Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Doi:10.3390/ma7020787) - Please Calculate I: Advanced Electrochemical Materials Homework #6
Uploaded by
Amalia Rizki Fauziah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pages-
Original Title
AEM-HW-06
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document-
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesDoi:10.3390/ma7020787) - Please Calculate I: Advanced Electrochemical Materials Homework #6
Uploaded by
Amalia Rizki Fauziah-
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Advanced Electrochemical Materials Homework #6
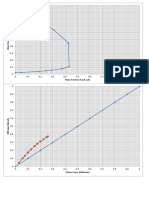
1 The below Tafel curves are the mild steel in 1.0 M H2SO4 with 0.25 mM of the
corrosion inhibitor at different temperatures [Materials 2014, 7(2), 787-804,
doi:10.3390/ma7020787]. Please calculate i0, k0, α and Rct from Tafel plot at 30oC.
2 The saturated calomel electrode (SCE) is generally used as a reference electrode,
which its redox reaction is:
𝐻𝑔2 𝐶𝑙2 + 2𝑒 − ⇄ 2𝐻𝑔(𝑙) + 2𝐶𝑙 − 𝐸 0 = 0.2682 𝑉
This redox reaction is generally carried out in a KCl solution. The activity
coefficient of 𝐶𝑙 − is unity for Q2.1 and Q2.2.
2.1 If [KCl] is 3.5 M, what is the equilibrium potential of SCE?
2.2 If [KCl] is saturated, what is the equilibrium potential of SCE? The Ksp
(solubility product) of KCl is 21.7 M2.
2.3 The real values of SCE in 3.5 M and saturated KCl solution are 0.2500 V and
0.2444 V, respectively. Please give the reason about the differences between
the real values and the calculated values from Q2.1 and Q2.2.
3 Graphene, discovered in 2004, has excellent property for electrochemical
probing. The multilayer graphene nanoflake films were performed in the
solution containing 5 mM Fe(CN)63-/4- [1] with electrode area of 0.196 cm2,
please the answer the following questions:
3.1 Is it reversible, quasi-reversible or irreversible reaction? Please explain the
reason.
3.2 Plot the square root of scan rates vs. anodic peaks (Ip,a) and cathodic peaks
(Ip,c).
3.3 Is it diffusion-controlled or kinetic-controlled reaction? Please explain the
reason.
3.4 Calculate DO.
3.5 Calculate E1/2.
4 A redox reaction of 1 mM A2+/A3+ demonstrates the LSV curves on a 0.196 cm2
platinum electrode, showing the peak currents of 0.16, 0.22, 0.32, 0.50, 0.59 and
0.71 mA at the scan rates of 5, 10, 20, 50, 70 and 100 mV/s, respectively.
4.1 Plot the peak currents vs. the square root of scan rates.
4.2 Determine DO from the slope of Figure 2.1.
[1] N.G. Shang, P. Papakonstantinou, M. McMullan, M. Chu, A. Stamboulis, A.
Potenza, S.S. Dhesi, H. Marchetto, Advanced Functional Materials, 18 (2008) 3506-
3514.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Solution Manual For Chemical Biochemical and Engineering Thermodynamics Stanley SandlerDocument10 pagesSolution Manual For Chemical Biochemical and Engineering Thermodynamics Stanley SandlerAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- A Study of The Relation of Piezoelectricproperties and Nano Structures Through Methodsin Computational PhysicsDocument122 pagesA Study of The Relation of Piezoelectricproperties and Nano Structures Through Methodsin Computational PhysicsAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Z-Scheme Photocatalytic Systems For Solar Water SplittingDocument42 pagesZ-Scheme Photocatalytic Systems For Solar Water SplittingAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Monolithic Cells For Solar FuelsDocument20 pagesMonolithic Cells For Solar FuelsAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- CO2 Activation and Hydrogenation A Comparative DFT Study of Ru10TiO2 and Cu10TiO2 Model CatalystsDocument11 pagesCO2 Activation and Hydrogenation A Comparative DFT Study of Ru10TiO2 and Cu10TiO2 Model CatalystsAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen From Sunlight and Water A Side-By-Side Comparison Between Photoelectrochemical and Solar Thermochemical Water SplittingDocument18 pagesHydrogen From Sunlight and Water A Side-By-Side Comparison Between Photoelectrochemical and Solar Thermochemical Water SplittingAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Plasmon-Enhanced Light-Matter Interactions and ApplicationsDocument14 pagesPlasmon-Enhanced Light-Matter Interactions and ApplicationsAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- PEC Vs Solar - Belum EditDocument12 pagesPEC Vs Solar - Belum EditAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- M10806824 - Paper Report 4Document3 pagesM10806824 - Paper Report 4Amalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties and Applications of Plasmonic-Metal NanoparticlesDocument28 pagesOptical Properties and Applications of Plasmonic-Metal NanoparticlesAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- M10806824 - Paper Report 2Document3 pagesM10806824 - Paper Report 2Amalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Time Travel Machine Inspired by TARDIS: Smart Technology (CH5308701) Amalia Rizki Fauziah (M10806824) - Master StudentDocument2 pagesTime Travel Machine Inspired by TARDIS: Smart Technology (CH5308701) Amalia Rizki Fauziah (M10806824) - Master StudentAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of Bioethics Nowadays: Smart Technology (CH5308701) Amalia Rizki Fauziah (M10806824) - Master StudentDocument3 pagesThe Challenges of Bioethics Nowadays: Smart Technology (CH5308701) Amalia Rizki Fauziah (M10806824) - Master StudentAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Low-Carbon Society and Circulating Society: Smart Technology (CH5308701) Amalia Rizki Fauziah (M10806824) - Master StudentDocument2 pagesLow-Carbon Society and Circulating Society: Smart Technology (CH5308701) Amalia Rizki Fauziah (M10806824) - Master StudentAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- M10806824 - Paper Report 1Document3 pagesM10806824 - Paper Report 1Amalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakaAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- MIK Acetone WaterDocument1 pageMIK Acetone WaterAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- SPRAY DRYER - Neraca EnergiDocument26 pagesSPRAY DRYER - Neraca EnergiAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid Water Isopropyl EtherDocument4 pagesAcetic Acid Water Isopropyl EtherAmalia Rizki FauziahNo ratings yet