Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment
Uploaded by
Haris Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesProject Management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProject Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesAssignment
Uploaded by
Haris KhanProject Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
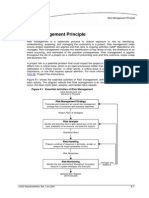
Plan Risk Management
The organization's risk management framework is reviewed and adapted to define the project
risk management plan at project initiation. The risks management plan includes the following
guidelines:
List of possible sources and categories of risk
Impact and probability matrix
Risk reduction and action plan
Intervention plan
Threshold and risk values
Identifying risks
Risk analysis
Risk management
Risk control
Feedback
Step 1 – Identification of risks:
Risks should be identified and addressed as early as possible in the project. Risk identification
is made throughout the life cycle of the project, with a particular focus on the key stages. Some
risks may be readily apparent to the project team (known risks); others will have more rigors
to be discovered, but they are still predictable. The tool for recording all the risks identified
during the project is the risk register, which is stored in the central server of the project.
Step 2 – Risk Analyses:
Risk analysis or assessment involves examining how the project's results and objectives may
change due to the impact of the risk event. After identifying the risks, they are analyzed to
identify the qualitative and quantitative impact of the risk on the project, so that appropriate
measures can be taken to mitigate them.
Likelihood of risk occurrence
High probability: (80% ≤ x ≤ 100%)
Medium-high probability: (60% ≤ x <80%)
Medium-low probability: (30% ≤ x <60%)
Low probability: (0%<x<30%)
Step 3 – Risk management:
Risk management involves:
planning the risk response, identifying the risk triggers, and establishing the person
responsible for resolving the risk.
The risk response plans are aimed at the following objectives:
Elimination of risk
Decreased probability of occurrence of risk
Reducing the impact of risk on the project objectives.
Risk response plans usually have an impact on time and costs.
Therefore, it is mandatory that the time and cost of the defined response plan be calculated as
accurately as possible.
Step 4– Risk control:
Risk monitoring and control include:
Identifying new risks and planning for them
Track existing risks to verify that
Reassessment of risks is necessary, and Any risk conditions have been triggered
Monitor any risks that may become more critical over time
Addressing other risks that require a long-term, planned, and managed approach with
risk action plans.
During the project course, the anticipated risks are verified and recorded, having the aim
of reducing or resolving.
You might also like
- Adventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementFrom EverandAdventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- Risk Management1Document10 pagesRisk Management1ubadjateNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis and Management - Nokia-SiemensDocument7 pagesRisk Analysis and Management - Nokia-SiemensOleksandr ZagnoiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument8 pagesRisk Management PlanubadjateNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Risk ManagemDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Risk ManagemSerhat GünerNo ratings yet
- 3 & 4 Risk Analysis & MitigationDocument16 pages3 & 4 Risk Analysis & MitigationQila HusinNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument7 pagesRisk ManagementubadjateNo ratings yet
- HR ExecutiveDocument16 pagesHR ExecutiveAli AbbasNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument16 pagesRisk Management Plandrsuresh26No ratings yet
- Risk IdentificationDocument8 pagesRisk IdentificationubadjateNo ratings yet
- Risk Management 2Document8 pagesRisk Management 2ubadjateNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Risk ManagementDocument43 pages6.0 Risk ManagementAizuddinHakimBennyNo ratings yet
- Project Risk ManagementDocument12 pagesProject Risk ManagementRadeeshaNo ratings yet
- RiskDocument10 pagesRiskFabian YslaNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesRisk ManagementSandesh Thakurdas SachdevNo ratings yet
- Project Risk ManagementDocument16 pagesProject Risk ManagementRishabhGuptaNo ratings yet
- Risk Response PlanningDocument5 pagesRisk Response Planningubadjate100% (1)
- 1 Risk Management Principle: Tool 2EDocument6 pages1 Risk Management Principle: Tool 2EpekanselandarNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument2 pagesRisk Managementfr33rageNo ratings yet
- Manage Risk - Summative Asssessment 2Document14 pagesManage Risk - Summative Asssessment 2Raj0% (1)
- Risk ManualDocument19 pagesRisk ManualLoc Vinh PhungNo ratings yet
- Project Risk Management ProcessesDocument12 pagesProject Risk Management ProcessesHaerul yakin ananda romadhon Haerul yakin ananda romadhonNo ratings yet
- Tugas Individu 2 - George Juan Susanto - 2106781893Document4 pagesTugas Individu 2 - George Juan Susanto - 2106781893George Juan SusantoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Purpose of The Risk Management PlanDocument3 pages1.1 Purpose of The Risk Management PlanJLA5375No ratings yet
- Introduction To Risk ManagementDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Risk ManagementVenkatesh PethurajNo ratings yet
- Bec 3324: Project Management Year Iii - Semester Ii Session 7Document35 pagesBec 3324: Project Management Year Iii - Semester Ii Session 7Tharindu PereraNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis: Group Members: Reshma Ravindran Sidhiq Shamweel Vinod VipinDocument18 pagesRisk Analysis: Group Members: Reshma Ravindran Sidhiq Shamweel Vinod VipinReshma AnandNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Executive Planning-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANODocument14 pagesRisk Management in Executive Planning-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANOPHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANONo ratings yet
- Tarekegn PPT - FinalDocument16 pagesTarekegn PPT - FinalGemechu BeriNo ratings yet
- 01 Project Risk Management PDFDocument99 pages01 Project Risk Management PDFabelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Risk - AnalysisDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Risk - Analysisadabotor7No ratings yet
- Riskmanagement 12592328544536 Phpapp02Document29 pagesRiskmanagement 12592328544536 Phpapp02Jyothi RameshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document15 pagesChapter 6hailegebraelNo ratings yet
- 4.5 PresentationDocument13 pages4.5 PresentationHajar SadikiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management-1Document13 pagesRisk Management-1ar56481188No ratings yet
- Session 5 Managing Risks in Project ManagementDocument23 pagesSession 5 Managing Risks in Project Managementallahgodallah1992No ratings yet
- ManagementDocument13 pagesManagementMOHAMED SLIMANINo ratings yet
- Risk Management For A Construction ProjectDocument10 pagesRisk Management For A Construction Projectkamini kowsalyaNo ratings yet
- #Assignment AbangDocument5 pages#Assignment AbangNurul SyahirahNo ratings yet
- 08 MarchewkaDocument57 pages08 Marchewkablackphoenix303No ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument6 pagesRisk ManagementAlabi David oluwatobilobaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Plan: Shangrila May Dimol-Bergonio, MDDocument15 pagesRisk Management Plan: Shangrila May Dimol-Bergonio, MDShang DimolNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Unit-VIDocument31 pagesProject Management: Unit-VIskskNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument10 pagesRisk ManagementharanaliveNo ratings yet
- Question 1 & Question 2Document9 pagesQuestion 1 & Question 2UMAIR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Risk MangenmentDocument4 pagesRisk Mangenmentsami ullahNo ratings yet
- Saction RisksDocument10 pagesSaction RisksSD Islam Al Azhar 36 BandungNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Plan Preparation GuidelinesDocument17 pagesRisk Management Plan Preparation Guidelineszenagit123456No ratings yet
- Research 1Document4 pagesResearch 1karl facturanNo ratings yet
- SE-Lect-30 31 32Document9 pagesSE-Lect-30 31 32Ritesh RathodNo ratings yet
- Risk Management ProcessesDocument3 pagesRisk Management ProcessesrazamenesesNo ratings yet
- Gole ProjectDocument73 pagesGole ProjectAaditya GoleNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Purpose of The Risk Management PlanDocument1 page1.1 Purpose of The Risk Management PlanPraveen Varma VNo ratings yet
- SCS Nov PMP RiskDocument55 pagesSCS Nov PMP RiskRasha Al KhatibNo ratings yet
- Decision TMA2 AnswerDocument5 pagesDecision TMA2 AnswerYosef DanielNo ratings yet
- CDC UP Risk Management Practices GuideDocument7 pagesCDC UP Risk Management Practices GuidePoli MarkovaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management: Risk Management Risk Identification Risk Assessment Risk HandlingDocument14 pagesRisk Management: Risk Management Risk Identification Risk Assessment Risk HandlingRobenShresthaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Risk ManagementDocument14 pages12 - Risk ManagementHaseeb MianNo ratings yet
- Risk Register-GuidelineDocument2 pagesRisk Register-GuidelineMasbooksNo ratings yet
- Indian Ordnance FactoryDocument2 pagesIndian Ordnance FactoryAniket ChakiNo ratings yet
- Mss 202 Practice 19-20Document2 pagesMss 202 Practice 19-20fayinminu oluwaniyiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Installation of SSH Keys On Linux-A Step-By Step GuideDocument3 pages1.2 Installation of SSH Keys On Linux-A Step-By Step GuideMada ChouchouNo ratings yet
- Peace Corps Guatemala Welcome Book - June 2009Document42 pagesPeace Corps Guatemala Welcome Book - June 2009Accessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsNo ratings yet
- 3a. Systems Approach To PoliticsDocument12 pages3a. Systems Approach To PoliticsOnindya MitraNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Wire Die Springs ISO-10243 Standard: Red Colour Heavy LoadDocument3 pagesRectangular Wire Die Springs ISO-10243 Standard: Red Colour Heavy LoadbashaNo ratings yet
- Taller Sobre Preposiciones y Vocabulario - Exhibición Comercial SergioDocument5 pagesTaller Sobre Preposiciones y Vocabulario - Exhibición Comercial SergioYovanny Peña Pinzon100% (2)
- Philips Chassis Lc4.31e Aa Power Dps 181 PDFDocument9 pagesPhilips Chassis Lc4.31e Aa Power Dps 181 PDFAouadi AbdellazizNo ratings yet
- Baterías YuasaDocument122 pagesBaterías YuasaLuisNo ratings yet
- Invoice 1281595768Document3 pagesInvoice 1281595768vikas9849No ratings yet
- List of Approved Journals For Promoting Purposes at The University of JordanDocument3 pagesList of Approved Journals For Promoting Purposes at The University of JordanZaid MarwanNo ratings yet
- Splunk Certification: Certification Exam Study GuideDocument18 pagesSplunk Certification: Certification Exam Study GuidesalemselvaNo ratings yet
- Juniper M5 M10 DatasheetDocument6 pagesJuniper M5 M10 DatasheetMohammed Ali ZainNo ratings yet
- Navi Mumbai C.A. ListDocument48 pagesNavi Mumbai C.A. ListManish Shetty67% (9)
- Evaporator EfficiencyDocument15 pagesEvaporator EfficiencySanjaySinghAdhikariNo ratings yet
- Operational Business Suite Contract by SSNIT Signed in 2012Document16 pagesOperational Business Suite Contract by SSNIT Signed in 2012GhanaWeb EditorialNo ratings yet
- Ad CVDocument2 pagesAd CVzahid latifNo ratings yet
- Energy Facts PDFDocument18 pagesEnergy Facts PDFvikas pandeyNo ratings yet
- Bridging: Transportation: Chapter 3: The Transportation Planning ProcessDocument28 pagesBridging: Transportation: Chapter 3: The Transportation Planning ProcesspercyNo ratings yet
- Presentation The New Condominium Rules 9 1 2018 PDFDocument35 pagesPresentation The New Condominium Rules 9 1 2018 PDFYe AungNo ratings yet
- KEC International Limited: Pile FoundationDocument49 pagesKEC International Limited: Pile FoundationDinesh Kumar100% (1)
- Compose Testing CheatsheetDocument1 pageCompose Testing CheatsheetEstampados SIn ApellidoNo ratings yet
- Fashion Designing Sample Question Paper1Document3 pagesFashion Designing Sample Question Paper1Aditi VermaNo ratings yet
- Samarth Arora: Curriculum VitaeDocument2 pagesSamarth Arora: Curriculum VitaeAditya SinghalNo ratings yet
- Pivacare Preventive-ServiceDocument1 pagePivacare Preventive-ServiceSadeq NeiroukhNo ratings yet
- ZX400LCH 5GDocument16 pagesZX400LCH 5Gusmanitp2No ratings yet
- David-Huynh Indeed ResumeDocument3 pagesDavid-Huynh Indeed Resumeapi-546353822No ratings yet
- Mysuru Royal Institute of Technology. Mandya: Question Bank-1Document2 pagesMysuru Royal Institute of Technology. Mandya: Question Bank-1chaitragowda213_4732No ratings yet
- Job Description: Extensive ReadingDocument12 pagesJob Description: Extensive ReadingNatalia VivonaNo ratings yet
- Network Protection Automation Guide Areva 1 PDFDocument500 pagesNetwork Protection Automation Guide Areva 1 PDFEmeka N Obikwelu75% (4)