Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IJSRD - Boiler Tube Failures & Prevention Methods
Uploaded by
Thanhluan NguyenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IJSRD - Boiler Tube Failures & Prevention Methods
Uploaded by
Thanhluan NguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development| Vol.
4, Issue 05, 2016 | ISSN (online): 2321-0613
Boiler Tubes Overheating Failures and Actions to Control Them
S N S P Ramya Harini1 Ch.Tirumala Rao2
1
P.G. Student 2Assistant Professor
1,2
Department of Mechanical Engineering
1,2
ANUCET, Guntur, A.P, India
Abstract— Boiler tube failures continue to be the leading operational problems that can lead to these short-term
cause of forced outages in fossil-fired boilers. To get your high-temperature failures include, among others:
boiler back on line and reduce or eliminate future forced Flame impingement from misaligned or worn burners
outages due to tube failure, it is extremely important to that leads to the formation of a steam blanket, as the
determine the specific root cause. One of the main reasons local heat flux is too great for the fluid flow through
for boiler forced outages is boiler tube leakage. The plan was the tube.
to carry out for experimental investigation and analysis of the Blockage of a superheater tube with condensate or
boiler tube failure, and then strategy is to implementation of foreign material that prevents steam flow. These
plan with different power plants and failure techniques until problems are more frequent during start-up.
it was considered effective. This paper aims to covers the Reduced flow in either a water or steam circuit that
major reasons of Boiler tube Leakages and effective design leads to inadequate cooling. Pinhole leaks, especially
considerations and recommended suggestions to avoid the at poor welds or slag falls, severe dents from slag
same. Failure analysis methodology is applied to the falls or ruptured tubes, and partial blockage from
principal mechanisms by which boiler tubes fail during debris or other foreign matter are some of the more
service. Several important factors often associated with obvious causes.
component failures are deficiency in design, fabrication, Foreign objects, broken attemperation- spray nozzles,
operating conditions and expended useful life. for example, in headers that partially block a
Key words: Boiler Tubes Failure, Boiler Tubes Overheating superheater or reheater tube.[3]
Failures Regardless of the location within the boiler that
these failures occur, the appearance is similar. There is a
I. INTRODUCTION wide-open burst with the failure edge drawn to a near
The operation of a boiler is a dynamic balance between heat knife-edge condition, and the length of the opening four
flow from the combustion of a suitable fuel and either steam or five tube diameters. These failures display considerable
formation within the furnace or steam super heating within ductility; the thinning at the failure lip may be more than
the superheater or reheater. In effect, the steel tube is 90% of the original wall at the instant of rupture. The
"heated" by the flame or hot flue gas and simultaneously microstructures throughout the failure will usually
"cooled" by the fluid (steam, water or a mixture of steam indicate, in the case of ferritic steel, the peak temperature
and water) flow. When this balance is maintained within the at the time of failure. For ferritic steels there is a
design limits, metal temperatures are also maintained within transformation from ferrite and iron carbide or pearlite, to
design parameters. However, when the balance is upset, ferrite and austenite. This temperature is referred to as the
metal temperatures rise and failures occur sooner than lower-critical transformation temperature and occurs at
expected. Depending on the relative temperature rise, 1340oF or higher, depending on the exact alloy
failures can occur either very quickly, that is, in a matter of composition.[4]
minutes; or over a much longer time period, that is, in matter
of many months. For convenience these two regimes are
defined as "long term" and "short-term" overheating. This
article will discuss on these high-temperature failures. [1]
II. SHORT TERM OVERHEATING
The simplest explanation for all "short-term" overheating
failures is: when the tube metal temperature rises so that the
hoop stress from the internal steam pressure equals the
tensile strength at elevated temperature, rupture occurs. For
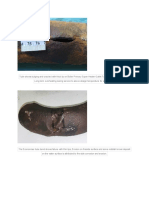
example, in a super-heater of SA192 tubes, with a designed Fig. 1: Fish mouth opening due to short term failure
metal temperature of 800oF, the ASME Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Code gives the allowable stress at 800oF as 9,000 psi.
If the tube-metal temperature should rise to a temperature of
around 1300oF, the hoop stress would be equal to or slightly
greater than the tensile strength at 1300oF, and failure would
occur in a few minutes.[2]
In a superheater or reheater, DNB-departure from
nucleate boiling cannot occur as only steam super heating
takes place, no boiling. However, short-term overheating Fig. 2: longitudinal splitting and external scaling due to
failures do occur but usually during start-up. Boiler long term overheat
All rights reserved by www.ijsrd.com 1453
Boiler Tubes Overheating Failures and Actions to Control Them
(IJSRD/Vol. 4/Issue 05/2016/355)
Ductile failures can also occur at normal operating IV. ACTIONS TO BE TAKEN TO PREVENT & CONTROL BOILER
conditions but are not as high-temperature failures. Wastage TUBE FAILURES
of a tube from corrosion or erosion can reduce the wall During overhauling of Steam Generator, Internal Washing
thickness, which, in turn, raises the hoop stress. Such of passes should be carried out so that proper scanning of
failures occur in waterwall tubes, for example, where tubes can be carried out.
sootblower erosion has reduced the wall thickness, or in the Intensive 'D' metering of boiler tubes at pre-
convection pass from fly-ash erosion. These failures can determined locations to be carried out & comparison with
occur at normal operating temperatures if the wall thickness respect to last overhaul should be done, especially in wear
reduction is sufficient. While these microstructures and the prone areas.
estimated peak temperature at the time of failure cannot The limit of 20% reduction in thickness due to fly
predict the sole cause of the failure, the metallurgical ash erosion must be adhered to, for replacement of worn out
analysis can suggest the kind of boiler-operational problem portion of boiler tubes.
that is likely to be the cause of the rupture.[5] DPT of attachment welds should be carried out,
especially in Pent House.
III. LONG TERM OVERHEATING 100% radiography of weld it’s during overhaul &
Long term overheating tube failures are due to operating also during tube failure repair is to be carried out.
metal temperature of the boiler tubes going above the Platen S/H, R/H & Final super heater Coils must be
allowable limit. These types of failure are seen in steam checked for overheating during over hauling. During
cooled tubes like superheaters and reheaters and in water operation of units, the metal temperature excursions in
cooled tubes of waterwalls. These tubes are of various sizes above area should be avoided and monitored by Operation
and thicknesses depending upon the pressure and the mid- Department and should be discussed in daily Planning
wall metal temperature.When the mid-wall metal meeting.
temperature exceeds the allowable metal temperature of the For determining the fire side corrosion and internal
tube material, overheating sets in. When the metal corrosion of furnace tubes, samples from each corner of
temperature of the tube exceeds the allowable limit the furnace must be sent to R & D in each unit overhaul. [8]
material strength reduces drastically, depending upon the
material composition. V. CONCLUSION
During this period of long term overheating the In conclusion it may, therefore, be said that overheating is
tube outer surface develops bulging, creeping elongate one of the major reasons responsible for the failure of boiler
fissures along the axis of the tube. There will be little or no tubes, carbon steel tubes and final superheater tubes
wall thickness reduction in the non-blistered area. These are respectively. Analysis of large database clearly indicates
the typical identifiable signs of long term overheating. These that irrespective of operating temperature and pressure to
failures are also called as high temperature creep failures. which the boiler tubes are exposed as well as loss of wall
Areas in boilers prone for long term overheating are thickness due to the corrosion oxidation and erosion
Waterwalls and superheaters. processes in service, modified steel exhibited the longest
Waterwalls normally, due to internal deposits and life/resistance to creep damage. The next candidate material
partial choking of the tube internally, are subjected to long recommended for such operating condition is another
term overheating. Superheaters are subjected to high variation of steel upto a mid wall temperature beyond which
desuperheating, higher radiant heat fluxes in the region, and steel shows longer creep life.
lower grade material at transition points. Reheaters are also
prone for long term overheating, but not so much like REFERENCES
superheaters.This can happen due to many reasons like
internal deposit, low flow though the tube due to partial [1] DavidN.French President, David N. French Inc,
choking of the tube internal diameter, due to sudden load Mettalurgists
raise, due to sudden fuel input, etc.[6] [2] DavidN.French President, David N. French Inc,
Long term overheating failures can occur in tubes Mettalurgists
throughout the boiler. The following can be causes of this [3] April 1991 National Board BULLETIN
mechanism of failure: [4] April 1991 National Board BULLETIN
Blockage by debris, scale, or deposits restricting flow. [5] Boiler failure mechanisms by Douglas-DewitDtick
Excessive magnetite on the internal surfaces has an ,StephenMcIntyre and Joseph Hofilena
insulating effect. This can cause over-firing of the [6] Boiler failure mechanisms by Douglas-DewitDtick
furnace, subsequently increasing metal temperatures. ,StephenMcIntyre and Joseph Hofilena
[7] S. CHAUDHURI and R. SINGH National Metallurgical
Exposure to radiant heat or excessive gas temperature
Laboratory, Jamshedpur - 831 007, India
due to blockage of gas passages or are located before
[8] Steag O&M company
the final outlet header.
[9] S. CHAUDHURI and R. SINGH National Metallurgical
Incorrect material selection relative to the design
Laboratory, Jamshedpur - 831 007, India
operating temperatures.
Have higher stresses due to welded attachments or
insufficient support.[7]
All rights reserved by www.ijsrd.com 1454
You might also like
- WARTSILA-SG18V34 Manual PDFDocument230 pagesWARTSILA-SG18V34 Manual PDFАндрей ВасильевNo ratings yet
- Boiler Corrosion MagnetiteDocument14 pagesBoiler Corrosion MagnetiteJakeTheSnake69No ratings yet
- Steam BoilersDocument143 pagesSteam BoilersThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- ASME1Document3 pagesASME1ck19654840No ratings yet
- Cycling Tolerance - Natural Circulation Vertical HRSGSDocument10 pagesCycling Tolerance - Natural Circulation Vertical HRSGSdrainer6666No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Boiler System Failures: Deaerator CrackingDocument22 pagesChapter 14 Boiler System Failures: Deaerator CrackingVijay RajaindranNo ratings yet
- Reduce Boiler Tube Leakages Through Proper MaintenanceDocument7 pagesReduce Boiler Tube Leakages Through Proper MaintenanceNorman IskandarNo ratings yet
- Steam Boiler Inspections Using Remote Field TestingDocument11 pagesSteam Boiler Inspections Using Remote Field TestingAnonymous lmCR3SkPrKNo ratings yet
- Integrated Approach RLA of Reformer Tubes NDT (ARTiS) PDFDocument8 pagesIntegrated Approach RLA of Reformer Tubes NDT (ARTiS) PDFSatya RaoNo ratings yet
- Engineering 360 - Engineer's Guide To Boiler Tube InspectionsDocument3 pagesEngineering 360 - Engineer's Guide To Boiler Tube InspectionsIsmal AdrianNo ratings yet
- Cooling Systems: Don'T Underestimate The Problems Caused by Condenser Tube LeaksDocument5 pagesCooling Systems: Don'T Underestimate The Problems Caused by Condenser Tube Leakspym1506gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Thailand Power Workshop Grouping: Bangkok Office 29 & 30-Mar-2012Document29 pagesThailand Power Workshop Grouping: Bangkok Office 29 & 30-Mar-2012Prakasit JuangpanichNo ratings yet
- Steve Mcintyre, Boiler Tube Failures-Nace 2006 Read-OnlyDocument83 pagesSteve Mcintyre, Boiler Tube Failures-Nace 2006 Read-OnlyLeire MeigaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube InvestigationDocument6 pagesBoiler Tube InvestigationWaleed EmaraNo ratings yet
- Caustic Corrosion in Boiler Waterside Tube Root Cause & MechanismDocument9 pagesCaustic Corrosion in Boiler Waterside Tube Root Cause & Mechanismعزت عبد المنعمNo ratings yet
- Best Practice in Boiler Water Treatment Part 2Document6 pagesBest Practice in Boiler Water Treatment Part 2Adrian MicuNo ratings yet
- Boiler CleaningDocument11 pagesBoiler CleaningRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Caustic GougingDocument5 pagesCaustic GougingChristian Paul Salazar SanchezNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube LeakageDocument9 pagesBoiler Tube LeakageSoham MallickNo ratings yet
- Cathotic ProtectionDocument5 pagesCathotic Protectionkrishna_swaroop99No ratings yet
- Boiler InspectionsDocument6 pagesBoiler InspectionsAndre YosiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube AssessmentDocument7 pagesBoiler Tube AssessmentNorman IskandarNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Corrosion Water Tube BoilersDocument3 pagesCase Study On Corrosion Water Tube BoilersSalem Garrab100% (2)
- Critical Analysis of Boiler Pressure PartsDocument51 pagesCritical Analysis of Boiler Pressure PartsSCE SOLAPURNo ratings yet
- Fallas Boiler (Babcock and Wilcox)Document8 pagesFallas Boiler (Babcock and Wilcox)scofiel1No ratings yet
- Fatigue CorrosionDocument2 pagesFatigue Corrosionaop10468No ratings yet
- Asset Intelligence Report - A Primer On High Temperature Hydrogen AttackDocument9 pagesAsset Intelligence Report - A Primer On High Temperature Hydrogen AttackVajid MadathilNo ratings yet
- "Boiler Tube Failures": Project ReportDocument30 pages"Boiler Tube Failures": Project ReportmdjanNo ratings yet
- Waterbox InspectionDocument2 pagesWaterbox InspectionFallo SusiloNo ratings yet
- Flow Accelerated Corrosion of Pressure Vessels in Fossil Plants - DooleyDocument6 pagesFlow Accelerated Corrosion of Pressure Vessels in Fossil Plants - Dooleyvandrake10No ratings yet
- High Temperature Corrosion Problems in Waste Heat BoilersDocument2 pagesHigh Temperature Corrosion Problems in Waste Heat BoilersEdenrafaNo ratings yet
- EPRI Atlas of Steamside Oxide ObservationsDocument12 pagesEPRI Atlas of Steamside Oxide Observationsekrem turan100% (2)
- Corrosion FatigueDocument1 pageCorrosion Fatiguevarun chenaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Monitoring PDFDocument24 pagesCorrosion Monitoring PDFMohamedGhanemNo ratings yet
- 1584Document6 pages1584malsttarNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Hydrogen Damage in A CFBC BoilerDocument38 pagesA Case Study On Hydrogen Damage in A CFBC Boilerparthi20065768100% (1)
- Flow Accelerated Corrosion: Forms, Mechanisms and Case StudiesDocument13 pagesFlow Accelerated Corrosion: Forms, Mechanisms and Case StudiesMuralimohan MolabantiNo ratings yet
- Interpret Boiler Tube Cleanliness Test ResultsDocument7 pagesInterpret Boiler Tube Cleanliness Test ResultsJose100% (1)
- BDooley ACC Corrosion FAC1Document19 pagesBDooley ACC Corrosion FAC1DSGNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube FailureDocument7 pagesBoiler Tube FailureBhupendra GobadeNo ratings yet
- CLSCC LiteratureDocument62 pagesCLSCC LiteratureNakarin PotidokmaiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube AssessmentDocument2 pagesBoiler Tube Assessmentjunkhaed4018No ratings yet
- LPR EquipmentDocument12 pagesLPR EquipmentsantoshgprNo ratings yet
- I HRSGDocument7 pagesI HRSGJayanath Nuwan SameeraNo ratings yet
- Soot Blower Erosion: Typical Locations Corrective ActionDocument65 pagesSoot Blower Erosion: Typical Locations Corrective ActionSamNo ratings yet
- Lifetime Assessment of A Steam Pipeline: 1 2 Material 15 128 (14MOV6-3)Document6 pagesLifetime Assessment of A Steam Pipeline: 1 2 Material 15 128 (14MOV6-3)Costas AggelidisNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube Investigation PDFDocument6 pagesBoiler Tube Investigation PDFHussseinmubarkNo ratings yet
- PPChem 2017 19-02-92-102 Authors Copy PublicDocument11 pagesPPChem 2017 19-02-92-102 Authors Copy PublicJan RusaasNo ratings yet
- Waterwall - Fireside CorrosionDocument8 pagesWaterwall - Fireside CorrosionwahonodNo ratings yet
- Inspecton ProcedureDocument3 pagesInspecton ProcedureSanthosh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of A Superheater Tube Ruptured in A Power PlantDocument10 pagesFailure Analysis of A Superheater Tube Ruptured in A Power Plantadventius S.S100% (1)
- Failures in Boiler TubesDocument15 pagesFailures in Boiler Tubesniraj_hwb100% (2)
- Flow Accelerated CorrosionDocument3 pagesFlow Accelerated CorrosionJose HernandezNo ratings yet
- PPChem 2015 17 06 342-353 NewDocument12 pagesPPChem 2015 17 06 342-353 NewyogaNo ratings yet
- Aboveground storage tank inspection checklistDocument7 pagesAboveground storage tank inspection checklistES RouzaNo ratings yet
- Corex - Gunniting - Oct 09 - JSWDocument42 pagesCorex - Gunniting - Oct 09 - JSWSaumit PalNo ratings yet
- Boiler Boilout by RentechDocument4 pagesBoiler Boilout by RentechRonald MesinaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsFrom EverandCorrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsNo ratings yet
- Asset Integrity Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandAsset Integrity Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube Failure Analysis and Prevention MethodsDocument13 pagesBoiler Tube Failure Analysis and Prevention MethodsJude Philip MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Failure of Superheater Tubes in a Power PlantDocument23 pagesFailure of Superheater Tubes in a Power PlantAnand VarmaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Boiler Tube FailureDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Boiler Tube FailureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Cyclic Operation CompileDocument11 pagesCyclic Operation CompileprabodhvkNo ratings yet
- Astm A532 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm A532 PDFJuan Leon100% (1)
- Relationship Between Microstructure, Hardness, Impact Toughness and Wear Performance of Selected Grinding Media For Mineral Ore Milling OperationsDocument8 pagesRelationship Between Microstructure, Hardness, Impact Toughness and Wear Performance of Selected Grinding Media For Mineral Ore Milling Operationsgift mudimuNo ratings yet
- Metals: Effects of Rare Earth (Ce and La) On Steel Corrosion Behaviors Under Wet-Dry Cycle Immersion ConditionsDocument14 pagesMetals: Effects of Rare Earth (Ce and La) On Steel Corrosion Behaviors Under Wet-Dry Cycle Immersion ConditionsThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- GB700 88Document8 pagesGB700 88JJGM120No ratings yet
- Materials: Ffects of Mechanical Ball Milling Time On TheDocument17 pagesMaterials: Ffects of Mechanical Ball Milling Time On TheThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Types of White Cast Irons and HighDocument13 pagesAn Overview On Types of White Cast Irons and HighThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Entropy: Coal and Rock Hardness Identification Based On EEMD and Multi-Scale Permutation EntropyDocument15 pagesEntropy: Coal and Rock Hardness Identification Based On EEMD and Multi-Scale Permutation EntropyThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Real Life Wear Processes: J.D. GatesDocument13 pagesReal Life Wear Processes: J.D. GatesThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Astm A532Document4 pagesAstm A532Thanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 4188-22942-1-PB Failure Analysis of SH TubesDocument13 pages4188-22942-1-PB Failure Analysis of SH TubesEXECUTIVE ENGINEEER BOILER MAINTENANCENo ratings yet
- 41 AlexJankovicFINALDocument11 pages41 AlexJankovicFINALThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 3 - Mechnical Spares-Committt C1Document14 pages3 - Mechnical Spares-Committt C1Thanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 14Document16 pages14Ale MilicNo ratings yet
- Tube Shows Bulging and Cracked With Thick Lip On Boiler Primary Super Heater Outlet Tube Is Attributed ToDocument9 pagesTube Shows Bulging and Cracked With Thick Lip On Boiler Primary Super Heater Outlet Tube Is Attributed ToThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Boiler FailuresDocument14 pagesCase Studies in Boiler Failuresparthi2006576880% (5)
- Boiler System Failures: Analysis & Diagnostics ManualDocument43 pagesBoiler System Failures: Analysis & Diagnostics ManualThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Iso 16112 2017Document12 pagesIso 16112 2017Thanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Failure Analysis of Superheated Steam TDocument6 pagesRoot Cause Failure Analysis of Superheated Steam TThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 1 - Boiler Tube FailuresDocument54 pages1 - Boiler Tube FailuresMohamad EshraNo ratings yet
- Root Out The Cause of Boiler Tube FailuresDocument2 pagesRoot Out The Cause of Boiler Tube FailuresThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water Tube CasesDocument8 pagesBoiler Water Tube CasesjycortesNo ratings yet
- Fit and Tolerance PDFDocument15 pagesFit and Tolerance PDFLevi J SandyNo ratings yet
- A Metallurgical Investigation On A Failed Superheater Tube Used in A Thermal Biomass Power PlantDocument15 pagesA Metallurgical Investigation On A Failed Superheater Tube Used in A Thermal Biomass Power PlantThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Compacted Graphite Iron - Mechanical and Physical Properties For Engine DesignDocument22 pagesCompacted Graphite Iron - Mechanical and Physical Properties For Engine DesignThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Clearances and Fits: Guidelines and Tables Machine Drawing KL Narayana, P. Kannaiah, K. Venkata ReddyDocument16 pagesClearances and Fits: Guidelines and Tables Machine Drawing KL Narayana, P. Kannaiah, K. Venkata ReddyThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and wear properties of centrifugally cast graphite ironsDocument11 pagesMicrostructure and wear properties of centrifugally cast graphite ironsThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- FULLTEXT01Document46 pagesFULLTEXT01Thanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Compacted Graphite Iron - Mechanical and Physical Properties For Engine DesignDocument22 pagesCompacted Graphite Iron - Mechanical and Physical Properties For Engine DesignThanhluan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum Modelling Simulation 1686477167Document12 pagesSimple Pendulum Modelling Simulation 1686477167durssiNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio ES12-25WADocument38 pagesManual de Servicio ES12-25WARonald PiedrahitaNo ratings yet
- Hitachi ZX210LC 5 Spec en WebDocument8 pagesHitachi ZX210LC 5 Spec en WebridofambudiNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Exam Phyc2121Document42 pagesFirst Quarter Exam Phyc2121marcovy dela cruz100% (1)
- 156Document12 pages156Jorge Armando Carlos SixtoNo ratings yet
- Hand-Off-Automatic Controls Chapter SummaryDocument30 pagesHand-Off-Automatic Controls Chapter SummaryJohn Paul DaliopacNo ratings yet
- CFD simulation of turbulence downstream of a large diameter square knife gate valveDocument5 pagesCFD simulation of turbulence downstream of a large diameter square knife gate valveRaef kobeissiNo ratings yet
- Flow-Induced Fatigue Failure in Tubular Heat ExchangersDocument7 pagesFlow-Induced Fatigue Failure in Tubular Heat ExchangersVelpandian ManiNo ratings yet
- Simple, Low-Cost Vibration Monitoring of Cooling Towers at Bristol-Myers SquibbDocument4 pagesSimple, Low-Cost Vibration Monitoring of Cooling Towers at Bristol-Myers SquibbfazzlieNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 14: (SECTIONS 14.1-14.4, 14.6)Document63 pagesChapter No 14: (SECTIONS 14.1-14.4, 14.6)Farhan ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Ah 100 Technical PDFDocument526 pagesAh 100 Technical PDFAnonymous 9TYJjFNo ratings yet
- Fabric Expansion Joint - 2021Document46 pagesFabric Expansion Joint - 2021cemalNo ratings yet
- ANSI Standard Fits.-Tables 3 Through 9 Inclusive Show A Series of Standard Types andDocument11 pagesANSI Standard Fits.-Tables 3 Through 9 Inclusive Show A Series of Standard Types andmohamadelsb3No ratings yet
- The Roco geoLINE System - An innovative model railway conceptDocument9 pagesThe Roco geoLINE System - An innovative model railway conceptsuper2274No ratings yet
- Method Statement of Chiller Preventive MaintenanceDocument5 pagesMethod Statement of Chiller Preventive MaintenanceBalajiNo ratings yet
- Kubota Cylinder Head Kit for Industrial EnginesDocument1 pageKubota Cylinder Head Kit for Industrial EnginesWai MinNo ratings yet
- Crown-Fusion ASME B16.34 Threaded Ball Valves Brochure 2 CompressedDocument20 pagesCrown-Fusion ASME B16.34 Threaded Ball Valves Brochure 2 Compressedclaudio godinezNo ratings yet
- Cold Thermal Insulation SpecificationDocument13 pagesCold Thermal Insulation SpecificationCameliaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument46 pagesAir Conditioning SystemNurFarahinZakariahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report 1: Natural Frequency and Damping of Single Degree of Freedom SystemsDocument20 pagesLaboratory Report 1: Natural Frequency and Damping of Single Degree of Freedom SystemsNang TruongNo ratings yet
- Durlon Gasket ManualDocument84 pagesDurlon Gasket Manualhumberto.aranguiz2715No ratings yet
- 1989 Chevrolet Corvette Steering Column RepairDocument4 pages1989 Chevrolet Corvette Steering Column RepairJoel BacyNo ratings yet
- Lifting and Handling SolutionsDocument12 pagesLifting and Handling SolutionstarekhocineNo ratings yet
- Dynamic HPHT System - FANNDocument3 pagesDynamic HPHT System - FANNPaola Olivares SanchezNo ratings yet
- Genset BasicsDocument4 pagesGenset BasicsAshish MNo ratings yet
- Liebherr Over Height FrameDocument4 pagesLiebherr Over Height FrameLiebherrNo ratings yet
- DWV Series: Power RatingDocument2 pagesDWV Series: Power Ratingquangtruc106No ratings yet