - Endosperm formation
(C) A Emasculation, B- Pollination, C – Hybridisation / Crossing
(D) A- defeminization, B- Pollination, C – Hybridisation / Crossing
Q.6 The following table shows the genotypes for ABO blood grouping and their phenotypes. In which one of the
four options the components of reaction labelled as W, X, Y and Z are identified correctly?
W X Y Z
(A) IAi IBi AB ii
(B) IBi IAi B ii
(C) IBi IBi A ii
(D) IAi IAi O ii
Q.7 Match the statement with appropriate symbol
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 2
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
A. Heterozygous individuals with autosomal recessive
B. Diseased (or death)
C. Female carrier of an X-linked recessive gene
D. Individuals with normal trait 4.
E. Consanguineous mating (marriage of blood relatives)
F. Unknown sex
G. Mating
H. Male
I. Female
J. Affected individual
K. Abortion or still birth
B C E F
(A) 12 11 16 7
(B) 9 8 10 6
(C) 2 1 10 4
(D) 9 1 10 4
Q.8 Wife is PTC non taster and husband is PTC taster. Their son is taster but daughters are non tasters. This is not
a sex linked trait. Which pedigree is correct?
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Q.9 Predict from the following chart
(A) character is dominant and carried by X chromosomes
(B) character is carried by Y chromosomes
(C) character is sex linked recessive
(D) character is recessive autosomal
Q.10 The daughter was married to a normal person and their daughter had the trait.
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 3
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
It can be explained as
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Q.11 In the given figure of human hand pedigree analysis given
In the above pedigree which character is represented and what is the probability of disease occurrence in fifth
child?
(A) Polydactyly (autosomal dominant disorder), 50%
(B) Polydactyly (autosomal recessive disorder), 50%
(C) Polydactyly (X-linked dominant disorder), 50%
(D) Polydactyly (X-linked recessive disorder), 50%
Q.12 The diagram refer to the chromosome complement of each sex of fruit fly shown in the diagram.
By which number is a Y chromosome labeled?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Q.13 If a gamete mother cell of chromosome complement 44+ XY suffers a non-disjunction at the first meiotic
division, which of the following sets of gametes could result ?
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Q.14 Klinefelter's syndrome results from the fusion of
(A) an X egg and a YY sperm (B) an XY egg and an X sperm
(C) an XX egg and a Y sperm (D) an XX egg and YY sperm
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 4
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
@cbse10bystudentshelper on telegram
Q.15 A species of plant is known to have a diploid chromosome number of 14 in each of its cells. Which of the
following would be the number of chromosomes found in each cell of one of its polyploidy relatives ?
(A) 7 (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 25
Q.16 When a gene pair hides the effect of another, the phenomenon is called –
(A) mutation (B) dominance (C) epistasis (D) None of these
Q.17 An allele is dominant, if it is expressed in
(A) second generation (B) homozygous combination
(C) heterozygous combination (D) both homozygous and heterozygous condition
Q.18 The ratio 9 : 7 is produced due to –
(A) complementary genes (B) supplementary genes
(C) lethal genes (D) epistatic genes
Q.19 How many contrasting characters were selected Mendel?
(A) One (B) Two (C) Three (D) Seven
Q.20 Mendel's monohybrid ratio is –
(A) 1 : 2 (B) 3 : 1 (C) 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 (D) 9 : 7
Q.21 A cross between F1 hybrid and a recessive parent (Tt x tt) gives a ratio of –
(A) 1 : 1 (B) 2 : 1 (C) 3 : 1 (D) 4 : 1
Q.22 The different forms of a gene are called –
(A) heterozygotes (B) alleles (C) supplementary genes (D) complementary genes
Q.23 Mendel's dihybrid ratio is –
(A) 15 : 1 (B) 9 :3 : 3 : 1 (C) 1 : 2 : 1 (D) 9 : 6 : 6 :1
CAREER POINT, 128, Shakti Nagar, Kota-324009 (Raj.), Ph: 0744-2503892 Page # 5
downloaded from cyberworldforu.blogspot.com
You might also like
- Bio Ijso DPP PDFDocument15 pagesBio Ijso DPP PDFsureshNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesismr. vivo boyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: C3 vs C4 ComparisonDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants: C3 vs C4 ComparisonKrishna Nilesh Lodhia G 11No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Practice Questions SolvedDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesis Practice Questions SolvedIndu YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV Chapter-16. Photosynthesis: Important PointsDocument16 pagesUnit - IV Chapter-16. Photosynthesis: Important PointsSantosh ChavanNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV Chapter-16. Photosynthesis: Important PointsDocument16 pagesUnit - IV Chapter-16. Photosynthesis: Important PointsminaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Euee 2011/2019 Answer Sponserd by Qubee AcademyDocument15 pagesChemistry Euee 2011/2019 Answer Sponserd by Qubee AcademyIsmael NuredinNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11 ch11 Class 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 11 ch11 Class 11akilapaul17682No ratings yet
- Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument9 pagesChapter Practice ProblemsAbhinav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis CompressedDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Compressedsatwikdasmahapatra667No ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsDocument12 pagesRespiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsAditya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - STD XDocument28 pagesQuestion Bank - STD XParth DevNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Sheet - 258 - 4hpynztDocument3 pagesDaily Practice Sheet - 258 - 4hpynztŠhàm ŤîwarýNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument281 pagesPhotosynthesisKrishna Priyam SinghNo ratings yet
- CPP Nutrition in PlantsDocument2 pagesCPP Nutrition in Plants1445800No ratings yet
- BIO - AP Qus PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesBIO - AP Qus Photosynthesishi ingNo ratings yet
- Objective Biology - Chapter-Wis - Disha Experts - 111 PDFDocument8 pagesObjective Biology - Chapter-Wis - Disha Experts - 111 PDFRameshKumarNo ratings yet
- Step-t15-Ep by Saeed Mdcat TeamDocument20 pagesStep-t15-Ep by Saeed Mdcat TeamMuhammad AnwarNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit 2 2017 p1Document13 pagesCape Biology Unit 2 2017 p1Amarah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Biology 6th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael WindelspechtDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Biology 6th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspechtcarolynwilliamsidyxwtsojp100% (28)
- 13 Respiration in Plants Neet Biology Model Question PaperDocument5 pages13 Respiration in Plants Neet Biology Model Question PaperJosephNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam QuestionsDocument13 pagesBiology Exam QuestionsspsarathyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition ExerciseDocument10 pagesNutrition ExerciseupsahuNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology U2 p1 2010Document10 pagesCape Biology U2 p1 2010Nicholas CharlesNo ratings yet
- Biology_Cell RespirationDocument5 pagesBiology_Cell Respirationseoyoung3030No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesPhotosynthesis 90 QuestionsNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document3 pagesTest 2umairgulNo ratings yet
- 10-CBSE-Science-Full Test-1 - 27-3-21Document8 pages10-CBSE-Science-Full Test-1 - 27-3-21Rutvik SenjaliyaNo ratings yet
- TERM 1 Chapter 6 Topical RevisionDocument71 pagesTERM 1 Chapter 6 Topical Revisionlaiyinah 09No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Practice TestDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Practice Testcrqin qinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document35 pagesChapter 04javed iqbal KhanNo ratings yet
- Quiz - 1 Part - ADocument6 pagesQuiz - 1 Part - ATarang AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank Ch. 20 PDFDocument9 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank Ch. 20 PDFTony ChenNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Imp Ch13 2Document4 pages11 Biology Imp Ch13 2Kiran KrutanjaliNo ratings yet
- Bio LO.10 Questions M.DiaaDocument22 pagesBio LO.10 Questions M.DiaaRoxanne RoxyNo ratings yet
- CPP - 10th - Ph-1 - Respiration in PlantsDocument3 pagesCPP - 10th - Ph-1 - Respiration in PlantsAbhinav RoyNo ratings yet
- POLL 2 P+C+B+Z OYM Batch Que Paper @CET - JEE - NEETDocument10 pagesPOLL 2 P+C+B+Z OYM Batch Que Paper @CET - JEE - NEETKrins GopaniNo ratings yet
- Topic: Ionic Equilibrium + IUPAC + Chemical Bonding Single Answer Type Question (+4, - 1) 1Document3 pagesTopic: Ionic Equilibrium + IUPAC + Chemical Bonding Single Answer Type Question (+4, - 1) 1Aadish JainNo ratings yet
- GRP 11Document5 pagesGRP 11Dishu BNo ratings yet
- Botany 4Document4 pagesBotany 4Vibushitha KabardineshwarNo ratings yet
- SQP1Document10 pagesSQP1The. Daksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Multiple ChoiceDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesis: Multiple ChoiceValentina RumhizhaNo ratings yet
- Notes 231228 144555Document12 pagesNotes 231228 144555刘素银No ratings yet
- NSEJS-CAMP Assignment - Plant PhysiologyDocument3 pagesNSEJS-CAMP Assignment - Plant PhysiologyetrdrssNo ratings yet
- 2-Poll BotanyDocument2 pages2-Poll Botanydnamazing1702No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones (Solutions)Document22 pagesAldehydes and Ketones (Solutions)Dhruv KuchhalNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chem ModeDocument12 pagesClass Xii Chem ModejerishNo ratings yet
- Tarea FotosíntesisDocument7 pagesTarea FotosíntesisAndy StevenNo ratings yet
- Sci16 PDFDocument6 pagesSci16 PDFNandine S SNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chapter 11Document1 page1st Year Chapter 11AbdulRehman KhokharNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 01Document15 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 01milanraj9148No ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Revision QuestionsDocument7 pagesCell Respiration Revision Questionsjohn-paulspeharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document4 pagesChapter 11bszool006No ratings yet
- c5 Microbiology Tortora TestbankDocument21 pagesc5 Microbiology Tortora Testbankwhitewave25No ratings yet
- Ncert Page Wise Q RespirationDocument34 pagesNcert Page Wise Q RespirationSagarNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology Australian and New Zealand 11th Edition Urry Test BankDocument20 pagesCampbell Biology Australian and New Zealand 11th Edition Urry Test Bankscarletnur0hxdr100% (26)
- Ebook Campbell Biology Australian and New Zealand 11Th Edition Urry Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument25 pagesEbook Campbell Biology Australian and New Zealand 11Th Edition Urry Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (13)
- CUNJCSSP 2 1 Question Paper CSIR UGC NET JRF June 2011 Chemical ScienceDocument42 pagesCUNJCSSP 2 1 Question Paper CSIR UGC NET JRF June 2011 Chemical Sciencehojibox903No ratings yet
- Cblechpu07 1Document8 pagesCblechpu07 1tenb38566No ratings yet
- Lorenzo's Oil Movie ReactionDocument4 pagesLorenzo's Oil Movie Reactionharley olzanskiNo ratings yet
- Animals Visual Encyclopedia SynopsisDocument1 pageAnimals Visual Encyclopedia SynopsisK Vinmalar SaravananNo ratings yet
- Iodiversity AND Onservation: HapterDocument7 pagesIodiversity AND Onservation: HapterAshritha SirivuriNo ratings yet
- Checked and Revised Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Science Himor and Aquino Group 124659Document6 pagesChecked and Revised Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Science Himor and Aquino Group 124659marktrisha07No ratings yet
- Fagus Sylvatica Fact SheetDocument2 pagesFagus Sylvatica Fact SheetnicafarafricaNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory - Bio 1Document41 pagesCell Theory - Bio 1Anand Wealth JavierNo ratings yet
- J P Sir HORTI GMVDocument77 pagesJ P Sir HORTI GMVNiveditaNo ratings yet
- Common Characteristics of Myxomycetes (Slime Molds)Document3 pagesCommon Characteristics of Myxomycetes (Slime Molds)Tài nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Vulnerable Species (Criteria)Document2 pagesVulnerable Species (Criteria)Faye Louise AnneNo ratings yet
- MG33100Document10 pagesMG33100vasundra1228100% (1)
- Carrot ProductionDocument15 pagesCarrot ProductionvenacysholzNo ratings yet
- Hay InfusionDocument2 pagesHay InfusionKizzie Mae DacanayNo ratings yet
- Phylum Rotifera: Body FormDocument4 pagesPhylum Rotifera: Body Formadeela akhterNo ratings yet
- Mollusc ADocument29 pagesMollusc AKarsah MintarsihNo ratings yet
- Everything You Must Know About Azospirillum and Its Impact On Agriculture and BeyondDocument19 pagesEverything You Must Know About Azospirillum and Its Impact On Agriculture and BeyondsausanNo ratings yet
- Kapa KapaDocument3 pagesKapa KapaCris Angelo Natanuan VispoNo ratings yet
- Psyquical AnthropologyDocument12 pagesPsyquical AnthropologyLinaMaríaZuluagaNo ratings yet
- Dr. S. Khatkar PCRDocument24 pagesDr. S. Khatkar PCRkusumNo ratings yet
- Csi Africa: Tracking Ivory Poachers: Teacher Guide To ActivityDocument5 pagesCsi Africa: Tracking Ivory Poachers: Teacher Guide To Activitybunser animationNo ratings yet
- Meiosis NotesDocument2 pagesMeiosis Notesapi-505203040No ratings yet
- Technical Note on Bagworms as Oil Palm PestsDocument2 pagesTechnical Note on Bagworms as Oil Palm PestsHappy Nurafni RNo ratings yet
- 003 143 Scottishbeavertrialfinalreport Dec2014 1417710135 PDFDocument176 pages003 143 Scottishbeavertrialfinalreport Dec2014 1417710135 PDFQuốc BìnhNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in BiopesticidesDocument19 pagesRecent Advances in BiopesticidesKhadijaNo ratings yet
- Arthropod ClassificationDocument6 pagesArthropod ClassificationArmaan AliNo ratings yet
- Ecology of The Microbiome of The Infected Root Canal System A Comparison Between Apical and Coronal Root SegmentsDocument15 pagesEcology of The Microbiome of The Infected Root Canal System A Comparison Between Apical and Coronal Root Segmentsabcder1234No ratings yet
- Bony FishesDocument16 pagesBony FishesmarisNo ratings yet
- How To Plant and Grow MoringaDocument5 pagesHow To Plant and Grow MoringaMoringaidNo ratings yet
- Advice Sheet Social Structure of Horse - IAABCDocument2 pagesAdvice Sheet Social Structure of Horse - IAABCHenrique GarciaNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction, Genetics, and DigestionDocument2 pagesPlant Reproduction, Genetics, and DigestionKint MackeyNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Life Science - November Paper 2-1Document20 pagesGrade 11 - Life Science - November Paper 2-1JustinCase1991No ratings yet