Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hatzdqr
Hatzdqr
Uploaded by
Amit singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesOriginal Title
hatzdqr
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesHatzdqr
Hatzdqr
Uploaded by
Amit singhCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Ref. No.: Ex/Met/ET/T/222/2018
B.MET.ENGG.2"” yr. 2°” SEM. EXAM.-2018
APPLIED ELECTRONICS & INSTRUMENTATION
TIME : 3HOURS FULL MARKS :100
(50 marks for each Part)
Use Separate Answer Scripts for Each Group
GROUP A
FULL MARKS : 50
Answer question no. 1 and any two from the rest (Q.2-Q.4)
Each Questions (Q.2-Q.4) has two options, choose only one
i. Explain the different techniques current flow through a semiconductor.
ii, When is a p-n junction diode said to be in () forward bias and (i) reverse bias.
iii, | How many diodes are there in a bridge rectifier and compare the properties of it with
full wave center tap rectifier?
iv. Why a transistor is also known as BJT. Explain the types of transistor.
vy. What do you mean by CMRR & Slew Rate?
Sx2-10
Define semiconductors. What are their characteristics properties?
Define the following terms — doping, dopants, donors, acceptor.
Explain the phenomenon of diffusion and drift of current carriers ina semiconductor.
Define the mobility of charge carriers in a semiconductor.
At 300 k the intrinsic carrier concentration of silicon is 1.5 x 10% m~*. If the
electron and the hole mobilities are 0.13 and 0.05 m2/V.s respectively, determine the
intrinsic resistivity of silicon at 300K
G+446+245)=20,
OR -
What is a p-n junction diode?
What is an abrupt and linearly graded p-n junction?
How does a p-n junction diode behave under- equilibrium, forward bias, and reverse
bias?
iv. The reverse saturation current at 300k of a p-n junction Ge diode is SA. Find the
voltage to be applied across the junction to obtain a forward current of 50 mA.
(243+10+5)=20
3.A)
ii,
iii,
8)
ik
3)
Draw the circuit diagram of a) a half wave rectifier and (b) a full wave rectifier.
Explain the operation of each circuit,
A bridge rectifier feeds a load resistance of 25000 from q 30v (rms) supply. Bach
diode of the rectifier has a forward resistance of $0Q.calculate (a) the de load voltage,
(b) the ripple voltage at the output.
Define the following terms for (a) DC load current (b) ripple factor.
Explain the circuit operation of a bridge rectifier with capacitive filter at the load.
(8454245)
oR
What are the different modes of operation of a transistor? What do you mean by static
characteristics ofa transistor?
With respect to CB mode input output characteristics of a transistor, explain the
active, saturation and the cutoff regions with diagram.
Explain the term transistor biasing. What are the factors determining the choice of the
Q point? Define the three stability factors,
Derive the relationship between a and B.
(6+6+642)-20
Write a short note on Wien Bridge Oscillator with frequency of oscillation
calculation,
Describe the use of an OP AMP as an adder.
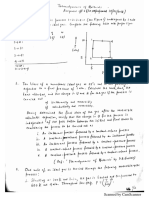
The inverting amplifier circuit of the figure below his R= 1KQ and Rf-3 KQ.
Determine the output voltage, input resistance, and the input current for an input
voltage of 2V.
ft
Vin Rt
et Vout
+
(10+5+5)=20
OR
Define the following terms in connection with an OP AMP — Input bias current, Input
offset voltage, Input offset current,
Explain the operating principle of a differentiator and integrator circuits with proper
circuit diagram using OPAMP.
Explain the concept of feedback in amplifiers, What do you mean by positive and
negative feedback?
(G+8+4)=20
GROUP B
FULL MARKS : 50
Answer question no. 5 and any two from the rest (Q.6-Q.8)
Each Questions (Q.6-Q.8) has two options, choose only one
&
a, What is the typical detector of AC Bridge?
, What are the advantages of potentiometer type transducer?
c. Name two applications of Wheatstone Bridge
4. What is opposite angle measurement bridge?
¢. What are disadvantages of Maxwell’s inductance capacitance bridge?
5x2=10
pe
’) Explain the operating principle of Wheatstone Bridge. Deduce the Thevenin
equivalent circuit to find out the Galvanometer resistance.
What are the typical measurement errors in DC bridge measurement?
84844920
Or
i) Caloulate the current through Galvanometer
ii) Why Kelvin Double Bridge hes been used as a modification of Wheatstone
Bridge?
iii) Explain the operation of Kelvin Double Bridge.
6+6+8=20
A
i) The impedance of the basic AC bridge are as follows Z1 = 100 (80°) Ohm , Z2=
250 Ohm, Z3= 400 (30°) Ohm and Z4= unknown . Determine the constant for unknown
arm.
In the following bridge R2 = 400 Ohm, R3= 600 Ohm, Ry = 1000 Ohm, Ce = 0.5
roFarad, Calculate the value of R; and Ly. Calculate the Q of coil if Frequency is
1000Hz.
iii) Explain the operation of Modified De- Sauty’s Bridge with proper Phasor
diagram. Why it is called as modified
6+648=20
Or
B
i) Explain with Phasor diagram of the operation of Hay’s Bridge.
ii) How an unknown frequency can be measured using bridge?
iii) A sheet of Bakelite 4.5mm Thick is tested at S0Hz between electrodes of 0.12m in
diameter. The Schering bridge employs a standard air capacitor C2 of 106 pF
capacitance, a non reactive resistance of Ry = 1000/z Ohm in parallel with a
variable capacitor Cy and a non reactive variable resistance Rx. Balance is
obtained with C, = 0.5 microFarad and Rs = 260 Ohm. Calculate the capacitance,
power factor and relative permittivity of sheet.
8+6+6=20
8
A
What is the working principle of Varley loop? Why it is advantageous over
‘Murray loop?
ii) A. bridge is balanced at 1000Hz and has the following constants, AB 0.2
microFarad pure capacitance, BC 500 Ohm, CD unknown and DA R= 300 Ohm
in parallel with C = 0.1 microFarad. Find R, C, L of arm CD considering they all
are in series circuit.
:) The Varley loop test set consists of a defective conductor and a healthy conductor
connected at the cable terminal located 10 miles from the test set. The cable have
resistance of 0.05 ohm per 1000 feet. When the switch is in position a and the
circuit is balanced, the balancing resistance is Rs = 100 Ohm, When the switch is
in position b the circuit is rebalanced and Rs = 99 Ohm. Find the distance from the
ground fault to the test set
4+4+6+6-20
Or
i) Explain the principle of operation of four probe method for measuring the
resistivity of metal, Proof that loge p = (By /2KT) - log. K
ii) ‘What are the drawbacks of two probe methods? How the resistivity of a
slice conducting surface can be performed?
in
446+6+4=20
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- DistrictWiseList324 PDFDocument2 pagesDistrictWiseList324 PDFAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Gyiet PDFDocument1 pageGyiet PDFAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Physics IIADocument2 pagesPhysics IIAAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Steel MakingDocument2 pagesPart - I: Steel MakingAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Combined Higher Secondary Level Examination 2019 Tier IDocument33 pagesCombined Higher Secondary Level Examination 2019 Tier IAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Mml372 Principles of Non Ferrous Extraction Metallurgy (3-0-0) 8 CreditsDocument1 pageMml372 Principles of Non Ferrous Extraction Metallurgy (3-0-0) 8 CreditsAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Project Management PDFDocument12 pagesProject Management PDFAmit singhNo ratings yet
- GyitDocument1 pageGyitAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Physics IIADocument2 pagesPhysics IIAAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Sl. No. Name of Students Address DOB Dept 1 Amit Kuamr 06/02/1996 METALLURGY Plot No. - Db/11 K.S.T.P South Dhadka ASANSOL-713302Document4 pagesSl. No. Name of Students Address DOB Dept 1 Amit Kuamr 06/02/1996 METALLURGY Plot No. - Db/11 K.S.T.P South Dhadka ASANSOL-713302Amit singhNo ratings yet
- 24 PDFDocument8 pages24 PDFAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Investigations On Corrosion Behaviour of Welded Joint in ASTM A355P5 Alloy Steel PipeDocument15 pagesInvestigations On Corrosion Behaviour of Welded Joint in ASTM A355P5 Alloy Steel PipeAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Testing of MaterialsDocument1 pageMechanical Testing of MaterialsAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Materials 20015Document3 pagesThermodynamics of Materials 20015Amit singhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Amit singhNo ratings yet
- B M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Etallurgical Ngineering XaminationDocument3 pagesB M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Etallurgical Ngineering XaminationAmit singhNo ratings yet
- B M E - E, 2009: (Old Syllabus)Document2 pagesB M E - E, 2009: (Old Syllabus)Amit singhNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument2 pages3 PDFAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Corrosion BasicsDocument4 pagesCorrosion BasicsAmit singhNo ratings yet
- Assgn 6Document2 pagesAssgn 6Amit singhNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument2 pages3 PDFAmit singhNo ratings yet