0% found this document useful (0 votes)
445 views7 pagesCisco Device Functions Lab Exercise
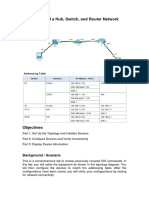
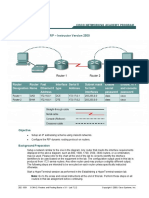
This lab explores MAC address tables on Cisco switches and routing tables on routers. The document provides steps to view MAC addresses learned on switches and IP routes on routers. It configures IP addresses on router interfaces to generate connected routes, and adds a static route to show how routes populate the routing table.
Uploaded by
Tent DorinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
445 views7 pagesCisco Device Functions Lab Exercise
This lab explores MAC address tables on Cisco switches and routing tables on routers. The document provides steps to view MAC addresses learned on switches and IP routes on routers. It configures IP addresses on router interfaces to generate connected routes, and adds a static route to show how routes populate the routing table.
Uploaded by
Tent DorinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd