Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Using Namespace Void: Int Int Int
Uploaded by
VENKATESAN R-20200 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThis C++ code implements the quicksort algorithm to sort an array of integers. It uses a partition function to choose a pivot element and rearrange the array such that all elements less than the pivot come before all elements greater than the pivot. The quicksort function then recursively calls itself on the sub-arrays to fully sort the original array. The code includes functions to swap elements, partition the array, perform the quicksort, and display the array.
Original Description:
Original Title
quicksort
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis C++ code implements the quicksort algorithm to sort an array of integers. It uses a partition function to choose a pivot element and rearrange the array such that all elements less than the pivot come before all elements greater than the pivot. The quicksort function then recursively calls itself on the sub-arrays to fully sort the original array. The code includes functions to swap elements, partition the array, perform the quicksort, and display the array.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesUsing Namespace Void: Int Int Int
Uploaded by
VENKATESAN R-2020This C++ code implements the quicksort algorithm to sort an array of integers. It uses a partition function to choose a pivot element and rearrange the array such that all elements less than the pivot come before all elements greater than the pivot. The quicksort function then recursively calls itself on the sub-arrays to fully sort the original array. The code includes functions to swap elements, partition the array, perform the quicksort, and display the array.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
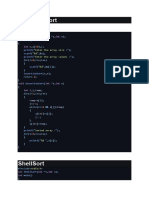
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Swap two elements - Utility function
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// partition the array using last element as pivot
int partition (int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high]; // pivot
int i = (low - 1);
for (int j = low; j <= high- 1; j++)
{
//if current element is smaller than pivot, increment the low element
//swap elements at i and j
if (arr[j] <= pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
//quicksort algorithm
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
//partition the array
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high);
//sort the sub arrays independently
quickSort(arr, low, pivot - 1);
quickSort(arr, pivot + 1, high);
}
}
void displayArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i < size; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<"\t";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {12,23,3,43,51,35,19,45};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout<<"Input array"<<endl;
displayArray(arr,n);
cout<<endl;
quickSort(arr, 0, n-1);
cout<<"Array sorted with quick sort"<<endl;
displayArray(arr,n);
return 0;
}
Output:
You might also like
- Experiment 3.1Document10 pagesExperiment 3.1Utkarsh RastogiNo ratings yet
- Quick SortDocument2 pagesQuick SortAhmed AlamNo ratings yet
- Quick SortDocument5 pagesQuick Sortsahil pahujaNo ratings yet
- Quicksort CodeDocument2 pagesQuicksort Codextremeuser8055No ratings yet
- Practical File of Data and File StructuresDocument21 pagesPractical File of Data and File Structuresrobanjeet chhinaNo ratings yet
- QuickSort AlgorithmDocument1 pageQuickSort Algorithmfovohe2257No ratings yet
- SemiFinals Lesson3Document4 pagesSemiFinals Lesson3THRISHA JOYCE GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- CheatsheetDocument6 pagesCheatsheetHữu HoàngNo ratings yet
- DAA Lab Exercise 2Document12 pagesDAA Lab Exercise 2Sneha TuladharNo ratings yet
- Paper QuestionsDocument4 pagesPaper Questionsarisharehan7No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3: Analyze The Time Complexity of Quicksort Algorithm. CodeDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 3: Analyze The Time Complexity of Quicksort Algorithm. Codedalip kumarNo ratings yet
- BCSL 045Document11 pagesBCSL 045Manas GhoshNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of AlgorithmsMahnoor MustafaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of AlgorithmsMahnoor MustafaNo ratings yet
- Templates For DSA9Document4 pagesTemplates For DSA9Sourav MalikNo ratings yet
- Nebil MohammedDocument5 pagesNebil MohammedNebil MHNo ratings yet
- Quick SortDocument5 pagesQuick SortNathan AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- IterativDocument9 pagesIterativGalatom YadetaNo ratings yet
- Templates For DSA11Document2 pagesTemplates For DSA11Sourav MalikNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 AADocument5 pagesExp 2 AAराजस करंदीकरNo ratings yet
- Templates For DSA10Document3 pagesTemplates For DSA10Sourav MalikNo ratings yet
- Templates For DSA7Document4 pagesTemplates For DSA7Sourav MalikNo ratings yet
- Bubble SortDocument38 pagesBubble SortAnjji SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Analysis Design of Algorithm Anshika Chauhan 0103CS191041Document51 pagesAssignment Analysis Design of Algorithm Anshika Chauhan 0103CS191041anshika chauhanNo ratings yet
- Templates For DSA6Document4 pagesTemplates For DSA6Sourav MalikNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms: PLSD210 SortingDocument44 pagesData Structures and Algorithms: PLSD210 SortingAnkit JainNo ratings yet
- Quick Sort CodeDocument2 pagesQuick Sort CodeIsrat DibaNo ratings yet
- Sorting AlgorithmsDocument14 pagesSorting AlgorithmsNonstop MasterNo ratings yet
- Sorting AlgorithmsDocument5 pagesSorting AlgorithmsHuzaifa Bin ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Algo NotiteDocument72 pagesAlgo NotiteCristina UngureanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Riphah International University, Islamabad, PakistanDocument9 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Riphah International University, Islamabad, PakistanNoman KhanNo ratings yet
- Practical File DaaDocument84 pagesPractical File Daa828Nitish KumarNo ratings yet
- CC DSADocument11 pagesCC DSAsurafel123emiruNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Algorithm (Lab)Document27 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithm (Lab)Vinay mauryaNo ratings yet
- Algoithms Notes pt2Document36 pagesAlgoithms Notes pt2Natalie SongNo ratings yet
- Quicksort: Pseudo Code For Recursive Quicksort FunctionDocument11 pagesQuicksort: Pseudo Code For Recursive Quicksort FunctionPedro FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Daa Practical FileDocument30 pagesDaa Practical FileSanam BirdiNo ratings yet
- DS ModuleDocument39 pagesDS ModuleÇháråñ ÇhèrryNo ratings yet
- Group Ass cc++DSADocument7 pagesGroup Ass cc++DSAsurafel123emiruNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algorithms & Data Structures: Lecturer: Karimzhan Nurlan BerlibekulyDocument47 pagesAdvanced Algorithms & Data Structures: Lecturer: Karimzhan Nurlan BerlibekulyNaski KuafniNo ratings yet
- Aoa LabDocument7 pagesAoa Labanshumanasr02No ratings yet
- DSL Experiment No 8 STDDocument7 pagesDSL Experiment No 8 STDLakshit PatilNo ratings yet
- Theory PDFDocument30 pagesTheory PDFNibedan PalNo ratings yet
- Raport 2Document21 pagesRaport 2GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Insertion Sort: Insertionsort MainDocument6 pagesInsertion Sort: Insertionsort Mainaswith Reddy. AtlaNo ratings yet
- DSA Assignment #3 LABDocument4 pagesDSA Assignment #3 LABTop10 EveryThingNo ratings yet
- Sorting, Searching, and The ComplexityDocument41 pagesSorting, Searching, and The ComplexityEva UliaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and DesignDocument15 pagesAnalysis and DesignTarvish SonkhlaNo ratings yet
- ADS Lab IDocument78 pagesADS Lab Itemp tempNo ratings yet
- QuickSort Is A Divide and Conquer AlgorithmDocument2 pagesQuickSort Is A Divide and Conquer AlgorithmAakash AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Quick Sort Variations TheoryDocument5 pagesQuick Sort Variations TheoryShediakhNo ratings yet
- AdaspamDocument15 pagesAdaspampoori.2819.hapoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 LabDocument11 pagesLesson 8 LabMangilal BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Q7) Write A C++ Program Using Types of Sorting.: 1. Bubble Sort 2. Insertion SortDocument19 pagesQ7) Write A C++ Program Using Types of Sorting.: 1. Bubble Sort 2. Insertion SortAyush JadhavNo ratings yet
- DSA Recursive Quick and Merge SortDocument4 pagesDSA Recursive Quick and Merge SortTop10 EveryThingNo ratings yet
- Daa Lab Form 1 - 10Document38 pagesDaa Lab Form 1 - 10master sahil spandanNo ratings yet
- Practical File of Design of Algorithms and AnalysisDocument18 pagesPractical File of Design of Algorithms and AnalysisAbidullahNo ratings yet
- DAA Lab FileDocument20 pagesDAA Lab FileIshan ParasharNo ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Cloud and Virtualization Concepts: M. Ammu Gangasri A. Gayathri P. Jayabarani P. Jeevitha ManDocument30 pagesCloud and Virtualization Concepts: M. Ammu Gangasri A. Gayathri P. Jayabarani P. Jeevitha ManVENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- Venkatesan Im CT2Document12 pagesVenkatesan Im CT2VENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- 4 Tromster 04: Cycle TestDocument8 pages4 Tromster 04: Cycle TestVENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- BRM Important TopicsDocument1 pageBRM Important TopicsVENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.VENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- Unit 1. Merchant Banking Indian Financial SystemDocument91 pagesUnit 1. Merchant Banking Indian Financial SystemVENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- SSLC, Hse, Diploma, B.E/B.Tech, M.E/M.Tech, Mba, McaDocument4 pagesSSLC, Hse, Diploma, B.E/B.Tech, M.E/M.Tech, Mba, McaVENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- SM 2 MarkDocument3 pagesSM 2 MarkVENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet
- SM Imp 13 MarkDocument3 pagesSM Imp 13 MarkVENKATESAN R-2020No ratings yet