Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design
Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design
Uploaded by
nujugtrCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design
Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design
Uploaded by
nujugtrCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design
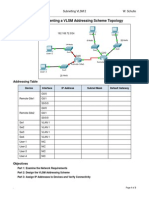
Topology Diagram
192.168.1.0/2 192.168.1.64/26
192.168.1.160/27 192.168.1.208/28
192.168.1.224/30 192.168.1.228/30
192.168.1.128/27 192.168.1.192/28
192.168.1.232/30
Addressing Table
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
HQ Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.192 N/A
Fa0/1 192.168.1.65 255.255.255.192 N/A
S0/0/0 192.168.1.225 255.255.255.252 N/A
S0/0/1 192.168.1.229 255.255.255.252 N/A
Branch Fa0/0 192.168.1.129 255.255.255.224 N/A
1
Fa0/1 192.168.1.161 255.255.255.224 N/A
S0/0/0 192.168.1.226 255.255.255.252 N/A
S0/0/1 192.168.1.233 255.255.255.252 N/A
Branch Fa0/0 192.168.1.193 255.255.255.240 N/A
2
Fa0/1 192.168.1.209 255.255.255.240 N/A
S0/0/0 192.168.1.234 255.255.255.252 N/A
S0/0/1 192.168.1.230 255.255.255.252 N/A
Learning Objectives:
Upon completion of this activity, you will be able to:
∙ Determine the number of subnets needed.
∙ Determine the number of hosts needed. for each subnet
∙ Design an appropriate addressing scheme using VLSM.
∙ Assign addresses and subnet mask pairs to device interfaces.
∙ Examine the use of the available network address space.
Scenario
In this Exercise, you have been given the network address 192.168.1.0/24 to subnet and provide the
IP addressing for the network shown in the Topology Diagram. VLSM will be used so that the
addressing requirements can be met using the 192.168.1.0/24 network. The network has the
following addressing requirements:
∙ The HQ LAN1 will require 50 host IP addresses.
∙ The HQ LAN2 will require 50 host IP addresses.
∙ The Branch1 LAN1 will require 20 host IP addresses.
∙ The Branch1 LAN2 will require 20 host IP addresses
∙ The Branch2 LAN1 will require 12 host IP addresses.
∙ The Branch2 LAN2 will require 12 host IP addresses.
∙ The link from HQ to Branch1 will require an IP address for each end of the link. ∙ The link from HQ
to Branch2 will require an IP address for each end of the link. ∙ The link Branch1 to Branch2 will
require an IP address for each end of the link. (Note: Remember that the interfaces of network
devices are also host IP addresses and are included
in the above addressing requirements.)
Task 1: Examine the Network Requirements.
Examine the network requirements and answer the questions below. Keep in mind that IP addresses
will be needed for each of the LAN interfaces.
1. How many subnets are needed? 9
2. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that are needed for a single subnet? 50
3. How many IP addresses are needed for each of the BranchBranch1 LANs? 40
4. How many IP addresses are needed for each of the BranchBranch2 LANs? 24
5. How many IP addresses are needed for each of the WAN links between routers? 6
6. What is the total number of IP addresses that are needed? 170
7. What is the total number of IP addresses that are available in the 192.168.1.0/24 network? 256
8. Can the network addressing requirements be met using the 192.168.1.0/24 network? no
2
Task 2: Design an IP Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Determine the subnet information for the largest network segment or
segments. In this case, the two HQ LANs are the largest subnets.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each LAN? 50
2. What is the smallest size subnet that can be used to meet this requirement? /26
3. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned in this size subnet? 62
Step 2: Assign subnets to HQ LANs.
Start at the beginning of the 192.168.1.0/24 network.
1. Assign the first available subnet to the HQ LAN1.
2. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
HQ LAN1 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Last Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet Mask Usable IP Usable IP Address
Address Address
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.19 /26 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.62 192.168.1.63
2
3. Assign the next available subnet to the HQ LAN2.
4. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
HQ LAN2 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR Subnet First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Mask IP Address IP Address Address
192.168.1.6 255.255.255.192 /26 192.168.1.65 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.127
4
Step 3: Determine the subnet information for the next largest network segment or
segments. In this case, the two Branch1 LANs are the next largest subnets.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each LAN? 20
2. What is the smallest size subnet that can be used to meet this requirement? /27
3. what is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned in this size subnet? 30
Step 4: Assign subnet to BRANCH1 LANs.
Start with the IP address following the HQ LAN subnets.
1. Assign the next subnet to the Branch1 LAN1.
2. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
Branch1 LAN1 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet IP Address IP Address Address
Mask
192.168.1.12 255.255.255.22 /27 192.168.1.12 192.168.1.15 192.168.1.15
8 4 9 8 9
3. Assign the next available subnet to the Branch1 LAN2.
4. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
Branch1 LAN2 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet IP Address IP Address Address
Mask
192.168.1.16 255.255.255.22 /27 192.168.1.16 192.168.1.19 192.168.1.19
0 4 1 0 1
3
Step 5: Determine the subnet information for the next largest network segment or
segments. In this case, the two Branch2 LANs are the next largest subnets.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each LAN? 12
2. What is the smallest size subnet that can be used to meet this requirement? /28
3. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned in this size subnet? 14
Step 6: Assign subnets to BRANCH2 LANs.
Start with the IP address following the Branch1 LAN subnets.
1. Assign the next subnet to the Branch2 LAN1. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate
information.
Branch2 LAN1 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet IP Address IP Address Address
Mask
192.168.1.19 255.255.255.24 /28 192.168.1.19 192.168.1.20 192.168.1.20
2 0 3 6 7
2. Assign the next available subnet to the Branch2 LAN2.
3. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
Branch2 LAN2 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet IP Address IP Address Address
Mask
192.168.1.20 255.255.255.24 /28 192.168.1.20 192.168.1.22 192.168.1.22
8 0 9 2 3
Step 7: Determine the subnet information for the links between the routers.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each link? 2
2. What is the smallest size subnet that can be used to meet this requirement? /30
3. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned in this size subnet? 2
Step 8: Assign subnets to links.
Start with the IP address following the Branch2 LAN subnets.
1. Assign the next available subnet to the link between the HQ and Branch1
routers. 2. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
Link between HQ and Branch1 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet IP Address IP Address Address
Mask
192.168.1.22 255.255.255.25 /30 192.168.1.22 192.168.1.22 192.168.1.22
4 2 5 6 7
3. Assign the next available subnet to the link between the HQ and Branch2
routers. 4. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
Link between HQ and Branch2 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet IP Address IP Address Address
Mask
192.168.1.22 255.255.255.25 /30 192.168.1.22 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.23
8 2 9 0 1
5. Assign the next available subnet to the link between the Branch1 and Branch2 routers.
4
6. Fill in the chart below with the appropriate information.
Link between Branch1 and Branch2 Subnet
Network Decimal CIDR First Usable Last Usable Broadcast
Address Subnet Mask Subnet IP Address IP Address Address
Mask
192.168.1.23 255.255.255.25 /30 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.23 192.168.1.23
2 2 3 4 5
Task 3: Assign IP Addresses to the Network Devices.
Assign the appropriate addresses to the device interfaces. Document the addresses to be used in
the Addressing Table provided under the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: Assign addresses to the HQ router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the HQ LAN 1 subnet to the Fa0/0 LAN
interface. 2. Assign the first valid host address in the HQ LAN 2 subnet to the Fao/1
LAN interface.
3. Assign the first valid host address in the link between HQ and Branch1 subnet to the S0/0/0
interface.
4. Assign the first valid host address in the link between HQ and Branch2 subnet to the S0/0/1
interface.
Step 2: Assign addresses to the Branch1 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the Branch1 LAN1 subnet to the Fa0/0 LAN
interface. 2. Assign the first valid host address in the Branch1 LAN2 subnet to the Fa0/1
LAN interface.
3. Assign the last valid host address on the link between Branch1 and HQ subnet to the S0/0/0
interface
4. Assign the first valid host address on the link between Branch1 and Branch2 subnet to the S0/0/1
interface.
Step 3: Assign addresses to the Branch2 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the Branch2 LAN1 subnet to the Fa0/0 LAN interface.
Assign the first valid host address in the Branch 2 LAN 2 subnet to the Fa0/1 LAN interface. 2. Assign
the last valid host address on the link between HQ and Branch2 subnet to the S0/0/1 interface
3. Assign the last valid host address on the link between Branch1 and Branch2 subnet to the S0/0/0
interface.
5
You might also like
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Using GNS3 For Switching LabsDocument7 pagesUsing GNS3 For Switching LabskinyNo ratings yet
- 6.3.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 SwitchesDocument22 pages6.3.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 SwitchesJson CañedaNo ratings yet
- SWITCH Lab: VLAN Configuration: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesSWITCH Lab: VLAN Configuration: ObjectiveBambang SubrataNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting SwitchDocument56 pagesTroubleshooting SwitchJaime Andres NiñoNo ratings yet
- 19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMDocument8 pages19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMjohannachicaNo ratings yet
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - SolutionDocument16 pages2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - SolutionVarinava Bola100% (3)
- How To Configure A Cisco Layer 3 SwitchDocument5 pagesHow To Configure A Cisco Layer 3 SwitchTuan PhamNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesLab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramPaintMeAnEpicNo ratings yet
- 9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsDocument3 pages9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsAhmadHijazi100% (2)
- E2 Lab 3 5 4Document3 pagesE2 Lab 3 5 4Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- 8.7.1.3 Lab - (Optional) Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and Client - InstructorDocument30 pages8.7.1.3 Lab - (Optional) Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and Client - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Basic Cisco Router Configuration StepsDocument2 pagesBasic Cisco Router Configuration StepsTeny VargheseNo ratings yet
- CCNASv1 1 Chp08 Lab B RMT Acc VPN Instructor PDFDocument33 pagesCCNASv1 1 Chp08 Lab B RMT Acc VPN Instructor PDFAhmadHijaziNo ratings yet
- CCNA Routing and Switching S3Document16 pagesCCNA Routing and Switching S3FiskoaujNo ratings yet
- ES CCNPv6 ROUTE Lab7-1 Branch Office Config InstructorDocument15 pagesES CCNPv6 ROUTE Lab7-1 Branch Office Config InstructorSebastian Molina FernandezNo ratings yet
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationDocument11 pages11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationRazvan Buicliu20% (5)
- Switch and Router ConfigurationDocument41 pagesSwitch and Router ConfigurationBroot KalNo ratings yet
- Lab 4.2.8 - Configure Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument5 pagesLab 4.2.8 - Configure Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN RoutingGabriel Julio Navarro PianetaNo ratings yet
- Variable Length Subnetting: Jim Blanco Aparicio-Levy Technical CenterDocument14 pagesVariable Length Subnetting: Jim Blanco Aparicio-Levy Technical Centerhussien amareNo ratings yet
- Calculating A VLSM Addressing Scheme: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCalculating A VLSM Addressing Scheme: ObjectivesDarshit PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab - Calculate Ipv4 Subnets: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLab - Calculate Ipv4 Subnets: ObjectivesJad Abou ZeidNo ratings yet
- Vlan, Trunk, VTPDocument32 pagesVlan, Trunk, VTPĐinh TúNo ratings yet
- Cisco First Hop Redundancy Protocol by TanmoyDocument38 pagesCisco First Hop Redundancy Protocol by TanmoyBIG BILLION DREAMSNo ratings yet
- Campus DesignDocument40 pagesCampus Designcooleng115No ratings yet
- Cisco Router Configuration CommandsDocument17 pagesCisco Router Configuration CommandsBazir AhamedNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Connecting Two LANs Using Multi-Router Topology With Static RoutesDocument8 pages1.2. Connecting Two LANs Using Multi-Router Topology With Static Routesராஜ்குமார் கந்தசாமி100% (1)
- LAB Inter Vlan Routing Using Layer 3 SwitchDocument9 pagesLAB Inter Vlan Routing Using Layer 3 SwitchinjectingfeverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and ClientDocument24 pagesChapter 8 Lab B: Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and ClientberlodonNo ratings yet
- Configure InterVLAN RoutingDocument5 pagesConfigure InterVLAN RoutingJuan Felipe Corso AriasNo ratings yet
- MPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesFrom EverandMPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- 3.6.1.1 Lab - Securing Administrative Access Using AAA and RADIUS - InstructorDocument35 pages3.6.1.1 Lab - Securing Administrative Access Using AAA and RADIUS - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Lab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Document4 pagesLab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Rico Agung FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technology: QUARTER 2 - Module 3Document20 pagesEmpowerment Technology: QUARTER 2 - Module 3Jezzivelle Albores100% (6)
- Routers: Modular FixedDocument17 pagesRouters: Modular FixedSurendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Configuring HSRP VRRP GLBPDocument13 pagesConfiguring HSRP VRRP GLBPTuấn BéoNo ratings yet
- He - Full - Update - 11 99 99.00 RG U500 STD Hel 04Document3 pagesHe - Full - Update - 11 99 99.00 RG U500 STD Hel 04AndresGarcia AndreusDjPro0% (1)
- Lab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument4 pagesLab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramMunkieBoneZNo ratings yet
- Configuring Multi-Area OSPFv3Document16 pagesConfiguring Multi-Area OSPFv3etitahNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructDocument4 pages9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- Configure Router On A Stick Inter VLAN Routing ExplainedDocument2 pagesConfigure Router On A Stick Inter VLAN Routing ExplainedQuang AnhNo ratings yet
- Cisco Commands - 2016-05-19Document26 pagesCisco Commands - 2016-05-19agaver2No ratings yet
- WAN Subnetting VLSMDocument3 pagesWAN Subnetting VLSMMuz QazNo ratings yet
- ACL Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewDocument3 pagesACL Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewBhupendar Singh100% (1)
- IP Subnet CalculationsDocument27 pagesIP Subnet Calculationsrajasekr1No ratings yet
- Lab 8.3.3.6Document10 pagesLab 8.3.3.6Justine DuranNo ratings yet
- Ccna 2 Final Exam All Sets 100Document67 pagesCcna 2 Final Exam All Sets 100radek1911No ratings yet
- Lab 3 - AAA Authentication On Cisco Routers - InstruccionesDocument6 pagesLab 3 - AAA Authentication On Cisco Routers - InstruccionesFelipe Andres Oyarzun QuirozNo ratings yet
- CCNA Training Hot Standby Router Protocol HSRP TutorialDocument4 pagesCCNA Training Hot Standby Router Protocol HSRP Tutorialokotete evidenceNo ratings yet
- 9.4.1.7 Lab - Configuring ASA 5510 Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM - InstructorDocument56 pages9.4.1.7 Lab - Configuring ASA 5510 Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationDocument4 pagesLab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationJosue Isahu Sanchez MedinaNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IGDocument8 pages9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IGKe Syukuran KuNo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure A Branch ConnectionDocument9 pagesLab - Configure A Branch Connectionratacle57% (7)
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument36 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolAvikNo ratings yet
- CCNP Switching LAB Preparation TestDocument2 pagesCCNP Switching LAB Preparation TestGiannisDemetriouNo ratings yet
- Cisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandCisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Programmes Available To International Students in New ZealandDocument10 pagesProgrammes Available To International Students in New ZealandnujugtrNo ratings yet
- Witnessing of Cheating-in-Exams Behavior and Factors Sustaining IntegrityDocument15 pagesWitnessing of Cheating-in-Exams Behavior and Factors Sustaining IntegritynujugtrNo ratings yet
- Call For Scholarship Applications Eac Hawassa University 2022 FinalDocument7 pagesCall For Scholarship Applications Eac Hawassa University 2022 FinalnujugtrNo ratings yet
- Refugee Scholarship The Graduate Institute, Geneva: CriteriaDocument1 pageRefugee Scholarship The Graduate Institute, Geneva: CriterianujugtrNo ratings yet
- Saving A Word Document 1Document3 pagesSaving A Word Document 1nujugtrNo ratings yet
- 4 - Challenging - VLSM IP AddressingDocument11 pages4 - Challenging - VLSM IP AddressingnujugtrNo ratings yet
- Lab - View Network Device MAC Addresses: TopologyDocument6 pagesLab - View Network Device MAC Addresses: TopologynujugtrNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnet An Ipv4 Network: Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnet An Ipv4 Network: Addressing TablenujugtrNo ratings yet
- Lab - Calculate Ipv4 Subnets: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLab - Calculate Ipv4 Subnets: ObjectivesnujugtrNo ratings yet
- Lab - Build A Switch and Router Network: TopologyDocument8 pagesLab - Build A Switch and Router Network: TopologynujugtrNo ratings yet
- STS - Module 8 - The Information AgeDocument1 pageSTS - Module 8 - The Information AgeCamil LeeNo ratings yet
- Finacle Support Connect - Edition 56Document2 pagesFinacle Support Connect - Edition 56suneel KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsDocument40 pagesData and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsChristian Allan LumakinNo ratings yet
- PM Debug InfoDocument221 pagesPM Debug InfoSian LAlbertNo ratings yet
- Browserstack ErrorDocument13 pagesBrowserstack ErrorRagNo ratings yet
- Going Viral British English StudentDocument2 pagesGoing Viral British English StudentlaraNo ratings yet
- Digital Etiquette Law and Responsibilities.g3 PDFDocument18 pagesDigital Etiquette Law and Responsibilities.g3 PDFMicah Ellah Reynoso PatindolNo ratings yet
- Quizzes 11Document16 pagesQuizzes 11Petter PNo ratings yet
- Current LogDocument69 pagesCurrent LogLiongsu 86No ratings yet
- DashboardServer e SeriesDocument7 pagesDashboardServer e Series徐海东No ratings yet
- Calculate Difference Between DatesDocument11 pagesCalculate Difference Between DatesTalk 2meNo ratings yet
- Dm766v10-90 SIPDocument55 pagesDm766v10-90 SIPEncarnación MedinaNo ratings yet
- Multicast Routing Configuration GuideDocument74 pagesMulticast Routing Configuration GuidedfsfsdfsdfdsNo ratings yet
- IBM TS7700 Release 4.1 and 4.1.1 Guide PDFDocument976 pagesIBM TS7700 Release 4.1 and 4.1.1 Guide PDFtedington2540No ratings yet
- ICT As Platform For ChangeDocument24 pagesICT As Platform For ChangeJerico CsmpuganNo ratings yet
- IoT ELE Model Question Paper 1Document2 pagesIoT ELE Model Question Paper 1Sathish SinghNo ratings yet
- (1st Batch) EXAMINEE GUIDE 2022Document3 pages(1st Batch) EXAMINEE GUIDE 2022Leicel John BelmesNo ratings yet
- Phoenixs Texture PackDocument16 pagesPhoenixs Texture PackRomasGuPro xDNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 - Unit 2 - Networks (Part 1)Document30 pagesLesson 14 - Unit 2 - Networks (Part 1)shahanaNo ratings yet
- 1.intro - Design IssuesDocument21 pages1.intro - Design IssuesDivya K.SNo ratings yet
- MuuuuuuDocument2 pagesMuuuuuumdhyderhasanNo ratings yet
- Compact NSX - Micrologic 5-6-7 - User Guide 7Document1 pageCompact NSX - Micrologic 5-6-7 - User Guide 7amnd amorNo ratings yet
- Error Detection and Correction in Data Link LayerDocument16 pagesError Detection and Correction in Data Link LayerAlexander PhiriNo ratings yet
- ManualesDocument22 pagesManualesAmilcar MoranNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Satellite C855 Quanta ZY9B Hannstar Rev1A SchematicDocument49 pagesToshiba Satellite C855 Quanta ZY9B Hannstar Rev1A SchematicMbolatiana AndriamilantoNo ratings yet
- The Internet Protocol: Eliot Grove Danny Friel Stuart AndersonDocument20 pagesThe Internet Protocol: Eliot Grove Danny Friel Stuart AndersonDlanor AvadecNo ratings yet
- LogDocument74 pagesLogMathurNo ratings yet
- DIAEnergie WebAPI v1.4Document9 pagesDIAEnergie WebAPI v1.4Diego Ramos LamaNo ratings yet