Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seattle Criteria
Uploaded by
Hershel Layton0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
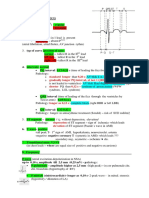
3 views1 pageThese criteria define abnormal and normal ECG findings in athletes. Abnormal findings include T wave inversion, ST segment depression, pathological Q waves, conduction abnormalities, and arrhythmias which require further evaluation as they may indicate cardiovascular disease. Normal variants seen in athletes due to training include sinus bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia, early repolarization patterns, and first degree AV block which do not require further evaluation in asymptomatic athletes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThese criteria define abnormal and normal ECG findings in athletes. Abnormal findings include T wave inversion, ST segment depression, pathological Q waves, conduction abnormalities, and arrhythmias which require further evaluation as they may indicate cardiovascular disease. Normal variants seen in athletes due to training include sinus bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia, early repolarization patterns, and first degree AV block which do not require further evaluation in asymptomatic athletes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageSeattle Criteria
Uploaded by
Hershel LaytonThese criteria define abnormal and normal ECG findings in athletes. Abnormal findings include T wave inversion, ST segment depression, pathological Q waves, conduction abnormalities, and arrhythmias which require further evaluation as they may indicate cardiovascular disease. Normal variants seen in athletes due to training include sinus bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia, early repolarization patterns, and first degree AV block which do not require further evaluation in asymptomatic athletes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
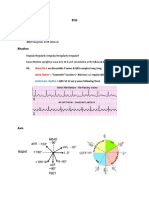
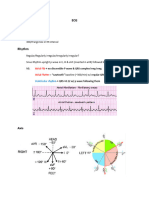
SEATTLE CRITERIA
Abnormal ECG findings in athletes
These ECG findings are unrelated to regular training or expected physiologic adaptation to exercise, may suggest the
presence of pathologic cardiovascular disease, and require further diagnostic evaluation.
Abnormal ECG finding Definition
T wave inversion > 1 mm in depth in two or more leads V2-V6, II and aVF, or I and aVL (excludes
III, aVR, and V1)
ST segment depression ≥ 0.5 mm in depth in two or more leads
Pathologic Q waves > 3 mm in depth or > 40 ms in duration in two or more leads (except III and aVR)
Complete left bundle branch block QRS ≥ 120 ms, predominantly negative QRS complex in lead V1 (QS or rS), and
upright monophasic R wave in leads I and V6
Intra-ventricular conduction delay Any QRS duration ≥ 140 ms
Left axis deviation -30° to -90°
Left atrial enlargement Prolonged P wave duration of > 120 ms in leads I or II with negative portion of
the P wave ≥ 1 mm in depth and ≥ 40 ms in duration in lead V1
Right ventricular hypertrophy R-V1 + S-V5 > 10.5 mm and right axis deviation > 120°
pattern
Ventricular pre-excitation PR interval < 120 ms with a delta wave (slurred upstroke in the QRS complex)
and wide QRS (> 120 ms)
Long QT interval* QTc ≥ 470 ms (male)
QTc ≥ 480 ms (female)
QTc ≥ 500 ms (marked QT prolongation)
Short QT interval* QTc ≤ 320 ms
Brugada-like ECG pattern High take-off and downsloping ST segment elevation followed by a negative T
wave in ≥ 2 leads in V1-V3
Profound sinus bradycardia < 30 BPM or sinus pauses ≥ 3 sec
Mobitz type II 2° AV block Intermittently non-conducted P waves not preceded by PR prolongation and
not followed by PR shortening
3° AV block Complete heart block
Atrial tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter
Premature ventricular contractions ≥ 2 PVCs per 10 second tracing
Ventricular arrhythmias Couplets, triplets, and non-sustained ventricular tachycardia
*The QT interval corrected for heart rate is ideally measured with heart rates of 60-90 bpm. Consider repeating the
ECG after mild aerobic activity for borderline or abnormal QTc values with a heart rate < 50 bpm.
Normal ECG findings in athletes
These common training-related ECG alterations are physiological adaptations to regular exercise, considered normal
variants in athletes, and do not require further evaluation in asymptomatic athletes.
Sinus bradycardia (≥ 30 bpm)
Sinus arrhythmia
Ectopic atrial rhythm
Junctional escape rhythm
1° AV block (PR interval > 200 ms)
Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach) 2° AV block
Incomplete RBBB
Isolated QRS voltage criteria for LVH
Except: QRS voltage criteria for LVH occurring with any non-voltage criteria for LVH such as left atrial enlargement, left
axis deviation, ST segment depression, T wave inversion, or pathologic Q waves
Early repolarisation (ST elevation, J point elevation, J waves, or terminal QRS slurring)
Convex (“domed”) ST segment elevation combined with T wave inversion in leads V1-V4 in Afro/Caribbean athletes
You might also like
- Abnormal ECG Findings in Athletes: Seattle CriteriaDocument1 pageAbnormal ECG Findings in Athletes: Seattle CriteriaCésar Morales GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg: - Department of Medicine BIMC Hospital 2013Document60 pagesBasic Ecg: - Department of Medicine BIMC Hospital 2013LexadkNo ratings yet
- Ecg CookbookDocument2 pagesEcg CookbookCalin Popa100% (1)
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocument69 pagesEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraNo ratings yet
- Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPDocument70 pagesJoseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPcarmsNo ratings yet
- ECGpedia Ghid Interpret AreDocument2 pagesECGpedia Ghid Interpret AreMarina VasilievNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument58 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesNathalia ValdesNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument168 pagesECG InterpretationPavi YaskarthiNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG ReadingDocument41 pagesBasic ECG ReadingBenj100% (3)
- EKG Interpretation: DR K P Tripathy Kims, BhubaneswarDocument58 pagesEKG Interpretation: DR K P Tripathy Kims, BhubaneswarAbhilash MohantyNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation 1Document56 pagesEKG Interpretation 1usmleusmle86No ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument58 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesanisaNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument58 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesHasnahdurrNo ratings yet
- EKG InterpretationDocument58 pagesEKG InterpretationHasnahdurrNo ratings yet
- EKG InterpretationDocument58 pagesEKG InterpretationIman Sama-aliNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument95 pagesECG InterpretationNur Rahmat Wibowo100% (9)
- EKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument85 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture Seriesandina rosmalianti100% (1)
- 5hypertrophy and MIDocument116 pages5hypertrophy and MIsamooanatenaNo ratings yet
- TH4-127 KreuzDocument113 pagesTH4-127 Kreuzakp892818No ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument58 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesrsadellaNo ratings yet
- Ecg For AnkiDocument3 pagesEcg For AnkijNo ratings yet
- ? Ecg ?Document60 pages? Ecg ?Nurul SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Basics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaDocument117 pagesBasics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaSimran KothariNo ratings yet
- Artigo 3Document59 pagesArtigo 3AnaLuísaGomesNo ratings yet
- ECG NormalDocument9 pagesECG NormalDya AndryanNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument169 pagesElectrocardiogramjitendra magarNo ratings yet
- All EcgDocument143 pagesAll EcgYenza FaheraNo ratings yet
- Basic of EcgDocument82 pagesBasic of Ecgpopescuioana1No ratings yet
- Asist. Univ. Dr. Tataru Ana LianaDocument45 pagesAsist. Univ. Dr. Tataru Ana LianaCasiana GuiNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: Amir Aziz AlkatiriDocument51 pagesEKG Interpretation: Amir Aziz AlkatiriShabrina Sari MedinaNo ratings yet
- ECG TutorialDocument40 pagesECG TutorialAnonymous HAbhRTs2TfNo ratings yet
- Abnormal ECGDocument55 pagesAbnormal ECGdevilbata50% (2)
- ECG Demographics Rate: 300/# Large Box in RR IntervalDocument11 pagesECG Demographics Rate: 300/# Large Box in RR IntervalJonathan DavisNo ratings yet
- Interpreting ECGsDocument4 pagesInterpreting ECGsdewitt.bernardNo ratings yet
- ECG%20 ReviewDocument103 pagesECG%20 ReviewJenna NiemiecNo ratings yet
- EKG NotesDocument4 pagesEKG NotesYien LiNo ratings yet
- Ecg Presentation 2013Document40 pagesEcg Presentation 2013Samuel FpNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi EKGDocument81 pagesInterpretasi EKGGyna MarsianaNo ratings yet
- ECG SummaryDocument11 pagesECG Summaryjackfruit5887No ratings yet
- Suatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisAnonymous 3LwVkUsdNo ratings yet
- Arrythmia Recognition Lecture FinalDocument54 pagesArrythmia Recognition Lecture FinalFlorencio D. Santos IVNo ratings yet
- Kuliah EKG II Unswagati 2016Document77 pagesKuliah EKG II Unswagati 2016iikNo ratings yet
- Superimposed ECG PDFDocument93 pagesSuperimposed ECG PDFEdalyn CapiliNo ratings yet
- Kursus Ekg DR Ismi-1Document78 pagesKursus Ekg DR Ismi-1Sekar Ayu WulandariNo ratings yet
- ECG Ischemie Si InfarctDocument34 pagesECG Ischemie Si InfarctOana CristinaNo ratings yet
- Ecg enDocument12 pagesEcg enKeep smileNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument58 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesRenn Karlo LindoNo ratings yet
- Suatu Alat LaboratorisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat LaboratorisHematology 2016No ratings yet
- ECG Praktis ParamedikDocument45 pagesECG Praktis ParamedikIndra KusumayadiNo ratings yet
- The Normal Adult ECGDocument84 pagesThe Normal Adult ECGkimiastroNo ratings yet
- EKG InterpretationDocument65 pagesEKG Interpretationpaskariatne probo dewi100% (1)
- Sally Aburumman Bushra SaleemDocument75 pagesSally Aburumman Bushra SaleemAbdulrahman AlsayyedNo ratings yet
- ECG Hipertrofii Atriale Si Ventriculare, Blocuri de Ramura, IschemieDocument60 pagesECG Hipertrofii Atriale Si Ventriculare, Blocuri de Ramura, IschemieAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument6 pagesEcgMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Interpretation: Cardiology and Vascular Department Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin UniversityDocument61 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation: Cardiology and Vascular Department Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin UniversityHayat Hamzah DawiNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi ElektrokardiografiDocument60 pagesInterpretasi ElektrokardiografiAditya Praja'schNo ratings yet
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocument4 pagesA Simplified ECG GuidekaelenNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Pricing enDocument2 pagesPricing enHershel LaytonNo ratings yet
- Seminar D Powerpoint - DR Yu Wai ChoDocument6 pagesSeminar D Powerpoint - DR Yu Wai ChoHershel LaytonNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Use of Oral Nystatin - NBT002812Document6 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Oral Nystatin - NBT002812Hershel LaytonNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Report - WHO - March 6, 2020Document9 pagesCoronavirus Report - WHO - March 6, 2020CityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Department of Intensive Care Duty Roster: 26-Oct-20 Mon SHDDocument1 pageDepartment of Intensive Care Duty Roster: 26-Oct-20 Mon SHDHershel LaytonNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide To Systems Trading (For Non-Programmers)Document29 pagesThe Essential Guide To Systems Trading (For Non-Programmers)Constantino L. Ramirez III100% (4)
- My Stock Market Power Day Trading EbookDocument22 pagesMy Stock Market Power Day Trading EbookTolmasxon Alaxonov0% (1)
- The NO BS Guide To Swing Trading PDFDocument19 pagesThe NO BS Guide To Swing Trading PDFVinesh Singh67% (3)
- Heart FailueDocument29 pagesHeart FailueriyanNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Manual2006Document170 pagesTuberculosis Manual2006Hershel LaytonNo ratings yet
- Erc - 2005Document58 pagesErc - 2005zulfantri1983No ratings yet
- Circulatory System LabDocument3 pagesCirculatory System LabMatt Joseph CabantingNo ratings yet
- TR 9000 Series BrochureDocument2 pagesTR 9000 Series BrochureSreejith SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Manual - ST Jude Pacemaker PM2140Document74 pagesManual - ST Jude Pacemaker PM2140Samaresh PalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument256 pagesCardiovascular NotesVipul RajoraNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogramm - Ecg InterpretationDocument56 pagesElectrocardiogramm - Ecg InterpretationKreshnik HAJDARI100% (1)
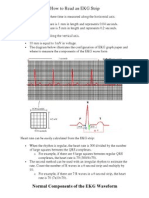
- How To Read An EKG StripDocument9 pagesHow To Read An EKG StripRavi PandeNo ratings yet
- Strong's EKG Chamber Enlargement - DraftDocument12 pagesStrong's EKG Chamber Enlargement - DraftMonica GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument7 pagesCardiac CycleKrishnakanth NNo ratings yet
- Tabela-De-Pressão-Arterial Inf Adolesc 2017 PDFDocument4 pagesTabela-De-Pressão-Arterial Inf Adolesc 2017 PDFTaináNo ratings yet
- Arie Bachtiar Dwitaryo Bagian Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskular FK. UNDIP / RS. Dr. Kariadi SemarangDocument34 pagesArie Bachtiar Dwitaryo Bagian Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskular FK. UNDIP / RS. Dr. Kariadi SemarangSebastiana Ratih LefebvreNo ratings yet
- SonoAce R5 Reference Manual P PDFDocument150 pagesSonoAce R5 Reference Manual P PDFNeto Infomab MedNo ratings yet
- VT Ventricular TachyDocument1 pageVT Ventricular Tachymadimadi11No ratings yet
- Euad 043Document29 pagesEuad 043Pedro SeguraNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Terminology, Definitions, and MechanismsDocument16 pagesArrhythmias: Terminology, Definitions, and MechanismshazelelNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs and Oxygen AdministrationDocument11 pagesVital Signs and Oxygen AdministrationCrisha Shane BoticarioNo ratings yet
- 127-Article Text-817-6-10-20180329Document4 pages127-Article Text-817-6-10-20180329Riri Andriani MinHoNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Classification, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology of HypertensionDocument35 pagesClassification, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology of Hypertensionastrid abrahamsNo ratings yet
- High Acuity Exam 1 Study Guide - 2Document12 pagesHigh Acuity Exam 1 Study Guide - 2Angelica WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Zoll M MCCT Series Defibrillator ManualDocument111 pagesZoll M MCCT Series Defibrillator Manualjuan alberto florez coteNo ratings yet
- 579-Article Text-1710-1-10-20220113Document10 pages579-Article Text-1710-1-10-20220113Nurul AdibahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 46 Vital SignsDocument6 pagesChapter 46 Vital SignsReymon RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Bench-To-bedside Review An Approach To Hemodynamic Monitoring Guyton at Bedside - Magder 2012Document7 pagesBench-To-bedside Review An Approach To Hemodynamic Monitoring Guyton at Bedside - Magder 2012Fransisca Dewi KumalaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Document36 pagesCalcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Nafisa TasnimNo ratings yet
- LAPSUS LAKI-LAKI 52 TAHUN DENGAN TRANSIENT ST SEGMENT ELEVATION - Dr. Yusuf Haz CondengDocument47 pagesLAPSUS LAKI-LAKI 52 TAHUN DENGAN TRANSIENT ST SEGMENT ELEVATION - Dr. Yusuf Haz CondengIrham Khairi100% (1)
- Cardiopulmonary NPTE Questions FlashcardsDocument61 pagesCardiopulmonary NPTE Questions Flashcardsdina sharaf100% (4)
- Abstract IctromiDocument2 pagesAbstract Ictromiyayasan harapan ummatNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Terapi Relaksasi Otot Progresif Dalam Menurunkan Hipertensi Pada LansiaDocument8 pagesEfektivitas Terapi Relaksasi Otot Progresif Dalam Menurunkan Hipertensi Pada LansiaLaila MunazaddNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDennis KimNo ratings yet