Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pneumococcal Pneumonia: Unvaccinated Status Community - Streptococcus Pneumoniae (+) Inhalation, Aspiration
Pneumococcal Pneumonia: Unvaccinated Status Community - Streptococcus Pneumoniae (+) Inhalation, Aspiration
Uploaded by
Terrence AntonioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pneumococcal Pneumonia: Unvaccinated Status Community - Streptococcus Pneumoniae (+) Inhalation, Aspiration
Pneumococcal Pneumonia: Unvaccinated Status Community - Streptococcus Pneumoniae (+) Inhalation, Aspiration
Uploaded by
Terrence AntonioCopyright:
Available Formats
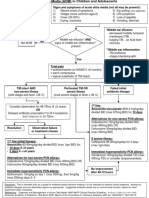
Exposure to Pathogen
Modifiable Risk Factors: Inhalation, Aspiration
Unvaccinated status
Community
Susceptible Host/Pathogen
Non-modifiable Risk
-Streptococcus Pneumoniae (+) PNEUMOCOCCAL
Factors: Age
Infection and Proliferation of
Pathogen in Lower PNEUMONIA
Respiratory Tract
Bacteria enters the Alveoli
then spreads and releases
ENDOTOXINS
Endotoxin damages the Capillaries increase
epithelium then bacteria permeable and fluid leakage
releases to the Interstitial and enters alveoli
Space
Macrophages releases
inflammatory markers such Because of this, WBC
as Cytokines, Interleukins comes in with large
and TNF. amounts
Local Inflammatory Response
Systemic Inflammatory Response
Neutrophils recruited to the site of infection (Lobar or Interstitial Pattern
Cytokine release
depending on pathogen) by epithelial cytokine release
Accumulation of Plasma Exudate (from capillary leakage Increase in respiratory Disruption of hypothalamic
Causes the respiratory at sites of inflammation), cell-debris, serious-fluid, drive thermoregulation
tract and alveoli to bacteria, fibrin
become the alveoli
Irritation of airways and
Fluid build up in spaces
Low effiency of gas failure of cilliary
Dry lips and between alveoli
Swollen nasal exchange clearance to keep with
(Interstitial Space)
mucous fluid build up
mucosa Tachypnea Fever/chills
membrane
Hypoxemia Cough Crackles Right lower lobe
opacity consistent
with pneumonia
Dyspnea
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- NBME 11 Answers To All SectionsDocument101 pagesNBME 11 Answers To All SectionsBenjaminTan100% (5)
- Self Assessment and Review of Plastic Surgery (2013) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Document292 pagesSelf Assessment and Review of Plastic Surgery (2013) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)faissal jameel88% (8)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Zygomatic Catalog Surgical ManualDocument32 pagesZygomatic Catalog Surgical ManualguhanderNo ratings yet
- Understanding Narcisistic PersonalityDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Narcisistic PersonalityCarla RiveraNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics MnemonicsDocument5 pagesPediatrics Mnemonicsarturschander3614100% (3)
- Emergency Department Crowd ManagementDocument4 pagesEmergency Department Crowd ManagementPrabhat Kumar100% (1)
- Khiveh 2017Document8 pagesKhiveh 2017Siti lestarinurhamidahNo ratings yet
- Ipratropium BromideDocument20 pagesIpratropium BromideAngelique Ramos PascuaNo ratings yet
- Exam 4Document10 pagesExam 4Hasan A AsFourNo ratings yet
- Writing About Science & Technology: Ariel C. LalisanDocument18 pagesWriting About Science & Technology: Ariel C. LalisanCatherine Fernandez InocentesNo ratings yet
- MammographyDocument2 pagesMammographybookish33sNo ratings yet
- The 90 Day Program To Beat Candida Restore Vibrant HealthDocument136 pagesThe 90 Day Program To Beat Candida Restore Vibrant HealthMihaela NNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of PoulticesDocument7 pagesHealth Benefits of PoulticesEduard50% (2)
- Gastroenteritis PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesGastroenteritis PATHOPHYSIOLOGYNiziu Bears100% (1)
- Collection, Transport and Storage of Specimens For Laboratory DiagnosisDocument25 pagesCollection, Transport and Storage of Specimens For Laboratory DiagnosisBrihadishwaran ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders StudentDocument32 pagesMood Disorders StudentRafly FernandaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To ArthritisDocument12 pagesA Guide To ArthritisConsidraCareNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia: A Comprehensive Review (5th Edition)Document1 pageAnesthesia: A Comprehensive Review (5th Edition)brakim23No ratings yet
- Company Rules AND RegulationsDocument5 pagesCompany Rules AND RegulationsJb Cano ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Final Boerhave SnydromeDocument3 pagesFinal Boerhave SnydromeAnugerah Putra GemilangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Clinical Trials - PDDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Clinical Trials - PDCristina SalcianuNo ratings yet
- Canada - Medical Exam FormDocument1 pageCanada - Medical Exam FormEsykiel Nool MedranoNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 001 Psychiatric Interview of The Medically Ill PDFDocument10 pagesPSYCH 001 Psychiatric Interview of The Medically Ill PDFKaye Nee100% (1)
- 3 Par Q FormsDocument5 pages3 Par Q FormsYhusi KarinaNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsDocument1 pageAcute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsSreya SanilNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument32 pagesMedical Surgical NursingtanishaNo ratings yet
- Complicaciones Pulmonares Asociadas Al Consumo de Cocaína Pulmonary Complications Associated With Cocaine ConsumptionDocument5 pagesComplicaciones Pulmonares Asociadas Al Consumo de Cocaína Pulmonary Complications Associated With Cocaine ConsumptionLuisa LaraNo ratings yet
- List of Students With Their Research Proposal For 2008-2009 BatchDocument5 pagesList of Students With Their Research Proposal For 2008-2009 Batchnoronisa talusobNo ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori Infection Is Not Associated With Specific SymptomsDocument7 pagesHelicobacter Pylori Infection Is Not Associated With Specific SymptomsNur Hasanah 112No ratings yet
- Wesleyan University - Philippines: N U R S I N G C A R e P L A NDocument2 pagesWesleyan University - Philippines: N U R S I N G C A R e P L A NKristine CastilloNo ratings yet