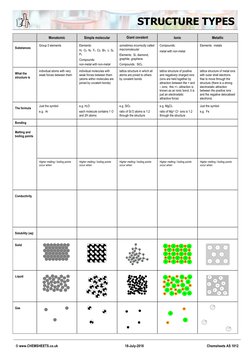
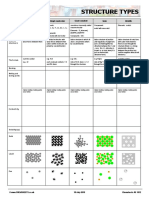
STRUCTURE TYPES
Monatomic Simple molecular Giant covalent Ionic Metallic
Group 0 elements Elements: sometimes incorrectly called Compounds: Elements: metals
Substances
H2 O2 N2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 S8 macromolecular metal with non-metal
P4 Elements: Si, diamond,
Compounds: graphite, graphene
non-metal with non-metal Compounds: SiO2
individual atoms with very individual molecules with lattice structure in which all lattice structure of positive lattice structure of metal ions
What the weak forces between them weak forces between them atoms are joined to others and negatively charged ions with outer shell electrons
structure is (atoms within molecules are by covalent bonds (ions are held together by free to move through the
joined by covalent bonds) attraction between the + and structure (there is a strong
– ions; this +/– attraction is electrostatic attraction
known as an ionic bond, it is between the positive ions
just an electrostatic and the negative delocalised
attractive force) electrons)
Just the symbol e.g. H2O e.g. SiO2 e.g. MgCl2 Just the symbol
The formula
e.g. Ar each molecule contains 1 O ratio of Si:O atoms is 1:2 ratio of Mg2+:Cl– ions is 1:2 e.g. Fe
and 2H atoms through the structure through the structure
Bonding
Melting and
boiling points
Higher melting / boiling points Higher melting / boiling points Higher melting / boiling points Higher melting / boiling points Higher melting / boiling points
occur when: occur when: occur when: occur when: occur when:
Conductivity
Solubility (aq)
Solid – + – + – + –
+ – + – + – +
– + – + – + –
+ – + – + – +
– + – + – + –
Liquid – + + –
+
– + +
–
+ – + +
+ + –
+
– + – +
+
+ – +
+ + + – +
– +
– +
+ – + – – + +
Gas +
+
– _
+ +
_
+
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 18-July-2018 Chemsheets AS 1012